|
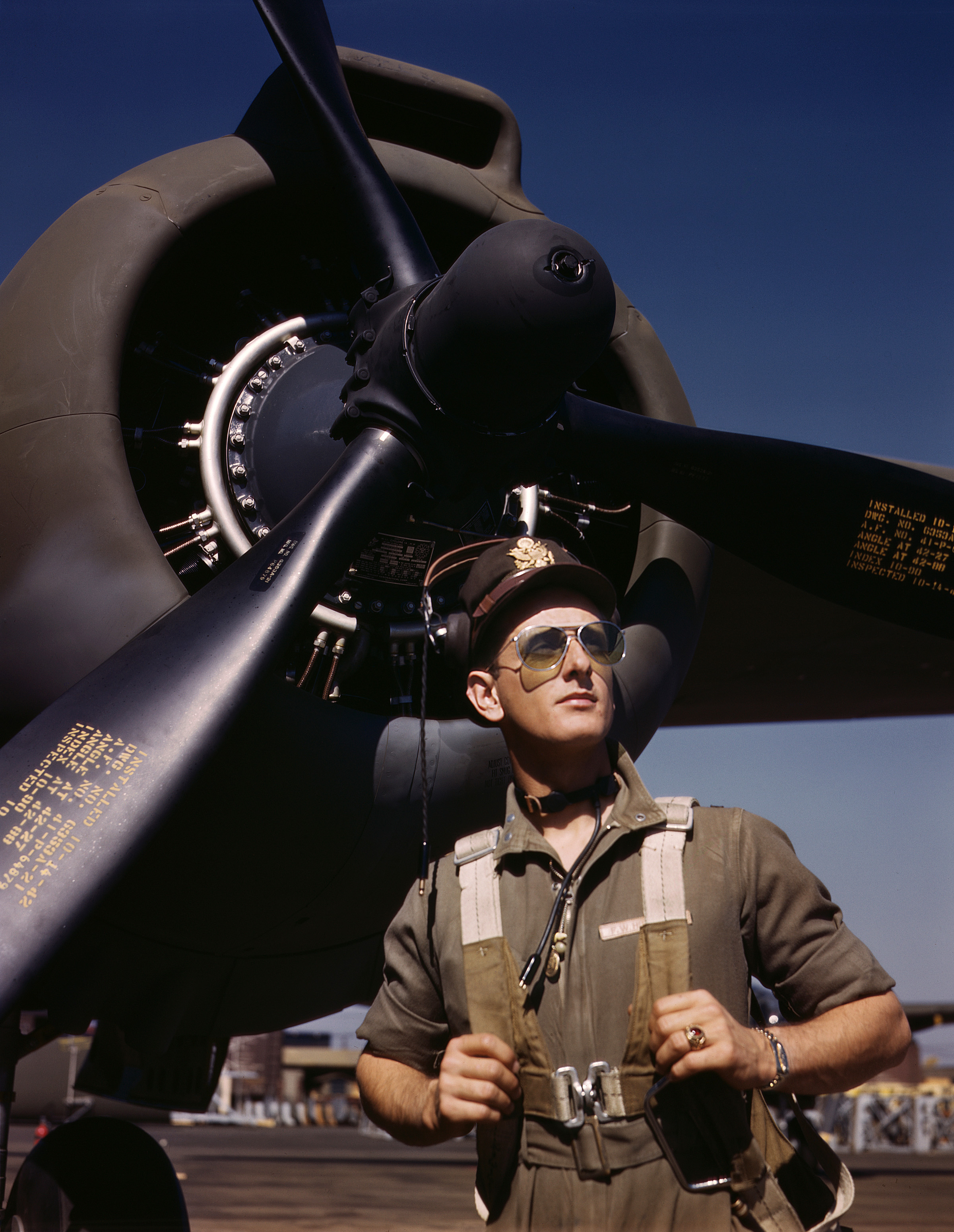
L. Gordon Cooper
Leroy Gordon "Gordo" Cooper Jr. (March 6, 1927 – October 4, 2004) was an American aerospace engineer, test pilot, United States Air Force pilot, and the youngest of the seven original astronauts in Project Mercury, the first human space program of the United States. Cooper learned to fly as a child, and after service in the United States Marine Corps during World War II, he was commissioned into the United States Air Force in 1949. After service as a fighter pilot, he qualified as a test pilot in 1956, and was selected as an astronaut in 1959. In 1963 Cooper piloted the longest and last Mercury spaceflight, Mercury-Atlas 9. During that 34-hour mission he became the first American to spend an entire day in space, the first to sleep in space, and the last American launched on an entirely solo orbital mission. Despite a series of severe equipment failures, he managed to successfully complete the mission under manual control, guiding his spacecraft, which he named ''F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Astronaut
The NASA Astronaut Corps is a unit of the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) that selects, trains, and provides astronauts as crew members for U.S. and international space missions. It is based at Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. History The first U.S. astronaut candidates were selected by NASA in 1959, for its Project Mercury with the objective of orbiting astronauts around the Earth in single-man capsules. The military services were asked to provide a list of military test pilots who met specific qualifications. After stringent screening, NASA announced its selection of the "Mercury Seven" as its first astronauts. Since then, NASA has selected 22 more groups of astronauts, opening the corps to civilians, scientists, doctors, engineers, and school teachers. As of the 2009 Astronaut Class, 61% of the astronauts selected by NASA have come from military service. NASA selects candidates from a diverse pool of applicants with a wide variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Exceptional Service Medal
The NASA Exceptional Service Medal is an award granted to U.S. government employees for significant sustained performance characterized by unusual initiative or creative ability that clearly demonstrates substantial improvement in engineering, aeronautics, space flight, administration, support, or space-related endeavors which contribute to NASA programs. The medal was inherited by NASA from its predecessor organization, the National Advisory Committee on Aeronautics (NACA) and featured the NACA emblem. The original NASA version featured the NASA seal. Notable recipients *Buzz Aldrin (1969) * Robert O. Aller (twice) *Neil Armstrong (1966) *Charles Bolden (thrice) * John R. Casani (1965) *Lin Chambers (2009) *Kevin Chilton *Eileen Collins (1998) *Michael Collins (1966) *Nagin Cox * William H. Dana *Jean Dickey (1998) * John H. Disher (twice, last in 1980) *Einar Enevoldson (1974 and 1980) *Christer Fuglesang (2010) * Fitzhugh L. Fulton (1977 and 1983) * Alfred Gessow (1974) *Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
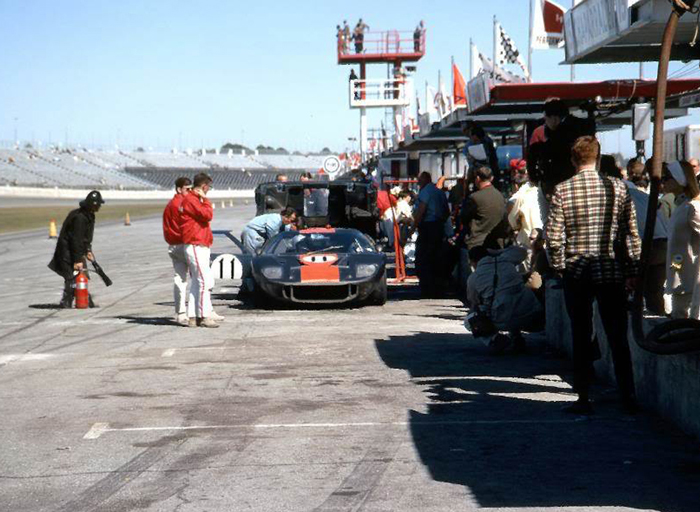
24 Hours Of Daytona
The 24 Hours of Daytona, also known as the Rolex 24 At Daytona for sponsorship reasons, is a 24-hour sports car endurance race held annually at Daytona International Speedway in Daytona Beach, Florida. It is run on the Sports Car Course layout, a combined road course that uses most of the tri-oval plus an infield road course. Held on the last weekend of January or first weekend of February as part of Speedweeks, it is the first major automobile race of the year in North America. The race is sanctioned by IMSA and is the first race of the season for the IMSA SportsCar Championship. The race has borne the names of several sponsors over the years. Since 1992, the Rolex Watch Company has been the title sponsor of the race, replacing Sunbank, which replaced Pepsi in 1984. Winning drivers of all classes receive a Rolex Daytona watch. The race has been known historically as a leg of the informal Triple Crown of endurance racing. Beginnings Shortly after the track opened, on Ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Adair
Paul Neal "Red" Adair (June 18, 1915 – August 7, 2004)Obituary: Red Adair , August 8, 2004 was an American fighter. He became notable internationally as an innovator in the highly specialized and hazardous profession of extinguishing and capping oil well blowouts, both land-based and offshore. Early life and education Adair was born in |
Pete Conrad
Charles "Pete" Conrad Jr. (June 2, 1930 – July 8, 1999) was an American NASA astronaut, aeronautical engineer, naval officer and aviator, and test pilot, and commanded the Apollo 12 space mission, on which he became the third person to walk on the Moon. Conrad was selected in NASA's second astronaut class in 1962. Conrad had dyslexia and yet earned his Bachelor of Science degree in Aerospace engineering, Aeronautical Engineering from Princeton University—being the first Ivy League astronaut—and joined the U.S. Navy. In 1954 he received his naval aviator wings, served as a fighter pilot and, after graduating from the United States Naval Test Pilot School, U.S. Naval Test Pilot School (Class 20), as a project test pilot. In 1959 he was an astronaut candidate for Project Mercury. Conrad set an eight-day space endurance record in 1965 along with his Command Pilot Gordon Cooper on his first spaceflight, Gemini 5. Later, Conrad commanded Gemini 11 in 1966, and Apollo 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
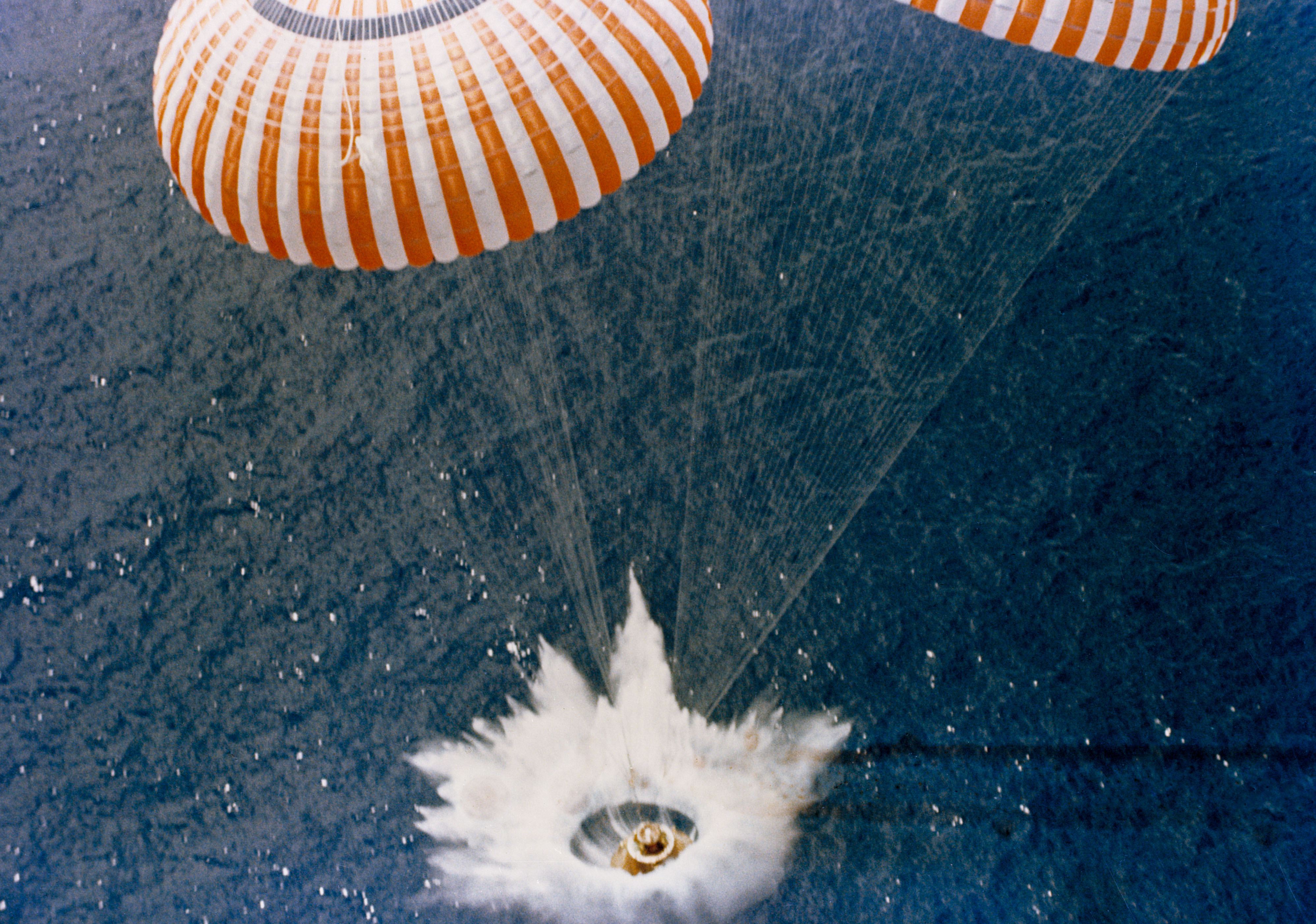
Splashdown
Splashdown is the method of landing a spacecraft by parachute in a body of water. It was used by crewed American space capsules prior to the Space Shuttle program, by SpaceX Dragon and Dragon 2 capsules and by NASA's Orion Multipurpose Crew Vehicle. It is also possible for the Russian Soyuz spacecraft to land in water, though this is only a contingency. The only example of an unintentional crewed splashdown in Soviet history is the Soyuz 23 landing. As the name suggests, the capsule parachutes into an ocean or other large body of water. The properties of water cushion the spacecraft enough that there is no need for a braking rocket to slow the final descent as is the case with Russian and Chinese crewed space capsules (while Shenzhou designed a raft and balanced capsule in case of splashdown), which return to Earth over land. The American practice came in part because American launch sites are on the coastline and launch primarily over water. Russian launch sites are far i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
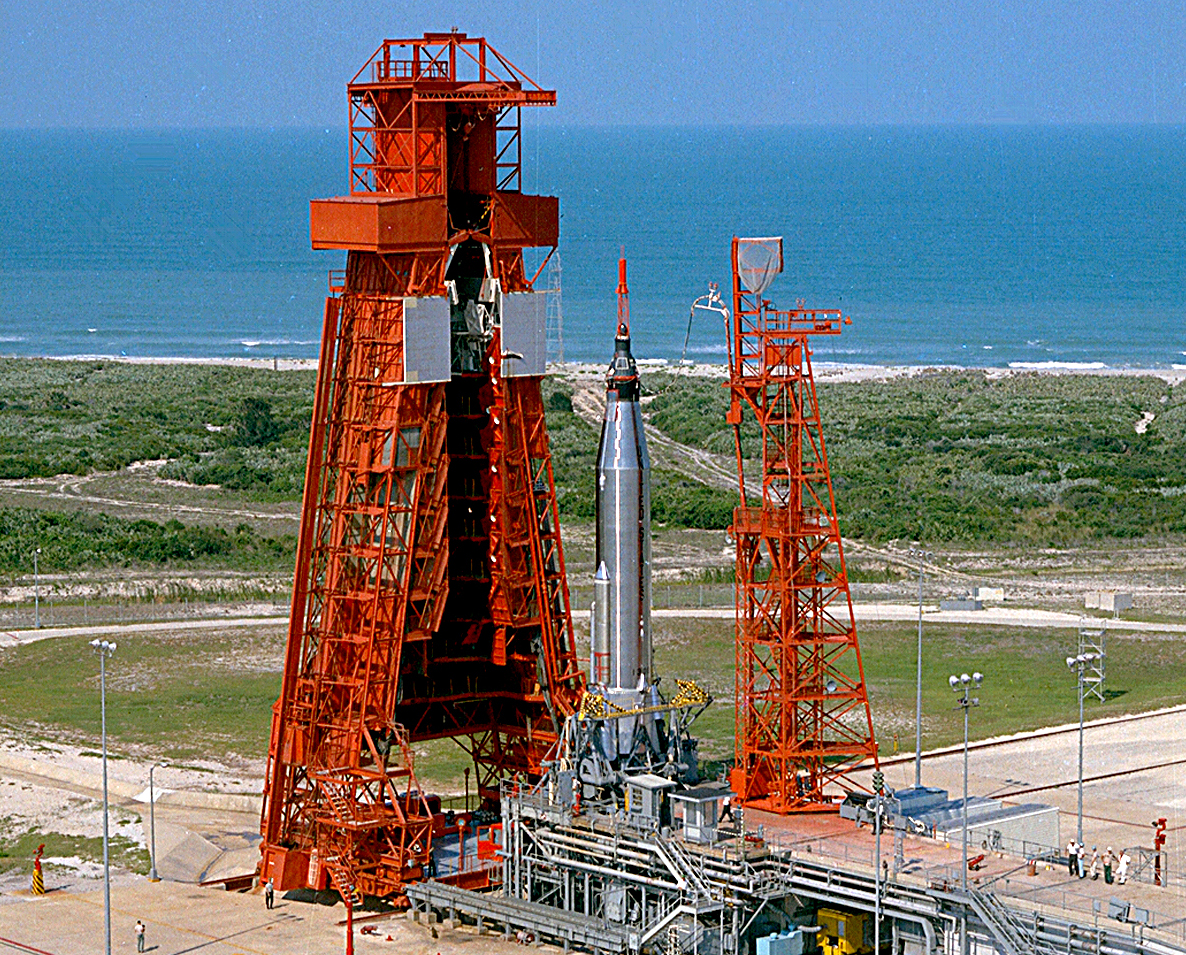
Faith 7
Mercury-Atlas 9 was the final crewed space mission of the U.S. Mercury program, launched on May 15, 1963, from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 14, Launch Complex 14 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Cape Canaveral, Florida. The spacecraft, named ''Faith 7'', completed 22 Earth orbits before splashing down in the Pacific Ocean, piloted by astronaut Gordon Cooper, then a United States Air Force Major (United States), major. The Atlas LV-3B, Atlas rocket was No. 130-D, and the Mercury spacecraft was No. 20. As of 2022, this mission marks the last time an American was launched alone to conduct an entirely solo orbital mission. Flight directors * Chris KraftRed team * John Hodge (engineer), John HodgeBlue team Mission parameters *Mass: *Perigee: 161 km *Apogee: 267 km *Inclination: 32.5° *Orbital period, Period: 88.5 min Mission background Debate over Mercury project continuation The Mercury-Atlas 8 flight of Walter Schirra on October 3, 1962, had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Spaceflight
An orbital spaceflight (or orbital flight) is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least one orbit. To do this around the Earth, it must be on a free trajectory which has an altitude at perigee (altitude at closest approach) around ; this is the boundary of space as defined by NASA, the US Air Force and the FAA. To remain in orbit at this altitude requires an orbital speed of ~7.8 km/s. Orbital speed is slower for higher orbits, but attaining them requires greater delta-v. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale has established the Kármán line at an altitude of as a working definition for the boundary between aeronautics and astronautics. This is used because at an altitude of about , as Theodore von Kármán calculated, a vehicle would have to travel faster than orbital velocity to derive sufficient aerodynamic lift from the atmosphere to support itself. Due to atmospheric drag, the lowest altitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combined arms, implementing its own infantry, artillery, aerial, and special operations forces. The U.S. Marine Corps is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. The Marine Corps has been part of the U.S. Department of the Navy since 30 June 1834 with its sister service, the United States Navy. The USMC operates installations on land and aboard sea-going amphibious warfare ships around the world. Additionally, several of the Marines' tactical aviation squadrons, primarily Marine Fighter Attack squadrons, are also embedded in Navy carrier air wings and operate from the aircraft carriers. The history of the Marine Corps began when two battalions of Continental Marines were formed on 10 November 1775 in Philadelphia as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Mercury
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbit and return him safely, ideally before the Soviet Union. Taken over from the US Air Force by the newly created civilian space agency NASA, it conducted 20 uncrewed developmental flights (some using animals), and six successful flights by astronauts. The program, which took its name from Roman mythology, cost $ (adjusted for inflation). The astronauts were collectively known as the "Mercury Seven", and each spacecraft was given a name ending with a "7" by its pilot. The Space Race began with the 1957 launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik 1. This came as a shock to the American public, and led to the creation of NASA to expedite existing US space exploration efforts, and place most of them under civilian control. After the successful launch of the Explorer 1 satellite in 1958, crewed spacef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aviator
An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its Aircraft flight control system, directional flight controls. Some other aircrew, aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are also considered aviators, because they are involved in operating the aircraft's navigation and engine systems. Other aircrew members, such as drone operators, flight attendants, Aircraft maintenance technician, mechanics and Line technician (aviation), ground crew, are not classified as aviators. In recognition of the pilots' qualifications and responsibilities, most militaries and many airlines worldwide award aviator badges to their pilots. History The first recorded use of the term ''aviator'' (''aviateur'' in French) was in 1887, as a variation of ''aviation'', from the Latin ''avis'' (meaning ''bird''), coined in 1863 by in ''Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne'' ("Aviation or Air Navigation"). The term ''aviatrix'' (''aviatrice'' in F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |