|
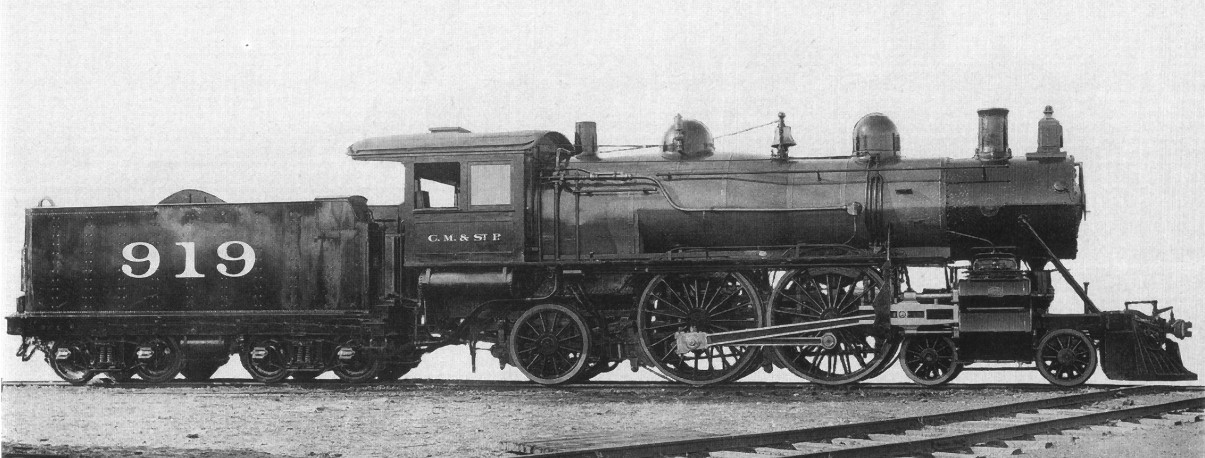
LNWR Class F
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Class F was a class of 2-8-0 steam locomotives in service between 1906 and 1928. History George Whale had rebuilt 26 of the Class B compound 0-8-0s with the simple addition of a leading pony truck between 1904-1908 to what would from 1911 become Class E. However, from 1906 rebuilds of Class Bs were given a larger 5'2" diameter boilers, and ten were so rebuilt. To these was added a pair of rebuilds of Class Es (Nos 1038 in 1907 and 647 in 1908). From 1921, the LNWR started rebuilding the Class Fs into Class G1 superheated 0-8-0s, and by the grouping of 1923, six had been rebuilt. The remaining six were allocated the LMS numbers 9610-5. The LMS rebuilt a further four to G1s, between 1923-5. The remaining pair were withdrawn in 1927 and 1928 without being rebuilt. None was preserved. List of locomotives LMS numbers in parentheses were not carried prior to rebuilding as G1 or withdrawal. Notes References * Further reading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Grey
Photographic grey, also known as works grey, was a paint scheme commonly applied to steam locomotives during the period before colour photography became commonplace. It was applied to allow sharper, more detailed images of the locomotive to be recorded. The first photographs of railways and their locomotives were made by private individuals, but by the 1860s the railway companies themselves were keen to create official photographs of the highest quality possible of their latest designs, which led to the adoption of photographic grey in railway photography. Use Railway companies wished to record their latest locomotives for use in publicity material and advertisements, and as a technical record of their work. This was especially the case in the United Kingdom, where all but the smallest of the 'pre-grouping' companies owned their own locomotive works and designed and built their own railway engines. For the numerous private locomotive builders it was especially important to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNWR Locomotive No
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the L&NWR was the largest joint stock company in the United Kingdom. In 1923, it became a constituent of the London, Midland and Scottish (LMS) railway, and, in 1948, the London Midland Region of British Railways: the LNWR is effectively an ancestor of today's West Coast Main Line. History The company was formed on 16 July 1846 by the amalgamation of the Grand Junction Railway, London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway. This move was prompted, in part, by the Great Western Railway's plans for a railway north from Oxford to Birmingham. The company initially had a network of approximately , connecting London with Birmingham, Crewe, Chester, Liverpool and Manchester. The headquarters were at Euston railway station. As traffic increased, it was greatly expanded with the opening in 1849 of the Great Hall, designed by Phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1906
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Locomotives
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in France, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to maintenance issues and because superheating provided similar efficiencies at lower cost. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway right up to 1952. Introduction In the usual arrangement for a compound engine the steam is first expanded in one or two high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinders, then having given up some heat and lost some pressure, it exhausts into a larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinder, (or two, - or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Western Railway Locomotives
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as ''Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished from the Lord Mayo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willie Yeadon
Willie Brayshaw Yeadon (28 June 1907 – 16 January 1997), was a British railway historian known for his ''magnum opus'', ''Yeadon's Register of LNER Locomotives'' and other works. Biography Willie Yeadon was born in Yeadon, West Riding of Yorkshire on 28 June 1907. He trained as a mechanical engineer, initially working for the Bradford Dyers' Association Ltd. After being made redundant in the 1930s he joined the Hull firm Fenner in 1931. Yeadon's initial railway interest was the London & North Western Railway. On moving to East Yorkshire he began to study the activities of the London and North Eastern Railway, starting to collect railway images around 1933. British Rail's 1955 modernisation plan prompted him to begin a systematic study of the locomotives of the LNER, during which he visited engine sheds and works, collecting locomotive related documentation such as works records. He joined the Railway Correspondence and Travel Society in 1936 and made significant contributi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Jenkinson
David Jenkinson (6 August 1934 – 27 April 2004) was a railway modeller and historian, who had a particular interest in the London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) and was president of the LMS Society. Biography Jenkinson was born in Leeds and educated at Prince Henry's Grammar School, Otley, which in 1951 took him to a field trip to the Settle-Carlisle Railway line (S&C), which would start a lengthy relationship with that line. He went to London University where he met his future wife Sheila, with whom he had four children (Christopher, Hilary, Timothy and Nicola). After graduating Jenkinson joined the Royal Air Force (RAF) in 1956, from which he retired in 1972 having achieved the rank of Squadron Leader. During this time he built his 4 mm scale EM gauge models ''Marthwaite'' and ''Garsdale Road'' (see Garsdale) representing a station on the S&C set during the 1930s period when it was run by the LMS. In 1963, with Bob Essery and others he founded the LMS Society. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Essery
Robert J. "Bob" Essery (22 November 1930 – 23 November 2021) was a British railway modeller and historian with a particular interest in the London Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) and one of its principal constituents, the Midland Railway (MR). Essery was one of the founding members of the LMS Society in 1963, and particularly with David Jenkinson has authored many books. He worked in his early working years as a fireman on the LMS. Essery also established the historical journals ''Midland Record'' and ''LMS Journal''. From 1999 in collaboration with the National Railway Museum The National Railway Museum is a museum in York forming part of the Science Museum Group. The museum tells the story of rail transport in Britain and its impact on society. It is the home of the national collection of historically significant r ..., Essery with others have produced monographs on individual locomotive classes. Bibliography * ''Locomotive Liveries of the LMS'' D Jenkinson & R J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LNWR Class G1
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR) Class G1 was a class of 0-8-0 steam locomotives. It was a superheated version of the LNWR Class G with 8 inch piston valves. The prototype was rebuilt in 1912 from a member of Class G and a further 170 new locomotives were built between 1912 and 1918. In addition, 278 older locomotives were rebuilt to the G1 specification between 1917 and 1934. Numbering Numbering is somewhat complicated. The LNWR used a numbering system based on the lowest available number, with the result that the numbers were scattered through the stock book. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) renumbered the engines into a more logical series. However, they also then continued to rebuild engines, which retained the numbers originally assigned by the LMS. British Railways (BR) inherited 98 locomotives in 1948 and numbered them in the range 48892-49384. The number series is not continuous because some numbers in the same range were given to G2A Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Whale
George Whale (7 December 1842 – 7 March 1910) was an English locomotive engineer who was born in Bocking, Essex, and educated in Lewisham, London. He worked for the London and North Western Railway (LNWR). Career In 1858 he entered the LNWR's Wolverton Works under James Edward McConnell, and when in 1862 the LNWR Board decided to concentrate locomotive construction and repair at Crewe Works under John Ramsbottom, Whale was one of around 400 workers transferred from Wolverton to Crewe. In 1865 he entered the drawing office at Crewe Works, and in 1867 joined the LNWR running department under J. Rigg. In 1898 he was made responsible for the running of all LNWR locomotives. Francis William Webb, the LNWR Locomotive Superintendent, gave twelve months notice of retirement to the LNWR Board in November 1902. On 22 April 1903, the Board announced that Whale had been chosen to succeed Webb, who was to retire at the end of July 1903. Webb's health was failing, and Whale soon took up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London, Midland And Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with LNER, GWR and SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally used in historical circles. The LMS occasionally also used the initials LM&SR. For consistency, this article uses the initials LMS.) was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railways into four. The companies merged into the LMS included the London and North Western Railway, Midland Railway, the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (which had previously merged with the London and North Western Railway on 1 January 1922), several Scottish railway companies (including the Caledonian Railway), and numerous other, smaller ventures. Besides being the world's largest transport organisation, the company was also the largest commercial enterprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |