|
L Function
In mathematics, an ''L''-function is a meromorphic function on the complex plane, associated to one out of several categories of mathematical objects. An ''L''-series is a Dirichlet series, usually convergent on a half-plane, that may give rise to an ''L''-function via analytic continuation. The Riemann zeta function is an example of an ''L''-function, and one important conjecture involving ''L''-functions is the Riemann hypothesis and its generalization. The theory of ''L''-functions has become a very substantial, and still largely conjectural, part of contemporary analytic number theory. In it, broad generalisations of the Riemann zeta function and the ''L''-series for a Dirichlet character are constructed, and their general properties, in most cases still out of reach of proof, are set out in a systematic way. Because of the Euler product formula there is a deep connection between ''L''-functions and the theory of prime numbers. The mathematical field that studies L-func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
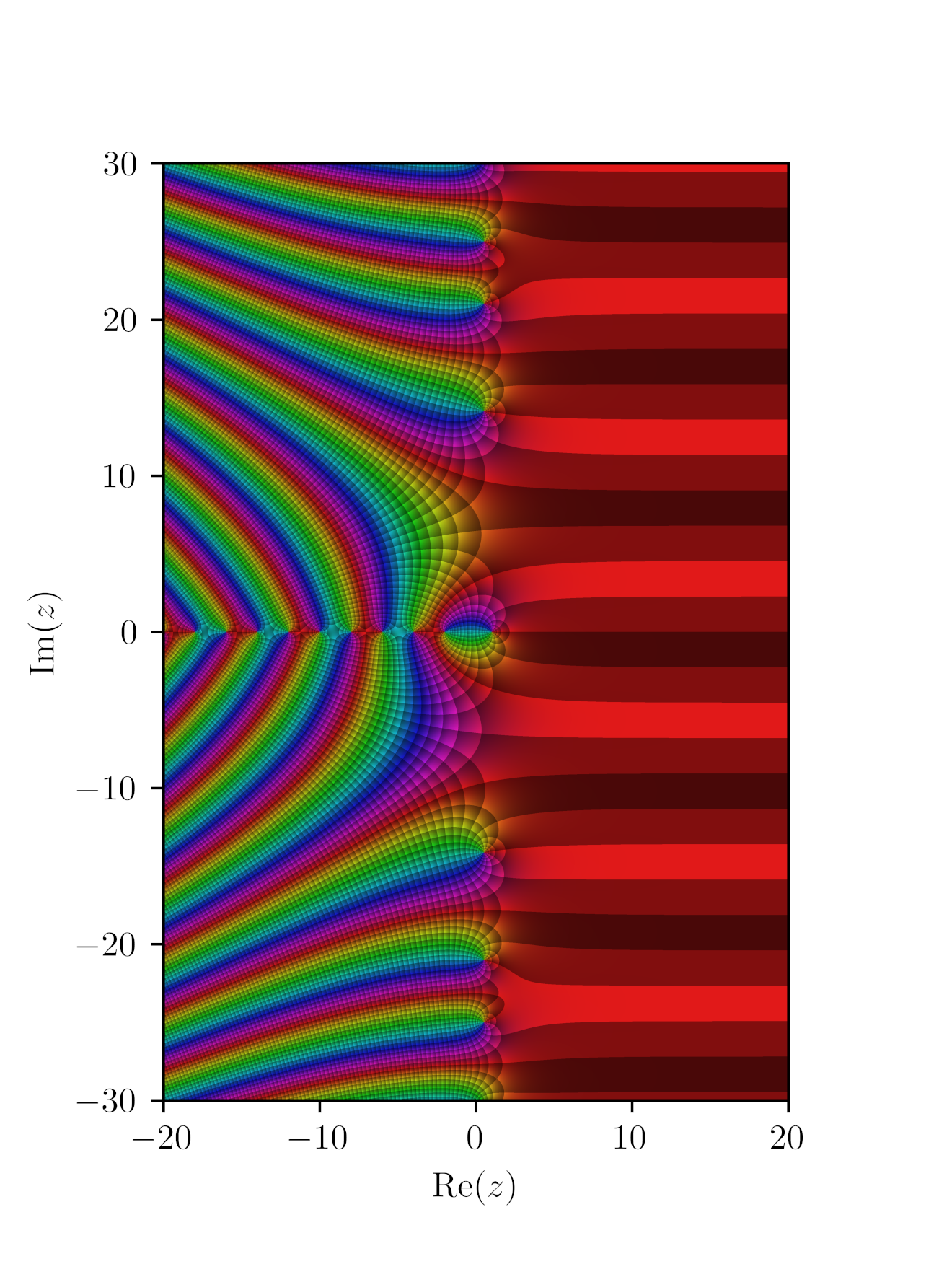
Riemann Hypothesis
In mathematics, the Riemann hypothesis is the conjecture that the Riemann zeta function has its zeros only at the negative even integers and complex numbers with real part . Many consider it to be the most important unsolved problem in pure mathematics. It is of great interest in number theory because it implies results about the distribution of prime numbers. It was proposed by , after whom it is named. The Riemann hypothesis and some of its generalizations, along with Goldbach's conjecture and the twin prime conjecture, make up Hilbert's eighth problem in David Hilbert's list of twenty-three unsolved problems; it is also one of the Clay Mathematics Institute's Millennium Prize Problems, which offers a million dollars to anyone who solves any of them. The name is also used for some closely related analogues, such as the Riemann hypothesis for curves over finite fields. The Riemann zeta function ζ(''s'') is a function whose argument ''s'' may be any complex number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, or , involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order. The property of being prime is called primality. A simple but slow method of checking the primality of a given number n, called trial division, tests whether n is a multiple of any integer between 2 and \sqrt. Faster algorithms include the Miller–Rabin primality test, which is fast but has a small chance of error, and the AKS primality test, which always pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Chaos
Quantum chaos is a branch of physics which studies how chaos theory, chaotic classical dynamical systems can be described in terms of quantum theory. The primary question that quantum chaos seeks to answer is: "What is the relationship between quantum mechanics and classical chaos?" The correspondence principle states that classical mechanics is the classical limit of quantum mechanics, specifically in the limit as the ratio of Planck's constant to the Action (physics), action of the system tends to zero. If this is true, then there must be quantum mechanisms underlying classical chaos (although this may not be a fruitful way of examining classical chaos). If quantum mechanics does not demonstrate an exponential sensitivity to initial conditions, how can exponential sensitivity to initial conditions arise in classical chaos, which must be the correspondence principle limit of quantum mechanics?''Quantum Signatures of Chaos'', Fritz Haake, Edition: 2, Springer, 2001, , .Michae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Random Matrix
In probability theory and mathematical physics, a random matrix is a matrix-valued random variable—that is, a matrix in which some or all elements are random variables. Many important properties of physical systems can be represented mathematically as matrix problems. For example, the thermal conductivity of a lattice can be computed from the dynamical matrix of the particle-particle interactions within the lattice. Applications Physics In nuclear physics, random matrices were introduced by Eugene Wigner to model the nuclei of heavy atoms. Wigner postulated that the spacings between the lines in the spectrum of a heavy atom nucleus should resemble the spacings between the eigenvalues of a random matrix, and should depend only on the symmetry class of the underlying evolution. In solid-state physics, random matrices model the behaviour of large disordered Hamiltonians in the mean-field approximation. In quantum chaos, the Bohigas–Giannoni–Schmit (BGS) conjecture asserts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero Distribution
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. In place-value notation such as the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, 0 also serves as a placeholder numerical digit, which works by multiplying digits to the left of 0 by the radix, usually by 10. As a number, 0 fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and other algebraic structures. Common names for the number 0 in English are ''zero'', ''nought'', ''naught'' (), ''nil''. In contexts where at least one adjacent digit distinguishes it from the letter O, the number is sometimes pronounced as ''oh'' or ''o'' (). Informal or slang terms for 0 include ''zilch'' and ''zip''. Historically, ''ought'', ''aught'' (), and ''cipher'', have also been used. Etymology The word ''zero'' came into the English language via French from the Italian , a contraction of the Venetian form of Italian via ''ṣafira'' or ''ṣifr''. In pre-Islamic time the word (Arabic ) had the meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galois Module
In mathematics, a Galois module is a ''G''-module, with ''G'' being the Galois group of some extension of fields. The term Galois representation is frequently used when the ''G''-module is a vector space over a field or a free module over a ring in representation theory, but can also be used as a synonym for ''G''-module. The study of Galois modules for extensions of local or global fields and their group cohomology is an important tool in number theory. Examples *Given a field ''K'', the multiplicative group (''Ks'')× of a separable closure of ''K'' is a Galois module for the absolute Galois group. Its second cohomology group is isomorphic to the Brauer group of ''K'' (by Hilbert's theorem 90, its first cohomology group is zero). *If ''X'' is a smooth proper scheme over a field ''K'' then the ℓ-adic cohomology groups of its geometric fibre are Galois modules for the absolute Galois group of ''K''. Ramification theory Let ''K'' be a valued field (with valuation denoted ''v'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-adic L-function
In mathematics, a ''p''-adic zeta function, or more generally a ''p''-adic ''L''-function, is a function analogous to the Riemann zeta function, or more general ''L''-functions, but whose domain and target are ''p-adic'' (where ''p'' is a prime number). For example, the domain could be the ''p''-adic integers Z''p'', a profinite ''p''-group, or a ''p''-adic family of Galois representations, and the image could be the ''p''-adic numbers Q''p'' or its algebraic closure. The source of a ''p''-adic ''L''-function tends to be one of two types. The first source—from which Tomio Kubota and Heinrich-Wolfgang Leopoldt gave the first construction of a ''p''-adic ''L''-function —is via the ''p''-adic interpolation of special values of ''L''-functions. For example, Kubota–Leopoldt used Kummer's congruences for Bernoulli numbers to construct a ''p''-adic ''L''-function, the ''p''-adic Riemann zeta function ζ''p''(''s''), whose values at negative odd integers are those of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernoulli Numbers
In mathematics, the Bernoulli numbers are a sequence of rational numbers which occur frequently in analysis. The Bernoulli numbers appear in (and can be defined by) the Taylor series expansions of the tangent and hyperbolic tangent functions, in Faulhaber's formula for the sum of ''m''-th powers of the first ''n'' positive integers, in the Euler–Maclaurin formula, and in expressions for certain values of the Riemann zeta function. The values of the first 20 Bernoulli numbers are given in the adjacent table. Two conventions are used in the literature, denoted here by B^_n and B^_n; they differ only for , where B^_1=-1/2 and B^_1=+1/2. For every odd , . For every even , is negative if is divisible by 4 and positive otherwise. The Bernoulli numbers are special values of the Bernoulli polynomials B_n(x), with B^_n=B_n(0) and B^+_n=B_n(1). The Bernoulli numbers were discovered around the same time by the Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli, after whom they are named, and inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic K-theory
Algebraic ''K''-theory is a subject area in mathematics with connections to geometry, topology, ring theory, and number theory. Geometric, algebraic, and arithmetic objects are assigned objects called ''K''-groups. These are groups in the sense of abstract algebra. They contain detailed information about the original object but are notoriously difficult to compute; for example, an important outstanding problem is to compute the ''K''-groups of the integers. ''K''-theory was discovered in the late 1950s by Alexander Grothendieck in his study of intersection theory on algebraic varieties. In the modern language, Grothendieck defined only ''K''0, the zeroth ''K''-group, but even this single group has plenty of applications, such as the Grothendieck–Riemann–Roch theorem. Intersection theory is still a motivating force in the development of (higher) algebraic ''K''-theory through its links with motivic cohomology and specifically Chow groups. The subject also includes classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Equation (L-function)
In mathematics, the L-functions of number theory are expected to have several characteristic properties, one of which is that they satisfy certain functional equations. There is an elaborate theory of what these equations should be, much of which is still conjectural. Introduction A prototypical example, the Riemann zeta function has a functional equation relating its value at the complex number ''s'' with its value at 1 − ''s''. In every case this relates to some value ζ(''s'') that is only defined by analytic continuation from the infinite series definition. That is, writingas is conventionalσ for the real part of ''s'', the functional equation relates the cases :σ > 1 and σ < 0, and also changes a case with :0 < σ < 1 in the ''critical strip'' to another such case, reflected in the line σ = ½. Therefore, use of the functional equation is basic, in order to study the zeta-function in the whole |