|
L-functions
In mathematics, an ''L''-function is a meromorphic function on the complex plane, associated to one out of several categories of mathematical objects. An ''L''-series is a Dirichlet series, usually convergent on a half-plane, that may give rise to an ''L''-function via analytic continuation. The Riemann zeta function is an example of an ''L''-function, and one important conjecture involving ''L''-functions is the Riemann hypothesis and its generalization. The theory of ''L''-functions has become a very substantial, and still largely conjectural, part of contemporary analytic number theory. In it, broad generalisations of the Riemann zeta function and the ''L''-series for a Dirichlet character are constructed, and their general properties, in most cases still out of reach of proof, are set out in a systematic way. Because of the Euler product formula there is a deep connection between ''L''-functions and the theory of prime numbers. The mathematical field that studies L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-adic L-function
In mathematics, a ''p''-adic zeta function, or more generally a ''p''-adic ''L''-function, is a function analogous to the Riemann zeta function, or more general ''L''-functions, but whose domain and target are ''p-adic'' (where ''p'' is a prime number). For example, the domain could be the ''p''-adic integers Z''p'', a profinite ''p''-group, or a ''p''-adic family of Galois representations, and the image could be the ''p''-adic numbers Q''p'' or its algebraic closure. The source of a ''p''-adic ''L''-function tends to be one of two types. The first source—from which Tomio Kubota and Heinrich-Wolfgang Leopoldt gave the first construction of a ''p''-adic ''L''-function —is via the ''p''-adic interpolation of special values of ''L''-functions. For example, Kubota–Leopoldt used Kummer's congruences for Bernoulli numbers to construct a ''p''-adic ''L''-function, the ''p''-adic Riemann zeta function ζ''p''(''s''), whose values at negative odd integers are those of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
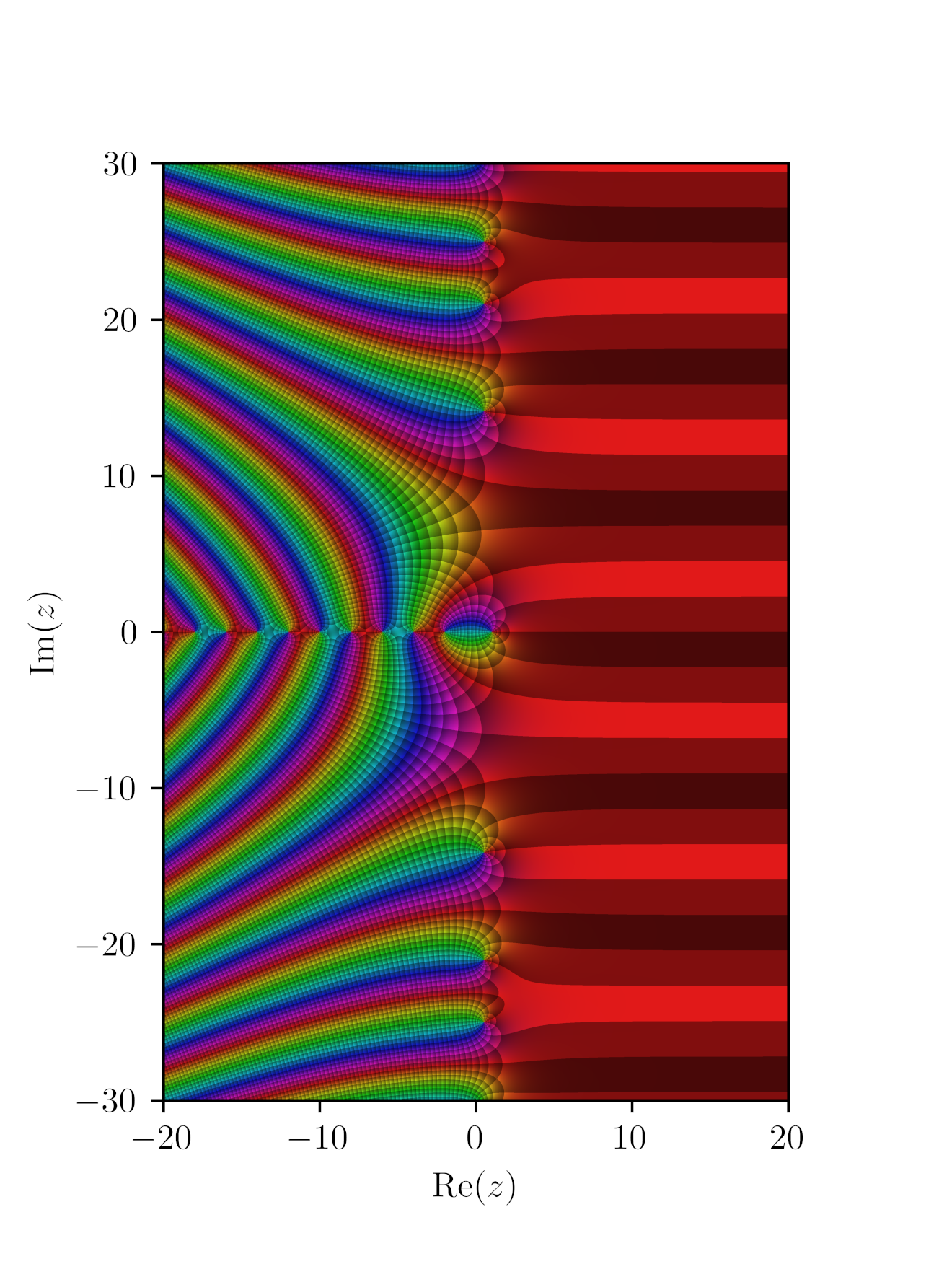
Riemann Hypothesis
In mathematics, the Riemann hypothesis is the conjecture that the Riemann zeta function has its zeros only at the negative even integers and complex numbers with real part . Many consider it to be the most important unsolved problem in pure mathematics. It is of great interest in number theory because it implies results about the distribution of prime numbers. It was proposed by , after whom it is named. The Riemann hypothesis and some of its generalizations, along with Goldbach's conjecture and the twin prime conjecture, make up Hilbert's eighth problem in David Hilbert's list of twenty-three unsolved problems; it is also one of the Clay Mathematics Institute's Millennium Prize Problems, which offers a million dollars to anyone who solves any of them. The name is also used for some closely related analogues, such as the Riemann hypothesis for curves over finite fields. The Riemann zeta function ζ(''s'') is a function whose argument ''s'' may be any complex number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |