|
LM3914
The LM3914 is an integrated circuit (IC), designed by National Semiconductor in the late 1970s, used to operate displays that visually show the magnitude of an analog signal. It can drive up to 10 LEDs, LCDs, or vacuum fluorescent displays on its outputs. The linear scaling of the output thresholds makes the device usable, for example, as a voltmeter. In the basic configuration it provides a ten step scale which is expandable to over 100 segments with other LM3914 ICs in series. Features The LM3914 / LM3915 / LM3916 are identical except for the ten resistor divider inside each part. * LM3914 - linear steps, scaled by a resistor divider consisting of ten 1000 ohm resistors. * LM3915 - 3 dB logarithmic steps, scaled by a resistor divider consisting of 6630, 4690, 3310, 2340, 1660, 1170, 830, 590, 410, 1000 ohm resistors. * LM3916 - VU-meter steps, scaled by a resistor divider consisting of 1087, 970, 864, 769, 1298, 1031, 819, 923, 1531, 708 ohm resistors. All the devices in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
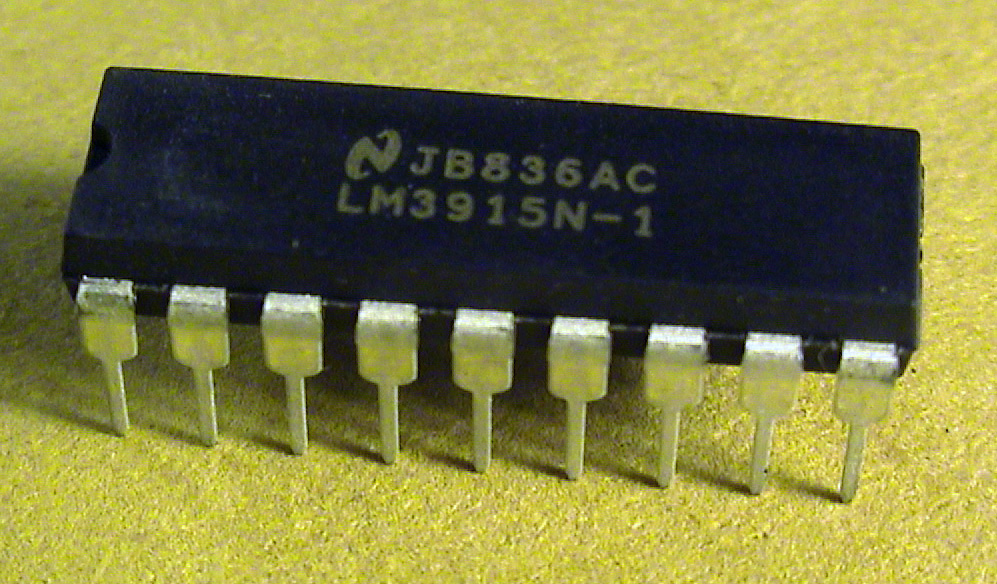
LM3915
The LM3914 is an integrated circuit (IC), designed by National Semiconductor in the late 1970s, used to operate displays that visually show the magnitude of an analog signal. It can drive up to 10 LEDs, LCDs, or vacuum fluorescent displays on its outputs. The linear scaling of the output thresholds makes the device usable, for example, as a voltmeter. In the basic configuration it provides a ten step scale which is expandable to over 100 segments with other LM3914 ICs in series. Features The LM3914 / LM3915 / LM3916 are identical except for the ten resistor divider inside each part. * LM3914 - linear steps, scaled by a resistor divider consisting of ten 1000 ohm resistors. * LM3915 - 3 dB logarithmic steps, scaled by a resistor divider consisting of 6630, 4690, 3310, 2340, 1660, 1170, 830, 590, 410, 1000 ohm resistors. * LM3916 - VU-meter steps, scaled by a resistor divider consisting of 1087, 970, 864, 769, 1298, 1031, 819, 923, 1531, 708 ohm resistors. All the devices in this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of LM-series Integrated Circuits
The following is a list of LM-series integrated circuits. Many were among the first analog integrated circuits commercially produced since late 1965; some were groundbreaking innovations. As of 2007, many are still being used. The LM series originated with integrated circuits made by National Semiconductor. The prefix LM stands for ''linear monolithic'', referring to the analog components integrated onto a single piece of silicon. Because of the popularity of these parts, many of them were second-sourced by other manufacturers who kept the sequence number as an aid to identification of compatible parts. Several generations of pin-compatible descendants of the original parts have since become ''de facto'' standard electronic components. Operational amplifiers Differential comparators Current-mode (Norton) amplifiers Instrumentation amplifiers Audio amplifiers Precision reference Voltage regulators Voltage-to-frequency converters Current s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Semiconductor
National Semiconductor was an American semiconductor manufacturer which specialized in analog devices and subsystems, formerly with headquarters in Santa Clara, California. The company produced power management integrated circuits, display drivers, audio and operational amplifiers, communication interface products and data conversion solutions. National's key markets included wireless handsets, displays and a variety of broad electronics markets, including medical, automotive, industrial and test and measurement applications. On September 23, 2011, the company formally became part of Texas Instruments as the "Silicon Valley" division. History Founding National Semiconductor was founded in Danbury, Connecticut, by Dr. Bernard J. Rothlein on May 27, 1959, when he and seven colleagues, Edward N. Clarke, Joseph J. Gruber, Milton Schneider, Robert L. Hopkins, Robert L. Koch, Richard R. Rau and Arthur V. Siefert, left their employment at the semiconductor division of Sperry Rand Corp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnitude (mathematics)
In mathematics, the magnitude or size of a mathematical object is a property which determines whether the object is larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind. More formally, an object's magnitude is the displayed result of an order theory, ordering (or ranking)—of the class (mathematics), class of objects to which it belongs. In physics, magnitude can be defined as quantity or distance. History The Greeks distinguished between several types of magnitude, including: *Positive fractions *Line segments (ordered by length) *Geometric shape, Plane figures (ordered by area) *Solid geometry, Solids (ordered by volume) *Angle, Angles (ordered by angular magnitude) They proved that the first two could not be the same, or even isomorphic systems of magnitude. They did not consider negative number, negative magnitudes to be meaningful, and ''magnitude'' is still primarily used in contexts in which zero is either the smallest size or less than all possible sizes. Numbers Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Signal
An analog signal or analogue signal (see spelling differences) is any continuous signal representing some other quantity, i.e., ''analogous'' to another quantity. For example, in an analog audio signal, the instantaneous signal voltage varies continuously with the pressure of the sound waves. In contrast, a digital signal represents the original time-varying quantity as a sampled sequence of quantized values which imposes some bandwidth and dynamic range constraints on the representation. The term ''analog signal'' usually refers to electrical signals; however, mechanical, pneumatic, hydraulic and other systems may also convey or be considered analog signals. Representation An analog signal uses some property of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses rotary position as the signal to convey pressure information. In an electrical signal, the voltage, current, or frequency of the signal may be varied to represent the information. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Fluorescent Displays
A vacuum fluorescent display (VFD) is a display device once commonly used on consumer electronics equipment such as video cassette recorders, car radios, and microwave ovens. A VFD operates on the principle of cathodoluminescence, roughly similar to a cathode ray tube, but operating at much lower voltages. Each tube in a VFD has a phosphor-coated carbon anode that is bombarded by electrons emitted from the cathode filament.Chen, J., Cranton, W., & Fihn, M. (Eds.). (2016). Handbook of Visual Display Technology. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-14346-0 page 1610 onwards In fact, each tube in a VFD is a triode vacuum tube because it also has a mesh control grid. Unlike liquid crystal displays, a VFD emits very bright light with high contrast and can support display elements of various colors. Standard illumination figures for VFDs are around 640 cd/m2 with high-brightness VFDs operating at 4,000 cd/m2, and experimental units as high as 35,000 cd/m2 depending on the drive voltag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resistor Divider
In electronics, a voltage divider (also known as a potential divider) is a passive linear circuit that produces an output voltage (''V''out) that is a fraction of its input voltage (''V''in). Voltage division is the result of distributing the input voltage among the components of the divider. A simple example of a voltage divider is two resistors connected in series, with the input voltage applied across the resistor pair and the output voltage emerging from the connection between them. Resistor voltage dividers are commonly used to create reference voltages, or to reduce the magnitude of a voltage so it can be measured, and may also be used as signal attenuators at low frequencies. For direct current and relatively low frequencies, a voltage divider may be sufficiently accurate if made only of resistors; where frequency response over a wide range is required (such as in an oscilloscope probe), a voltage divider may have capacitive elements added to compensate load capacitance. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a power ratio of 101/10 (approximately ) or root-power ratio of 10 (approximately ). The unit expresses a relative change or an absolute value. In the latter case, the numeric value expresses the ratio of a value to a fixed reference value; when used in this way, the unit symbol is often suffixed with letter codes that indicate the reference value. For example, for the reference value of 1 volt, a common suffix is " V" (e.g., "20 dBV"). Two principal types of scaling of the decibel are in common use. When expressing a power ratio, it is defined as ten times the logarithm in base 10. That is, a change in ''power'' by a factor of 10 corresponds to a 10 dB change in level. When expressing root-power quantities, a change in ''ampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithmic Scale
A logarithmic scale (or log scale) is a way of displaying numerical data over a very wide range of values in a compact way—typically the largest numbers in the data are hundreds or even thousands of times larger than the smallest numbers. Such a scale is nonlinear: the numbers 10 and 20, and 60 and 70, are not the same distance apart on a log scale. Rather, the numbers 10 and 100, and 60 and 600 are equally spaced. Thus moving a unit of distance along the scale means the number has been ''multiplied'' by 10 (or some other fixed factor). Often exponential growth curves are displayed on a log scale, otherwise they would increase too quickly to fit within a small graph. Another way to think about it is that the ''number of digits'' of the data grows at a constant rate. For example, the numbers 10, 100, 1000, and 10000 are equally spaced on a log scale, because their numbers of digits is going up by 1 each time: 2, 3, 4, and 5 digits. In this way, adding two digits ''multiplies'' the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)