|
LNWR Teutonic Class
The LNWR Teutonic class was a class of 10 passenger three-cylinder compound locomotive, compound 2-2-2-0 locomotives designed by F. W. Webb for the London and North Western Railway, and manufactured by them in their Crewe Works between 1889 and 1890. Design The design featured a boiler pressed to delivering saturated steam to two outside high-pressure cylinders, which exhausted to one low-pressure cylinder inside the frames. All three cylinders had a stroke of ; the high-pressure cylinders drove the rear wheels, while the low-pressure drove the leading driving wheels. As the two pairs of driving wheels were not connected, the locomotives were "duplex locomotive, duplex drive" or "double-singles". They were a development of Webb's LNWR Dreadnought Class, Dreadnought class; they had larger driving and leading wheels, and the additions of cylinder tail rods (which were later removed). There were also further modifications to the Joy valve gear, but the seven locomotives built i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Teutonic
The RMS ''Teutonic'' was an ocean liner built for the White Star Line in Belfast and was the first armed merchant cruiser. History Background In the late 1880s competition for the Blue Riband, the award for the fastest Atlantic crossing, was fierce amongst the top steamship lines, and White Star decided to order two ships from Harland and Wolff that would be capable of an average Atlantic crossing speed of . Construction of ''Teutonic'' and RMS Majestic (1889), ''Majestic'' began in 1887. When ''Teutonic'' was launched on 19 January 1889, she was the first White Star ship without square rigged sails. The ship was completed on 25 July 1889 and participated in the Spithead Naval Review on 5 and 6 August, in conjunction with the state visit of Emperor Wilhelm II, Kaiser Wilhelm II. Although Queen Victoria remained aboard the Royal Yacht, the Kaiser was given a two-hour tour of the new ship hosted by his "Uncle Bertie," (the Prince of Wales and future Edward VII). During the tour, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNWR Whale Experiment Class
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Experiment Class was a class of 4-6-0 steam locomotive designed by George Whale. Career They were an extended version of the Whale's Precursor Class 4-4-0, with slightly smaller driving wheels. The first of the class, 66 ''Experiment'' was built in 1905 and a total of 105 were constructed up until 1910. The LNWR reused numbers and names of withdrawn locomotives, with the result that the numbering system was completely haphazard. A 19in Express Goods Class with smaller driving wheels was also built from 1906. From 1911, a superheated version, the Prince of Wales Class was built. In 1915, 1361 ''Prospero'' was experimentally rebuilt with four cylinders, Dendy Marshall valve gear and superheated. The conversion was not repeated. Only two other engines were given superheaters; 2624 ''Saracen'' and 1993 (LMS 5472) ''Richard Moon''. All entered London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) stock upon grouping in 1923. The LMS gave them th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
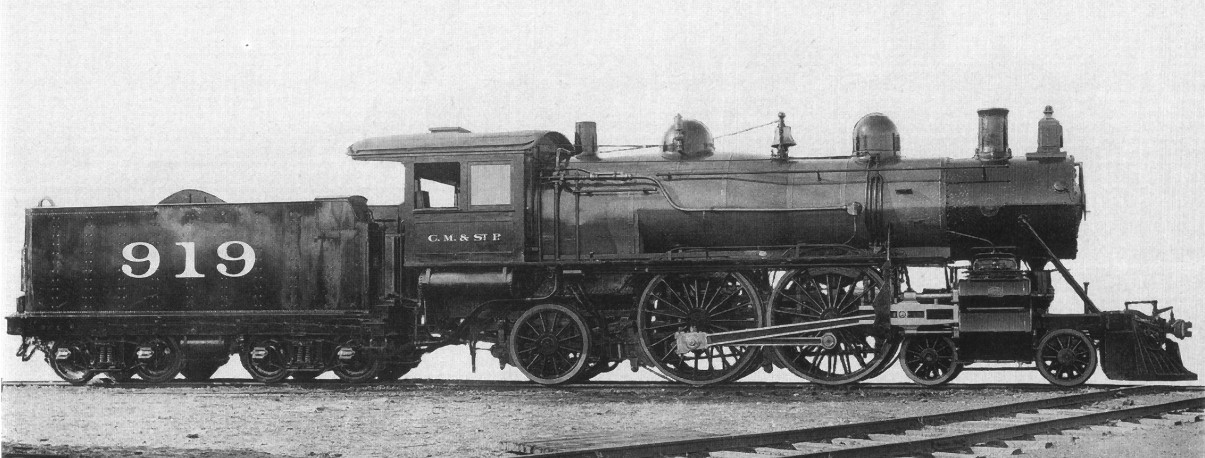
Compound Locomotives
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in France, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to maintenance issues and because superheating provided similar efficiencies at lower cost. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway right up to 1952. Introduction In the usual arrangement for a compound engine the steam is first expanded in one or two high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinders, then having given up some heat and lost some pressure, it exhausts into a larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinder, (or two, - or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1890
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-2-2-0 Locomotives
The hyphen-minus is the most commonly used type of hyphen, widely used in digital documents. It is the only character that looks like a minus sign or a dash in many character sets such as ASCII or on most keyboards, so it is also used as such. The name "hyphen-minus" derives from the original ASCII standard, where it was called "hyphen(minus)". The character is referred to as a "hyphen", a "minus sign", or a "dash" according to the context where it is being used. Description In early monospaced font typewriters and character encodings, a single key/code was almost always used for hyphen, minus, various dashes, and strikethrough, since they all have a roughly similar appearance. The current Unicode Standard specifies distinct characters for a number of different dashes, an unambiguous minus sign ("Unicode minus") at code point U+2212, and various types of hyphen including the unambiguous "Unicode hyphen" at U+2010 and the hyphen-minus at U+002D. When a hyphen is called for, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Western Railway Locomotives
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished from the Lord Mayo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Gallic (1894)
SS ''Gallic'' was a paddle steamer that built in Scotland 1894 as ''Birkenhead'', renamed ''Gallic'' in 1907 and scrapped in Liverpool in 1914. She was designed and built as a Mersey Ferry for Birkenhead Corporation. White Star Line bought her in 1907 to use as a passenger tender, and renamed her ''Gallic''. John Scott & Co built ''Birkenhead'' at its Abden shipyard in Kinghorn in Fife as yard number 87. She was launched on 7 June 1894 and completed that same month. Her registered length was , her beam was and her depth was . Her tonnages were and . ''Birkenhead'' was a side-wheel paddle steamer. Each wheel was driven by a four-cylinder diagonal compound steam engine. Between them her two engines were rated at a total of 177 NHP and gave her a speed of . Birkenhead Council registered ''Birkenhead'' at Liverpool. Her United Kingdom official number was 102164. White Star Line based ''Gallic'' at Cherbourg. She was soon considered too small for tending the company's increasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Celtic (1872)
SS ''Celtic'' was an ocean liner built for the White Star Line by shipbuilders Harland and Wolff of Belfast. The ''Celtic'' (later the ''Amerika''), the first of two White Star ships to bear the name, was the second of two ''Oceanic''-class liners commissioned by White Star, following the success of their first four steamships (the ''Adriatic'' being the earlier of the new pair). The new ship was originally proposed to be named ''Arctic'', but as the American Collins Line had a paddle-wheel steamer with that name (it sank in 1854) the White Star managers changed their minds, and settled on the name ''Celtic''. ''Celtic'' was one of six liners built for White Star to allow the line to operate a mail service across the Atlantic. (As the ships had a five week turnaround, five ships were needed to allow a weekly service, with the sixth ship acting as a spare). ''Celtic'' was a duplicate of ''Adriatic'' and like ''Adriatic'', was larger than the first four ships. ''Celtic'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Adriatic (1871)
SS ''Adriatic'' was the first of two White Star Line ocean liners to carry the name ''Adriatic''. The White Star Line's first four steamships, the ( ''Oceanic'' (I), ''Atlantic'', ''Baltic'', and the ''Republic'') met with great success in the trans-Atlantic market, and the line decided to build two more. The first of these was the SS ''Adriatic'', which was built by Harland and Wolff and launched on 17 October 1871; the second was the ''Celtic''. History During the remainder of 1871 and the early part of 1872, ''Adriatic'' was fitted out. As a part of this process, a technology new to that era was tried on the ship. Up to this point, ships' cabins had been lit by oil lamps, but the builders decided to try new gas lamps on ''Adriatic''. A machine was added to the engine room to produce gas from coal, the first ship in the world to have such a system, but problems with gas leaks meant it had to be removed before the ship went into service. ''Adriatic'' left on her maiden v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Coptic (1881)
SS ''Coptic'' was a steamship built in 1881, which was successively owned by the Oceanic Steam Navigation Company, the Pacific Mail Steamship Company, and the Japanese Oriental Steam Ship Co. (''Toyo Kisen Kabushiki Kaisha'') before being scrapped in 1926. She was filmed by Thomas Edison in 1897 in one of his early movies. The movie is currently stored in the Library of Congress, archive.org and other internet archives. Ship history A sister ship to , ''Coptic'' was built at the Harland & Wolff shipyard in Belfast, for service with the Oceanic Steam Navigation Company's White Star Line. Launched on 10 August 1881, she was delivered on 9 November 1881 and made her maiden voyage from Liverpool to New York on 16 November 1881 under the command of Captain Edward J. Smith, who later was the captain of on her disastrous 1912 maiden voyage. On the return voyage, a hurricane stove in several of her lifeboats and drowned two seamen who were swept overboard. On 11 March 1882, she sai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Ionic (1883)
SS ''Ionic'' was a cargo liner initially in service with White Star Line from 1883 until 1900. She was used on the company's joint route to New Zealand with the Shaw, Savill & Albion Line. She was sold to the Aberdeen Line in 1900 and renamed SS ''Sophocles'', and was withdrawn for service in 1906 and scrapped in 1908. Service ''Ionic'' was built by Harland and Wolff, Belfast and launched on 11 January 1883, being delivered to her new owners on 28 March 1883. She was almost immediately chartered for service with the New Zealand Shipping Company, along with the White Star ships and , to fill a gap while the company was awaiting the delivery of new ships. After being inspected by the Prince of Wales, ''Ionic'' began her maiden voyage from London to Wellington, sailing via the Cape of Good Hope, in April 1884, setting a new record for the passage. She was placed on the regular joint White Star - Shaw, Savill & Albion route from December 1884, managed by Shaw, Savill & Albion but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SS Doric (1883)
SS ''Doric'' was a British ocean liner operated by White Star Line. She was put into service in 1883. Built by the Harland and Wolff shipyards in Belfast, she was the sister ship of the ''Ionic'' which was put into service a few months earlier. Although the original purpose of the construction of the two ships was not known with certainty, both began their careers chartered by the New Zealand Shipping Co. which operated them on the route from London to Wellington. As early as 1885, the ''Doric'', like her sister ship and the ''Coptic'', was assigned to the same route, but this time for the joint service provided by the White Star Line and the Shaw, Savill & Albion Line. The ship carried out this mission without experiencing any major incident, until she was overhauled in 1895 in order to modernize it. Deemed unnecessary on the New Zealand route, the ''Doric'' was chartered by the Occidental and Oriental Steamship Company between Hong Kong and San Francisco. It was in 1906 tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |