|
LEP Pre-Injector
The LEP Pre-Injector (LPI) was the initial source that provided electrons and positrons to CERN's accelerator complex for the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP) from 1989 until 2000. LPI comprised the LEP Injector Linac (LIL) and the Electron Positron Accumulator (EPA). File:LEP Injector Linac.jpg, LEP Injector Linac File:LIL-W with electron-positron converter.jpg, LIL-W with electron-positron converter File:Electron Positron Accumulator.jpg, Electron Positron Accumulator History After groundbreaking for the LEP Collider had taken place in September 1983, the design for its injection scheme, the LEP Pre-Injector (LPI), was finalized in 1984. The construction was planned and implemented in close collaboration with Laboratoire de l'accélérateur linéaire (LAL) in Orsay, France. Since there had been no electron/positron accelerators at CERN before, LAL was a valuable source of expertise and experience in this regard. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrons
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, in accordance with the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer de Broglie wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S Band
The S band is a designation by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) for a part of the microwave band of the electromagnetic spectrum covering frequencies from 2 to 4 gigahertz (GHz). Thus it crosses the conventional boundary between the UHF and SHF bands at 3.0 GHz. The S band is used by airport surveillance radar for air traffic control, weather radar, surface ship radar, and some communications satellites, especially those used by NASA to communicate with the Space Shuttle and the International Space Station. The 10 cm radar short-band ranges roughly from 1.55 to 5.2 GHz. The S band also contains the 2.4–2.483 GHz ISM band, widely used for low power unlicensed microwave devices such as cordless phones, wireless headphones (Bluetooth), wireless networking (WiFi), garage door openers, keyless vehicle locks, baby monitors as well as for medical diathermy machines and microwave ovens (typically at 2.495 GHz). India's re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN Facilities
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in a northwestern suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises 23 member states, and Israel (admitted in 2013) is currently the only non-European country holding full membership. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2019, it had 2,660 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,400 users from institutions in more than 70 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research — consequently, numerous experiments have been constructed at CERN through international collaborations. CERN is the site of the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Experiments
In the Outline of physical science, physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small wikt:local, localized physical body, object which can be described by several physical property, physical or chemical property, chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass. They vary greatly in size or quantity, from subatomic particles like the electron, to microscopic scale, microscopic particles like atoms and molecules, to macroscopic scale, macroscopic particles like powder (substance), powders and other granular materials. Particles can also be used to create scientific models of even larger objects depending on their density, such as humans moving in a crowd or celestial bodies in motion (physics), motion. The term ''particle'' is rather general in meaning, and is refined as needed by various scientific fields. Anything that is composed of particles may be referred to as being particulate. However, the noun ''particulates, particulate'' is most frequently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics Facilities
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass. They vary greatly in size or quantity, from subatomic particles like the electron, to microscopic particles like atoms and molecules, to macroscopic particles like powders and other granular materials. Particles can also be used to create scientific models of even larger objects depending on their density, such as humans moving in a crowd or celestial bodies in motion. The term ''particle'' is rather general in meaning, and is refined as needed by various scientific fields. Anything that is composed of particles may be referred to as being particulate. However, the noun ''particulate'' is most frequently used to refer to pollutants in the Earth's atmosphere, which are a suspension of unconnected particles, rather than a connected particle aggregation. Conceptual properties The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Rays
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies above 30 exahertz (), it imparts the highest photon energy. Paul Villard, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays in ascending order of penetrating power. Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range from a few kiloelectronvolts (keV) to approximately 8 megaelectronvolts (MeV), corresponding to the typical energy levels in nuclei with reasonably long lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
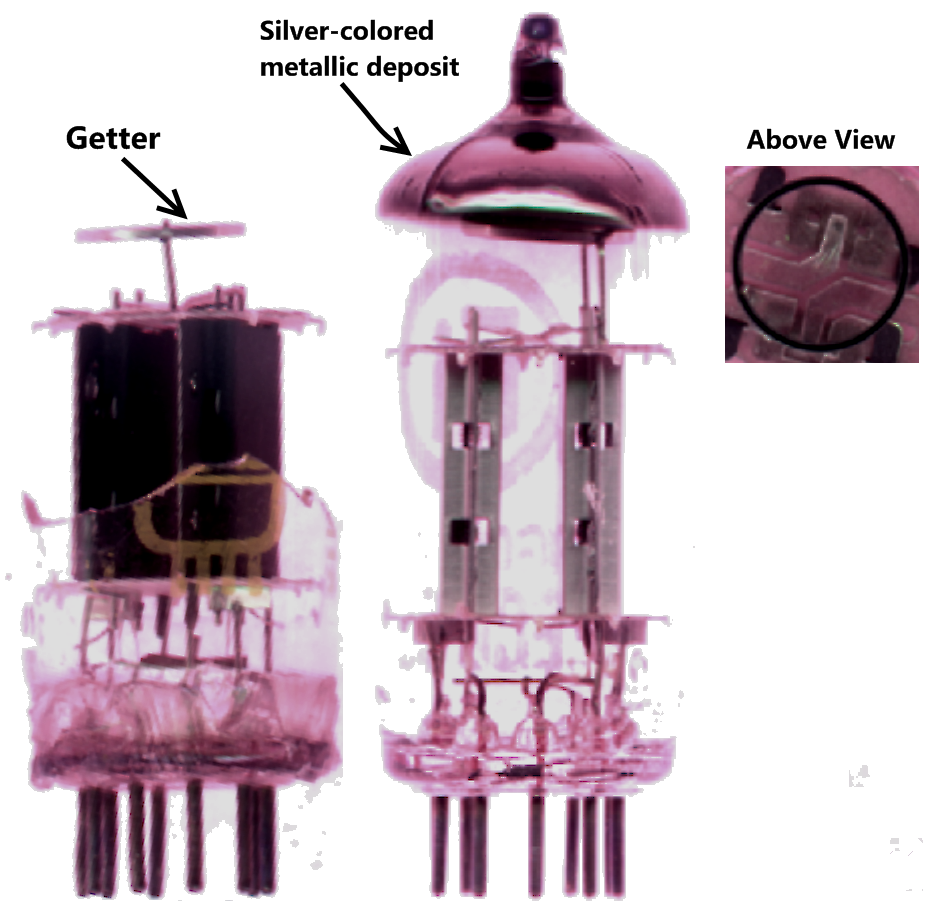
Getter
A getter is a deposit of reactive material that is placed inside a vacuum system to complete and maintain the vacuum. When gas molecules strike the getter material, they combine with it chemically or by . Thus the getter removes small amounts of gas from the evacuated space. The getter is usually a coating applied to a surface within the evacuated chamber. A vacuum is initially created by connecting a container to a vacuum pump. After achieving a sufficient vacuum, the container can be sealed, or the vacuum pump can be left running. Getters are especially important in sealed systems, such as vacuum tubes, including cathode ray tubes (CRTs), Vacuum Insulating Glass (or Vacuum Glass) and vacuum insulated panels, which must maintain a vacuum for a long time. This is because the inner surfaces of the container release adsorbed gases for a long time after the vacuum is established. The getter continually removes residues of a reactive gas, such as oxygen, as long as it is desorbed f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
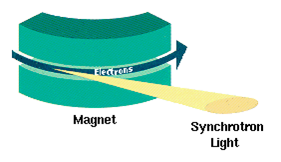
Synchrotron Radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in some types of particle accelerators, or naturally by fast electrons moving through magnetic fields. The radiation produced in this way has a characteristic polarization and the frequencies generated can range over a large portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Synchrotron radiation is similar to bremsstrahlung radiation, which is emitted by a charged particle when the acceleration is parallel to the direction of motion. The general term for radiation emitted by particles in a magnetic field is ''gyromagnetic radiation'', for which synchrotron radiation is the ultra-relativistic special case. Radiation emitted by charged particles moving non-relativistically in a magnetic field is called cyclotron emission. For particles in the mildly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Muon Solenoid
The Compact Muon Solenoid (CMS) experiment is one of two large general-purpose particle physics detectors built on the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN in Switzerland and France. The goal of the CMS experiment is to investigate a wide range of physics, including the search for the Higgs boson, extra dimensions, and particles that could make up dark matter. CMS is 21 metres long, 15 m in diameter, and weighs about 14,000 tonnes. Over 4,000 people, representing 206 scientific institutes and 47 countries, form the CMS collaboration who built and now operate the detector. It is located in a cavern at Cessy in France, just across the border from Geneva. In July 2012, along with ATLAS, CMS tentatively discovered the Higgs boson. By March 2013 its existence was confirmed. Background Recent collider experiments such as the now-dismantled Large Electron-Positron Collider and the newly renovated Large Hadron Collider (LHC) at CERN, as well as the () recently closed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
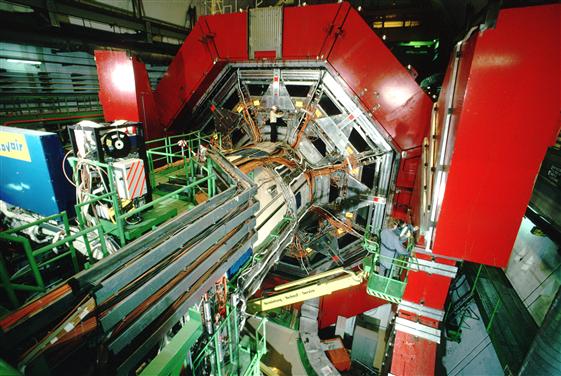
L3 Experiment
The L3 experiment was one of the four large detectors on the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP). The detector was designed to look for the physics of the Standard Model and beyond. It started up in 1989 and stopped taking data in November 2000 to make room for construction of the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). Now, the ALICE detector sits in the cavern that L3 used to occupy, reusing L3's characteristic red octagonal magnet. Detector The L3-detector was a multi-layered cylindrical set of different devices, each of them measuring physical quantities relevant to the reconstruction of the collision under study. Starting from the centre, close to the pipe where electrons and positrons circulate and collide, there were first the Silicon strip Microvertex Detector (SMD) and the Time Expansion Chamber (TEC). These two sub-detectors traced the paths of charged particles produced in the collision. One also gathered information about the momentum (a quantity related to mass and energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave Cavity
A microwave cavity or ''radio frequency (RF) cavity'' is a special type of resonator, consisting of a closed (or largely closed) metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields in the microwave region of the spectrum. The structure is either hollow or filled with dielectric material. The microwaves bounce back and forth between the walls of the cavity. At the cavity's resonant frequencies they reinforce to form standing waves in the cavity. Therefore, the cavity functions similarly to an organ pipe or sound box in a musical instrument, oscillating preferentially at a series of frequencies, its resonant frequencies. Thus it can act as a bandpass filter, allowing microwaves of a particular frequency to pass while blocking microwaves at nearby frequencies. A microwave cavity acts similarly to a resonant circuit with extremely low loss at its frequency of operation, resulting in quality factors (Q factors) up to the order of 106, compared to 102 for circuits made with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klystron
A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian,Pond, Norman H. "The Tube Guys". Russ Cochran, 2008 p.31-40 which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from UHF up into the microwave range. Low-power klystrons are used as oscillators in terrestrial microwave relay communications links, while high-power klystrons are used as output tubes in UHF television transmitters, satellite communication, radar transmitters, and to generate the drive power for modern particle accelerators. In a klystron, an electron beam interacts with radio waves as it passes through resonant cavities, metal boxes along the length of a tube. The electron beam first passes through a cavity to which the input signal is applied. The energy of the electron beam amplifies the signal, and the amplified signal is taken from a cavity at the other end of the tube. The output signal can be coupled back into the input cavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |