|
LUPEOL SYNTHESIS
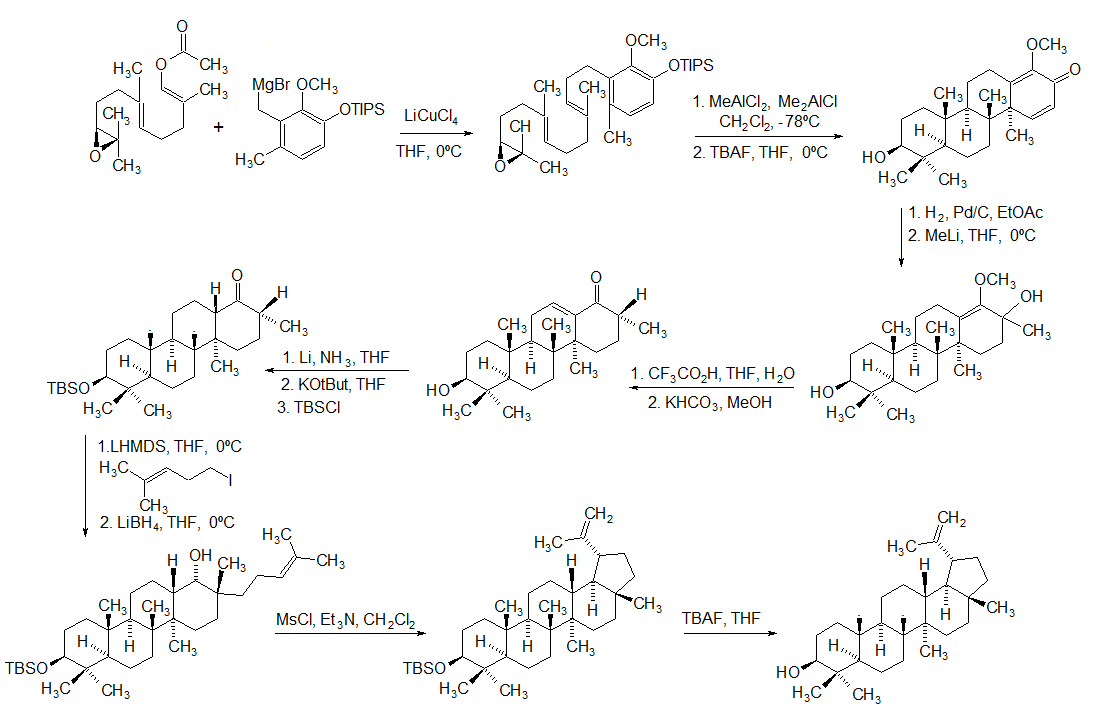
Lupeol is a pharmacologically active pentacyclic triterpenoid. It has several potential medicinal properties, like anticancer and anti-inflammatory activity. Natural occurrences Lupeol is found in a variety of plants, including mango, ''Acacia visco'' and ''Abronia villosa''. It is also found in dandelion coffee. Lupeol is present as a major component in ''Camellia japonica'' leaf. Total synthesis The first total synthesis of lupeol was reported by Gilbert Stork ''et al''. In 2009, Surendra and Corey reported a more efficient and enantioselective total synthesis of lupeol, starting from (''1E,5E'')-8- ''2S'')-3,3-dimethyloxiran-2-yl2,6-dimethylocta-1,5-dienyl acetate by use of a polycyclization. Biosynthesis Lupeol is produced by several organisms from squalene epoxide. Dammarane and baccharane skeletons are formed as intermediates. The reactions are catalyzed by the enzyme lupeol synthase. A recent study on the metabolomics of ''Camellia japonica'' leaf revealed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triterpenoid
Triterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of three terpene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of six isoprene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squalene, the precursor to all steroids. Structures Triterpenes exist in a great variety of structures. Nearly 200 different skeletons have been identified. These skeletons may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. In general pentacyclic structures (5 rings) tend to dominate. Squalene is biosynthesized through the head-to-head condensation of two farnesyl pyrophosphate units. This coupling converts a pair of C15 components into a C30 product. Squalene serves as precursor for the formation of many triterpenoids, including bacterial hopanoids and eukaryotic sterols. Triterpenoids By definition triterpenoids are triterpenes that possess heteroatoms, usually oxygen. The terms ''triterpene'' and ''triterpenoid'' ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemopreventive
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs (chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms (palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals (signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targets, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triterpenes
Triterpenes are a class of chemical compounds composed of three terpene units with the molecular formula C30H48; they may also be thought of as consisting of six isoprene units. Animals, plants and fungi all produce triterpenes, including squalene, the precursor to all steroids. Structures Triterpenes exist in a great variety of structures. Nearly 200 different skeletons have been identified. These skeletons may be broadly divided according to the number of rings present. In general pentacyclic structures (5 rings) tend to dominate. Squalene is biosynthesized through the head-to-head condensation of two farnesyl pyrophosphate units. This coupling converts a pair of C15 components into a C30 product. Squalene serves as precursor for the formation of many triterpenoids, including bacterial hopanoids and eukaryotic sterols. Triterpenoids By definition triterpenoids are triterpenes that possess heteroatoms, usually oxygen. The terms ''triterpene'' and ''triterpenoid'' oft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betulinic Acid
Betulinic acid is a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenoid which has antiretroviral, antimalarial, and anti-inflammatory properties, as well as a more recently discovered potential as an anticancer agent, by inhibition of topoisomerase. It is found in the bark of several species of plants, principally the white birch (''Betula pubescens'') from which it gets its name, but also the ber tree (''Ziziphus mauritiana''), selfheal (''Prunella vulgaris''), the tropical carnivorous plants '' Triphyophyllum peltatum'' and ''Ancistrocladus heyneanus'', '' Diospyros leucomelas'', a member of the persimmon family, '' Tetracera boiviniana'', the jambul (''Syzygium formosanum''), flowering quince (''Pseudocydonia sinensis'', former ''Chaenomeles sinensis KOEHNE''), (''Chaenomeles sinensis KOEHNE'' is now named ''Pseudocydonia sinensis'') rosemary, and ''Pulsatilla chinensis''. Antitumor activity In 1995, betulinic acid was reported as a selective inhibitor of human melanoma. Then i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betulin
Betulin is an abundant, naturally occurring triterpene. It is commonly isolated from the bark of birch trees. It forms up to 30% of the dry weight of silver birch bark. It is also found in birch sap. '' Inonotus obliquus'' and red alder also contain betulin. The compound in the bark gives the tree its white color which appears to protect the tree from mid-winter overheating by the sun. As a result, birches are some of the northernmost occurring deciduous trees. It can be converted to betulinic acid (the alcohol group replaced by a carboxylic acid group), which is biologically more active than betulin itself. History Betulin was discovered in 1788 by German-Russian chemist Johann Tobias Lowitz. Chemistry Chemically, betulin is a triterpenoid of lupane structure. It has a pentacyclic ring structure, and hydroxyl groups in positions C3 and C28. Biological activities Preliminary ''in vitro'' studies have shown that betulin demonstrates anti-cancer properties against a variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camellia Japonica
''Camellia japonica'', known as common camellia, or Japanese camellia, is a species of flowering plant in the family Theaceae. There are thousands of cultivars of ''C. japonica'' in cultivation, with many colors and forms of flowers. In the U.S. it is sometimes called japonica. In the wild, it is found in mainland China (Shandong, east Zhejiang), Taiwan, southern Korea and southwestern Japan. It grows in forests, at altitudes of around . Camellias are famous throughout East Asia; they are known as ''tsaa4 faa1'' (, lit. "tea flower") in Cantonese, ''cháhuā'' () in Mandarin Chinese, ''tsubaki'' () in Japanese, ''dongbaek-kkot'' () in Korean, and as ''hoa trà'' or ''hoa chè'' in Vietnamese. The leaves of this species are rich in anti-inflammatory terpenoids such as lupeol and squalene. Description ''Camellia japonica'' is a flowering tree or shrub, usually tall, but occasionally up to tall. Some cultivated varieties achieve a size of 72 m2 or more. The youngest branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
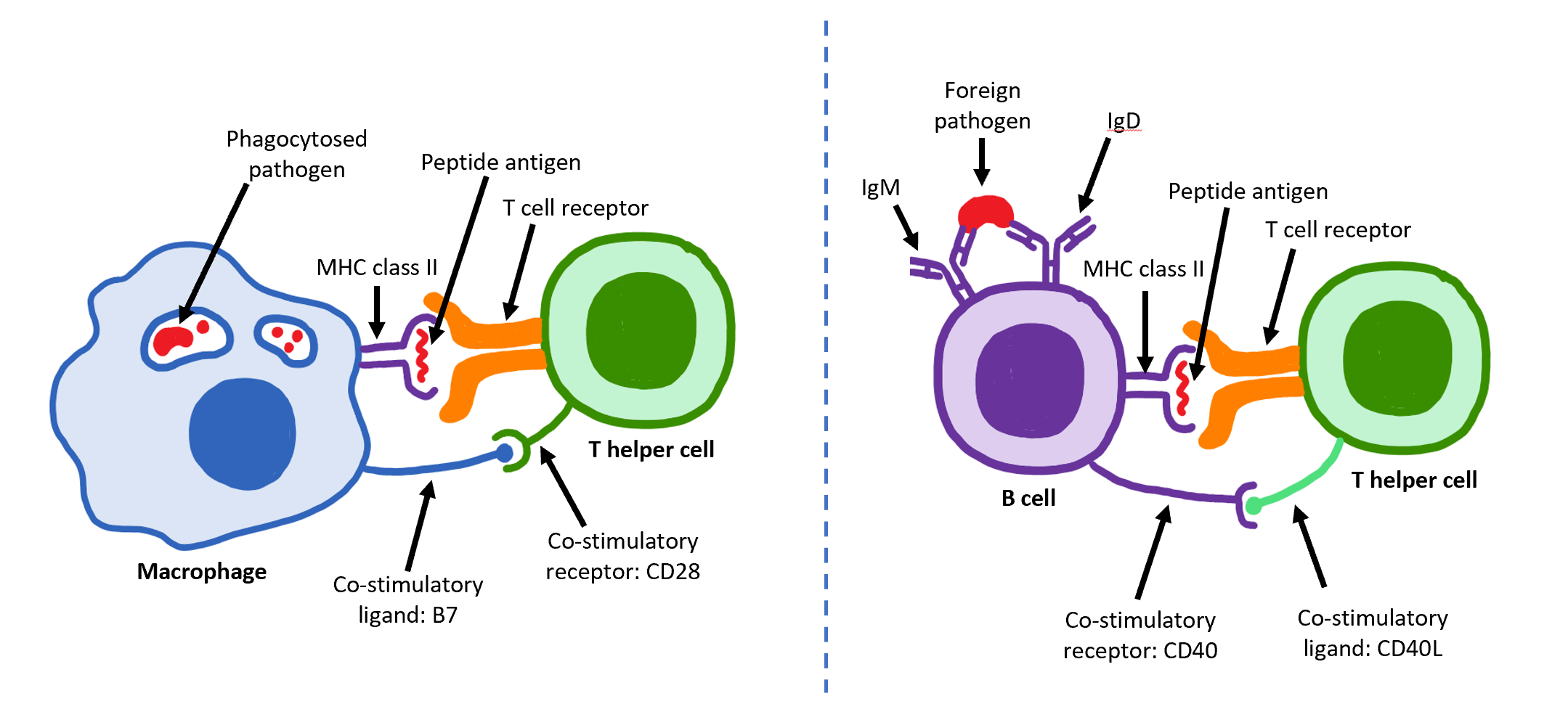
T Helper Cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considered essential in B cell antibody class switching, breaking cross-tolerance in dendritic cells, in the activation and growth of cytotoxic T cells, and in maximizing bactericidal activity of phagocytes such as macrophages and neutrophils. CD4+ cells are mature Th cells that express the surface protein CD4. Genetic variation in regulatory elements expressed by CD4+ cells determines susceptibility to a broad class of autoimmune diseases. Structure and function Th cells contain and release cytokines to aid other immune cells. Cytokines are small protein mediators that alter the behavior of target cells that express receptors for those cytokines. These cells help polarize the immune response depending on the nature of the immunological insult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin
Interleukins (ILs) are a group of cytokines (secreted proteins and signal molecules) that are expressed and secreted by white blood cells (leukocytes) as well as some other body cells. The human genome encodes more than 50 interleukins and related proteins. The function of the immune system primarily depends on interleukins, and rare deficiencies of a number of them have been described, all featuring autoimmune diseases or immune deficiency. The majority of interleukins are synthesized by CD4 helper T-lymphocyte, as well as through monocytes, macrophages, and endothelial cells. They promote the development and differentiation of T and B lymphocytes, and hematopoietic cells. Interleukin receptors on astrocytes in the hippocampus are also known to be involved in the development of spatial memories in mice. History and name The name "interleukin" was chosen in 1979, to replace the various different names used by different research groups to designate interleukin 1 (lymphocyte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC), squamous-cell skin cancer (SCC) and melanoma. The first two, along with a number of less common skin cancers, are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC). Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it but is unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death. It often appears as a painless raised area of skin that may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it or may present as a raised area with an ulcer. Squamous-cell skin cancer is more likely to spread. It usually presents as a hard lump with a scaly top but may also form an ulcer. Melanomas are the most aggressive. Signs include a mole that has changed in size, shape, color, has irregular edges, has more than one color, is itchy or bleeds. More than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostate
The prostate is both an Male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the Urinary bladder, bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue as well as connective tissue. The prostate glands produce and contain fluid that forms part of semen, the substance emitted during ejaculation as part of the male Human sexual response cycle, sexual response. This prostatic fluid is slightly alkaline, milky or white in appearance. The alkalinity of semen helps neutralize the acidity of the vagina, vaginal tract, prolonging the lifespan of sperm. The prostatic fluid is expelled in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prolyl Oligopeptidase
Prolyl endopeptidase (PE) also known as prolyl oligopeptidase or post-proline cleaving enzyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PREP'' gene. Function Prolyl endopeptidase is a large cytosolic enzyme that belongs to a distinct class of serine peptidases. It was first described in the cytosol of rabbit brain as an oligopeptidase, which degrades the nonapeptide bradykinin at the Pro-Phe bond. The enzyme is involved in the maturation and degradation of peptide hormones and neuropeptides such as alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH), thyrotropin-releasing hormone, angiotensin, neurotensin, oxytocin, substance P and vasopressin. PREP cleaves peptide bonds at the C-terminal side of proline residues. Its activity is confined to action on oligopeptides of less than 10 kD and it has an absolute requirement for the trans-configuration of the peptide bond preceding proline. Prolyl endopeptidases are involved in the maturation and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |