|
Kvitskarvhalsen Saddle
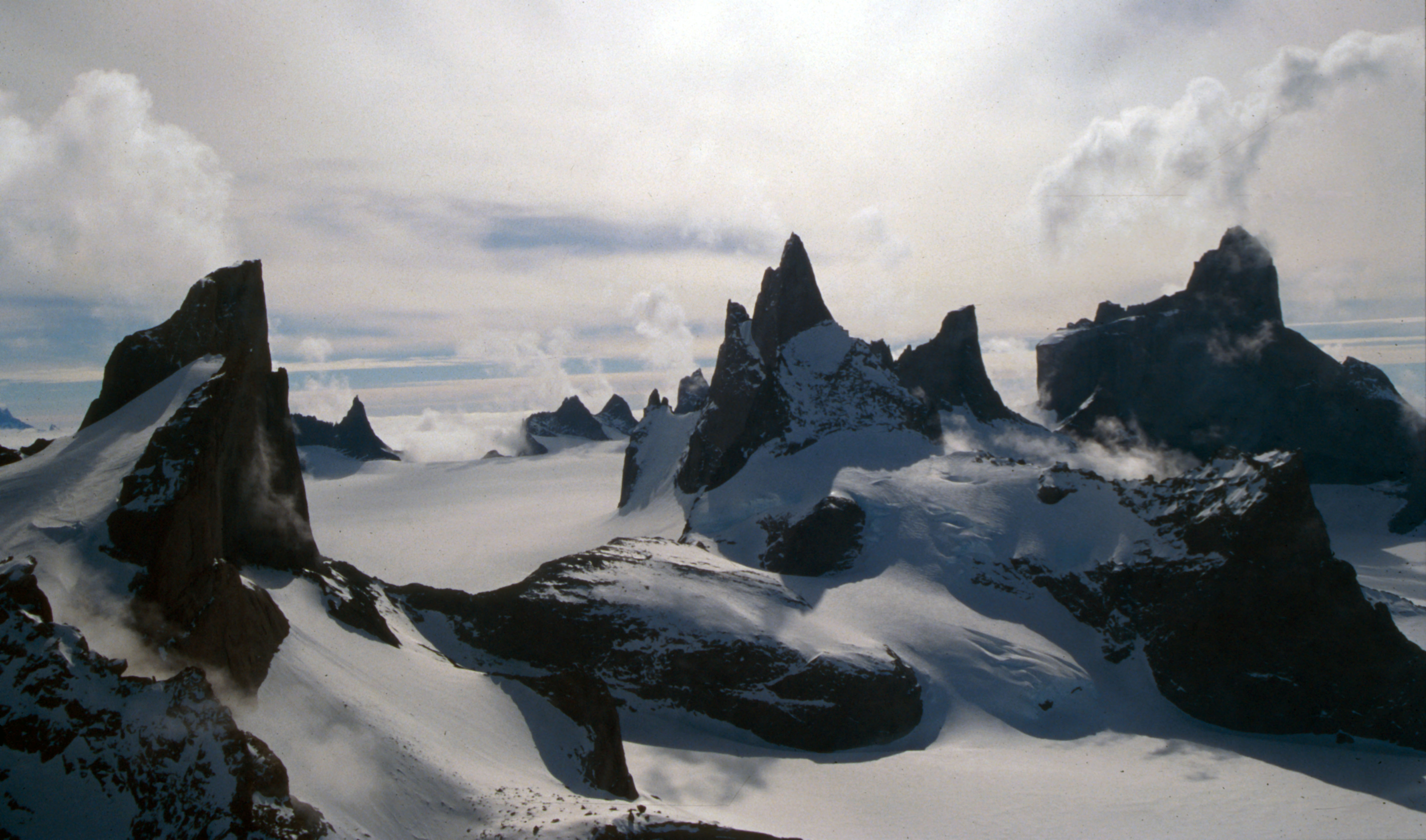
Kvitskarvhalsen Saddle () is an ice saddle between Mount Krüger and the Robin Heights in the Sverdrup Mountains The Sverdrup Mountains ( no, Sverdrupfjella) are a group of mountains about long, standing just west of the Gjelsvik Mountains in Queen Maud Land, East Antarctica. With its summit at , Hamartind Peak forms the highest point in the Sverdrup Mount ... of Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It was photographed from the air by the Third German Antarctic Expedition (1938–39). The feature was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–52) and air photos by the Norwegian expedition (1958–59) and named Kvitskarvhalsen (the white mountain neck). References Mountain passes of Queen Maud Land Princess Martha Coast {{PrincessMarthaCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
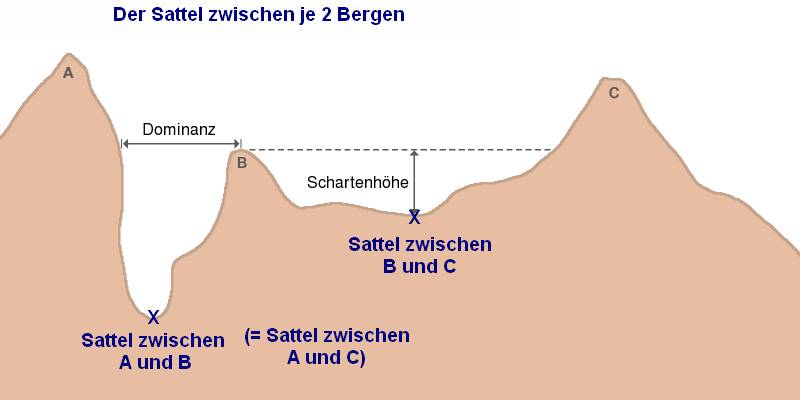
Saddle (landform)
The saddle between two hills or mountains is the region surrounding the saddle point, the lowest point on the line tracing the drainage divide (the col) connecting the peaks. When, and if, the saddle is navigable, even if only on foot, the saddle of a (optimal) pass between the two massifs, is the area generally found around the lowest route on which one could pass between the two summits, which includes that point which is a mathematically when graphed a relative high along one axis, and a relative low in the perpendicular axis, simultaneously; that point being by definition the col of the saddle. Topography A saddle is the lowest area between two highlands (prominences or peaks) which has two wings which span the divide (the line between the two prominences) by crossing the divide at an angle, and, so is concurrently the local highpoint of the land surface which falls off in the lower direction. That is, the drainage divide is a ridge along the high point of the saddle, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Krüger
Mount Krüger, or Krügerfjellet (german: Krügerberg), is a mountain standing southwest of Kvithø Peak in the Sverdrup Mountains of Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. The summit of Krüger is the highest point in the Sverdrup Mtns. Discovery and naming Mount Krüger was discovered by the Third German Antarctic Expedition (1938–1939), led by Captain Alfred Ritscher Alfred Ritscher (23 May 1879 in Bad Lauterberg – 30 March 1963 in Hamburg) was a German polar explorer. A ''Kapitän zur See'' in the ''Kriegsmarine'', he led the third German Antarctic Expedition in 1938–39, which mapped the New Swabia (ger ..., and named for Walter Krüger, a meteorological assistant on the expedition. It was surveyed by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–1952), led by John Schjelderup Giæver. See also * List of mountains of Queen Maud Land References External links Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR) {{DEFAULTSORT:Kruger, Mount Mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robin Heights
Robin Heights () is a cluster of high rock summits between Hei Glacier and Kvitsvodene Valley in the Sverdrup Mountains, Queen Maud Land Queen Maud Land ( no, Dronning Maud Land) is a roughly region of Antarctica claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20° west and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45° east. In addit .... It was photographed from the air by the German Antarctic Expedition (1938–39). It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian-British-Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE) (1949–52) and air photos by the Norwegian expedition (1958–59), and was named for Gordon de Q. Robin, third in command and a physicist with the NBSAE. Mountains of Queen Maud Land Princess Martha Coast {{PrincessMarthaCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sverdrup Mountains
The Sverdrup Mountains ( no, Sverdrupfjella) are a group of mountains about long, standing just west of the Gjelsvik Mountains in Queen Maud Land, East Antarctica. With its summit at , Hamartind Peak forms the highest point in the Sverdrup Mountains. Discovery and naming First photographed from the air and roughly plotted by the Third German Antarctic Expedition (3rd GAE), 1938–1939. Mapped in detail by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and aerial photographs taken by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE), and again by a later Norwegian expedition. Named for Harald Sverdrup, Chairman of the Norwegian Committee for the NBSAE. Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (NBSAE), 1949–1952 Norwegian Expedition Luncke Expedition, 1958–1959 List of important geographical features of the Sverdrup Mountains See also * List of mountains of Queen Maud Land This list of mountains of Quee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Maud Land
Queen Maud Land ( no, Dronning Maud Land) is a roughly region of Antarctica claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20° west and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45° east. In addition, a small unclaimed area from 1939 was annexed in June 2015. Positioned in East Antarctica, it makes out about one-fifth of the continent, and is named after the Norwegian queen Maud of Wales (1869–1938). In 1930, the Norwegian Hjalmar Riiser-Larsen was the first person known to have set foot in the territory. On 14 January 1939, the territory was claimed by Norway. On 23 June 1961, Queen Maud Land became part of the Antarctic Treaty System, making it a demilitarised zone. It is one of two Antarctic claims made by Norway, the other being Peter I Island. They are administered by the Polar Affairs Department of the Norwegian Ministry of Justice and Public Security in Oslo. Most of the territory is covered by the east Antarctic ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third German Antarctic Expedition
New Swabia (Norwegian and german: Neuschwabenland) was a disputed Antarctic claim by Nazi Germany within the Norwegian territorial claim of Queen Maud Land and is now a cartographic name sometimes given to an area of Antarctica between 20°E and 10°W in Queen Maud Land. New Swabia was explored by Germany in early 1939 and named after that expedition's ship, , itself named after the German region of Swabia.McGonigal, David, Antarctica', frances lincoln ltd, 2009, , p. 367 Background Like many other countries, Germany sent expeditions to the Antarctic region in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, most of which were scientific. The late 19th century expeditions to the Southern Ocean, South Georgia, the Kerguelen Islands, and the Crozet Islands were astronomical, meteorological, and hydrological, mostly in close collaboration with scientific teams from other countries. As the 19th century ended, Germany began to focus on Antarctica. The first German expedition to Antarctica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition
The Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (also known as NBSX or NBSAE) (1949–1952) was the first Antarctica expedition involving an international team of scientist A scientist is a person who conducts Scientific method, scientific research to advance knowledge in an Branches of science, area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, ...s. The team members came from Norway, Sweden and the Commonwealth of Nations, British Commonwealth of Nations. History The Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition was the first expedition to Antarctica involving an international team of scientists. The expedition was led by John Schjelderup Giæver, a Norwegian author and polar researcher. The expedition had the goal of establishing whether climatic fluctuations observed in the Arctic were also occurring in the Antarctic. A base known as Maudheim Station, Maudheim was established on the Quar Ice S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Passes Of Queen Maud Land
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |