|
LNWR Jubilee Class
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Jubilee Class was a class of 4-4-0 4-cylinder compound locomotives by F.W. Webb. A total of forty were built from 1897–1900. Slightly unusually for the LNWR, the class received a number series, this being 1901–1940. As with other Webb compounds, they were mechanically unreliable. As a result, George Whale rebuilt these as two cylinder simple locomotives of the Renown Class, starting with 1918 ''Renown'' in 1908. Rebuilt engines retained their numbers. Rebuilding continued so that at the grouping of 1923, only 9 Jubilees remained. These were 1903/4/8/11/12/15/23/27/29. 1908 ''Royal George'' was withdrawn in January 1923, but the remaining eight were allocated the LMS numbers 5110–5117, in sequence. Two, 1904 ''Rob Roy'' and 1923 ''Agamemnon'' were withdrawn 1923, without receiving new numbers. The LMS rebuilt the remaining six into Renowns in 1924, making the class extinct. (Their subsequent history is discussed at LNWR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previous British monarch and is known as the Victorian era. It was a period of industrial, political, scientific, and military change within the United Kingdom, and was marked by a great expansion of the British Empire. In 1876, the British Parliament voted to grant her the additional title of Empress of India. Victoria was the daughter of Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn (the fourth son of King George III), and Princess Victoria of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld. After the deaths of her father and grandfather in 1820, she was raised under close supervision by her mother and her comptroller, John Conroy. She inherited the throne aged 18 after her father's three elder brothers died without surviving legitimate issue. Victoria, a constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vintage Railway Album- 4 - Colossus At Harrow & Wealdstone Station C
Vintage, in winemaking, is the process of picking grapes and creating the finished product—wine (see Harvest (wine)). A vintage wine is one made from grapes that were all, or primarily, grown and harvested in a single specified year. In certain wines, it can denote quality, as in Port wine, where Port houses make and declare vintage Port in their best years. From this tradition, a common, though not strictly correct, usage applies the term to any wine that is perceived to be particularly old or of a particularly high quality. Most countries allow a vintage wine to include a portion of wine that is not from the year denoted on the label. In Chile and South Africa, the requirement is 75% same-year content for vintage-dated wine. In Australia, New Zealand, and the member states of the European Union, the requirement is 85%. In the United States, the requirement is 85%, unless the wine is designated with an AVA, (e.g., Napa Valley), in which case it is 95%. Technically, the 85% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
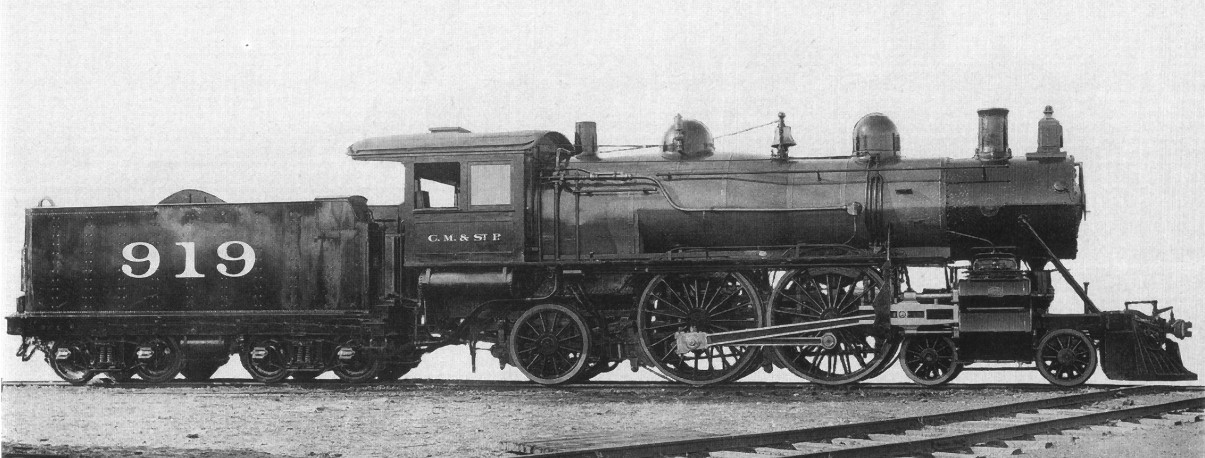
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1897
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles ( rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Western Railway Locomotives
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished from the Lord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Locomotives
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in France, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to maintenance issues and because superheating provided similar efficiencies at lower cost. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway right up to 1952. Introduction In the usual arrangement for a compound engine the steam is first expanded in one or two high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinders, then having given up some heat and lost some pressure, it exhausts into a larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinder, (or two, - or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposition Universelle (1900)
The Exposition Universelle of 1900, better known in English as the 1900 Paris Exposition, was a world's fair held in Paris, France, from 14 April to 12 November 1900, to celebrate the achievements of the past century and to accelerate development into the next. It was held at the esplanade of Les Invalides, the Champ de Mars, the Trocadéro and at the banks of the Seine between them, with an additional section in the Bois de Vincennes, and it was visited by more than 50 million people. Many international congresses and other events were held within the framework of the Exposition, including the 1900 Summer Olympics. Many technological innovations were displayed at the Fair, including the '' Grande Roue de Paris'' ferris wheel, the ''Rue de l'Avenir'' moving sidewalk, the first ever regular passenger trolleybus line, escalators, diesel engines, electric cars, dry cell batteries, electric fire engines, talking films, the telegraphone (the first magnetic audio recorder), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Henry Ismay
Thomas Henry Ismay (7 January 1837 – 23 November 1899) was the founder of the Oceanic Steam Navigation Company, more commonly known as the White Star Line. His son Joseph Bruce Ismay was managing director of the ''White Star Line''; and, in 1912, he sailed on the maiden voyage of the ocean liner . Early years Thomas Ismay was born on 7 January 1837, in a small cottage in the town of Maryport, Cumberland. Some time after Thomas's birth, his father Joseph Ismay started a timber business, shipbrokers and shipbuilder. He bought shares in five vessels coming in and out of Maryport. When Thomas was six, the Ismays moved to a much larger house in Grasslot, Maryport. The entire family moved to the dwelling because of the three sisters Thomas's mother had. The home's name was "The Ropery", the name deriving from the ropes being used at the shipyard laid out in front of the home. This house was near his grandfather's shipyard. This was the first place where he was employed. He spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNWR Renown Class
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Renown Class was a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives. They were rebuilds of F.W. Webb's 4-cylinder compounds of the Jubilee and Alfred the Great classes into 2-cylinder simple engines by George Whale, later continued by Charles Bowen-Cooke. The first to be rebuilt was number 1918 ''Renown'' in 1908. The rebuilds retained their original numbers. Unusually for the LNWR, the parent classes also had logical number series. Thus the Renowns were all numbered in the 1901–1940 series for ex-Jubilee Class and 1941–1980 for ex-Benbow class. In 1920, locomotive 1914 '' Invincible'' was renumbered 1257, and the number 1914 was then taken by the Claughton Class war memorial engine 1914 ''Patriot''. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) acquired 56 Renowns in 1923. The LMS allocated these numbers in the 5131–5186 series, listed according to date of rebuilding, though not all numbers were applied before withdrawals started in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Webb (engineer)
Francis William Webb (21 May 1836 – 4 June 1906) was an English railway engineer, responsible for the design and manufacture of locomotives for the London and North Western Railway (LNWR). Webb was born in Tixall Rectory, near Stafford, the second son of William Webb, Rector of Tixall. Career Crewe Works Showing early interest in mechanical engineering, on 11 August 1851 at the age of fifteen he was articled as a pupil of Francis Trevithick at Crewe Works.Griffiths, p.51 Webb joined the drawing office in 1856, at the end of his training. He became Chief Draughtsman on 1 March 1859. On 1 September 1861 he was appointed Works Manager at Crewe and Chief Assistant to John Ramsbottom (engineer), John Ramsbottom. Whilst Works Manager Webb was responsible for the installation of Bessemer process, Bessemer converters and the start of steel production at Crewe. Bolton Iron and Steel Company In July 1866 Webb resigned from the LNWR and moved to the John Hick (MP)#Bolton Iron and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Whale
George Whale (7 December 1842 – 7 March 1910) was an English locomotive engineer who was born in Bocking, Essex, and educated in Lewisham, London. He worked for the London and North Western Railway (LNWR). Career In 1858 he entered the LNWR's Wolverton Works under James Edward McConnell, and when in 1862 the LNWR Board decided to concentrate locomotive construction and repair at Crewe Works under John Ramsbottom, Whale was one of around 400 workers transferred from Wolverton to Crewe. In 1865 he entered the drawing office at Crewe Works, and in 1867 joined the LNWR running department under J. Rigg. In 1898 he was made responsible for the running of all LNWR locomotives. Francis William Webb, the LNWR Locomotive Superintendent, gave twelve months notice of retirement to the LNWR Board in November 1902. On 22 April 1903, the Board announced that Whale had been chosen to succeed Webb, who was to retire at the end of July 1903. Webb's health was failing, and Whale soon took up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Locomotive
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in France, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to maintenance issues and because superheating provided similar efficiencies at lower cost. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway right up to 1952. Introduction In the usual arrangement for a compound engine the steam is first expanded in one or two high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinders, then having given up some heat and lost some pressure, it exhausts into a larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinder, (or two, - o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)