|
Kv1.1
Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 1 also known as Kv1.1 is a shaker related voltage-gated potassium channel that in humans is encoded by the ''KCNA1'' gene. Isaacs syndrome is a result of an autoimmune reaction against the Kv1.1 ion channel. Genomics The gene is located on the Watson (plus) strand of the short arm of chromosome 12 (12p13.32). The gene itself is 8,348 bases in length and encodes a protein of 495 amino acids (predicted molecular weight 56.466 kiloDaltons). Alternative names The recommended name for this protein is potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily A member 1 but a number of alternatives have been used in the literature including HuK1 (human K+ channel I), RBK1 (rubidium potassium channel 1), MBK (mouse brain K+ channel), voltage gated potassium channel HBK1, voltage gated potassium channel subunit Kv1.1, voltage-gated K+ channel HuKI and AEMK (associated with myokymia with periodic ataxia). Structure The protein is believed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Episodic Ataxia
Episodic ataxia (EA) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by sporadic bouts of ataxia (severe discoordination) with or without myokymia (continuous muscle movement). There are seven types recognized but the majority are due to two recognized entities.Riant F, Vahedi K, Tournier-Lasserve E (2011) Hereditary episodic ataxia. Rev Neurol (Paris) Ataxia can be provoked by psychological stress or startle, or heavy exertion, including exercise. Symptoms can first appear in infancy. There are at least six loci for EA, of which 4 are known genes. Some patients with EA also have migraine or progressive cerebellar degenerative disorders, symptomatic of either familial hemiplegic migraine or spinocerebellar ataxia. Some patients respond to acetazolamide though others do not. Signs and symptoms Typically, episodic ataxia presents as bouts of ataxia induced by startle, stress, or exertion. Some patients also have continuous tremors of various motor groups, known as myokymia. Other pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GABRA3
Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GABRA3'' gene. Function GABA is the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the mammalian brain where it acts at GABAA receptors, which are ligand-gated chloride channels. Chloride conductance of these channels can be modulated by agents such as benzodiazepines that bind to the GABAA receptor. At least 16 distinct subunits of GABA-A receptors have been identified. GABA receptors are composed of 5 subunits with an extracellular ligand binding domains and ion channel domains that are integral to the membrane. Ligand binding to these receptors activates the channel. Subunit selective ligands Recent research has produced several ligands that are selective for GABAA receptors containing the α3 subunit. Subtype-selective agonists for α3 produce anxiolytic effects without sedative, amnesia, or ataxia. selective a3 agonists also show lack of dependence, and could make them superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Channel RNA Editing Signal
The potassium channel RNA editing signal is an RNA element found in human Kv1.1 and its homologues which directs the efficient modification of an adenosine to inosine by an adenosine deaminase acting on RNA ( ADAR). The ADAR modification causes an isoleucine/valine recoding event which lies in the ion-conducting pore of the potassium channel Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel found in virtually all organisms. They form potassium-selective pores that span cell membranes. Potassium channels are found in most cell types and control a wide variety of c .... It is thought that this editing event targets the process of fast inactivation and allows a more rapid recovery from inactivation at negative potentials. References External links * Cis-regulatory RNA elements {{molecular-cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADARB1
Double-stranded RNA-specific editase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ADARB1'' gene. The enzyme is a member of ADAR family. Function This gene encodes the enzyme responsible for pre-mRNA editing of the glutamate receptor subunit B by site-specific deamination of adenosines. Studies in rats found that this enzyme acted on its own pre-mRNA molecules to convert an AA dinucleotide to an AI dinucleotide which resulted in a new splice site. Alternative splicing of this gene results in several transcript variants, some of which have been characterized by the presence or absence of an Alu cassette insert and a short or long C-terminal region. ADARB1 requires the small molecule inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) for proper function. ADARB1 is an A-to-I RNA-editing enzyme that mostly acts on protein-coding substrates. See also * Adenosine deaminase Adenosine deaminase (also known as adenosine aminohydrolase, or ADA) is an enzyme () involved in purine metabolism. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball And Chain Inactivation
In neuroscience, ball and chain inactivation is a model to explain the fast inactivation mechanism of voltage-gated ion channels. The process is also called hinged-lid inactivation or N-type inactivation. A voltage-gated ion channel can be in three states: open, closed, or inactivated. The inactivated state is mainly achieved through fast inactivation, by which a channel transitions rapidly from an open to an inactivated state. The model proposes that the inactivated state, which is stable and non-conducting, is caused by the physical blockage of the pore. The blockage is caused by a "ball" of amino acids connected to the main protein by a string of residues on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane. The ball enters the open channel and binds to the hydrophobic inner vestibule within the channel. This blockage causes inactivation of the channel by stopping the flow of ions. This phenomenon has mainly been studied in potassium channels and sodium channels. Discovery Electrophysiolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulla Oblongata
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon. The myelencephalon is a secondary vesicle which forms during the maturation of the rhombencephalon, also referred to as the hindbrain. The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is retained for terms that relate to the medulla oblongata, particularly in reference to medical conditions. The word bulbar can refer to the nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from in the cervical and lumbar regions to in the thoracic area. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
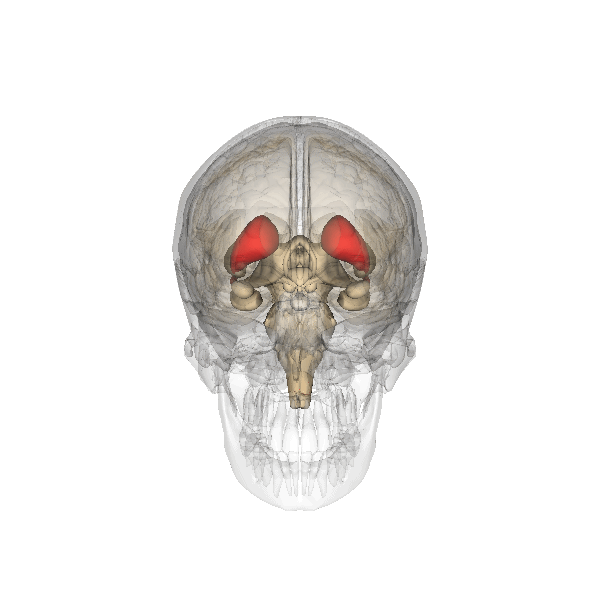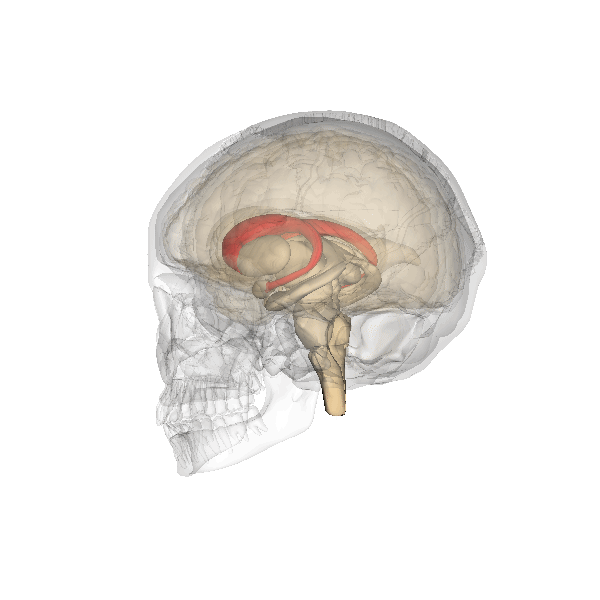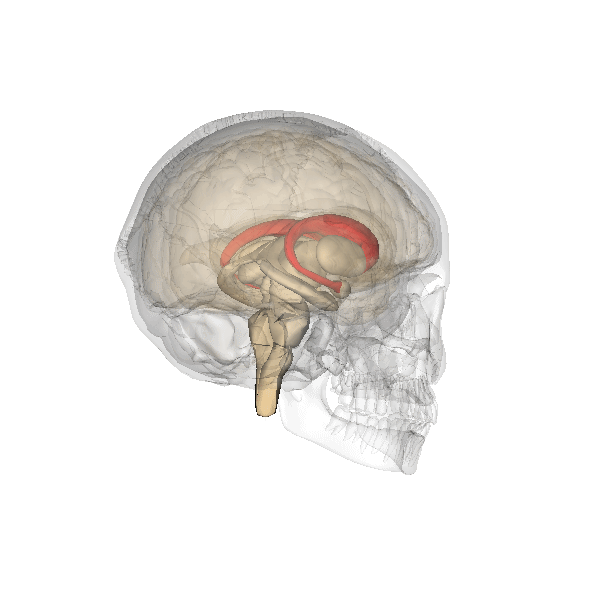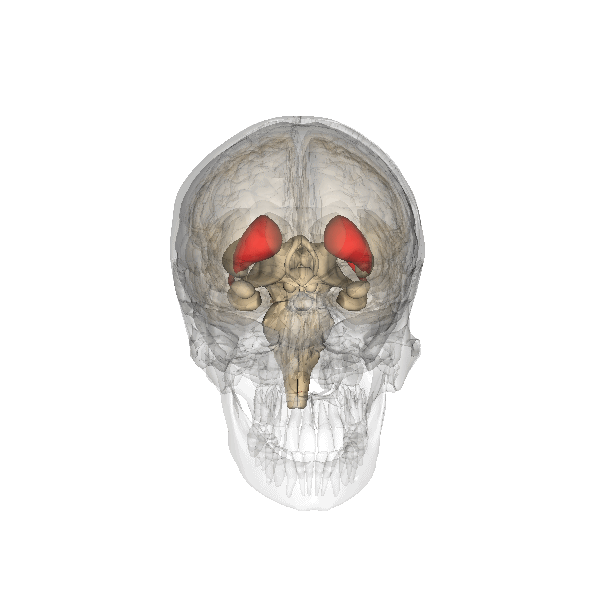
Caudate Nucleus
The caudate nucleus is one of the structures that make up the corpus striatum, which is a component of the basal ganglia in the human brain. While the caudate nucleus has long been associated with motor processes due to its role in Parkinson's disease, it plays important roles in various other nonmotor functions as well, including procedural learning, associative learning and inhibitory control of action, among other functions. The caudate is also one of the brain structures which compose the reward system and functions as part of the cortico–basal ganglia– thalamic loop. Structure Together with the putamen, the caudate forms the dorsal striatum, which is considered a single functional structure; anatomically, it is separated by a large white matter tract, the internal capsule, so it is sometimes also referred to as two structures: the medial dorsal striatum (the caudate) and the lateral dorsal striatum (the putamen). In this vein, the two are functionally distinct not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene... must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messenger – which I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions) – alternating with regions which will be expressed – exons." (Gilbert 1978) The term ''intron'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding RNA sequence in RNA transcripts. The non-intron sequences that become joined by this RNA processing to form the mature RNA are called exons. Introns are found in the genes of most organisms and many viruses and they can be located in both protein-coding genes and genes that function as RNA (noncoding genes). There are four main types of introns: tRNA introns, group I introns, group II introns, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence in RNA transcripts. In RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are covalently joined to one another as part of generating the mature RNA. Just as the entire set of genes for a species constitutes the genome, the entire set of exons constitutes the exome. History The term ''exon'' derives from the expressed region and was coined by American biochemist Walter Gilbert in 1978: "The notion of the cistron… must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messengerwhich I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions)alternating with regions which will be expressedexons." This definition was originally made for protein-coding transcripts that are spliced before being translated. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem-loop
Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when read in opposite directions, base-pair to form a double helix that ends in an unpaired loop. The resulting structure is a key building block of many RNA secondary structures. As an important secondary structure of RNA, it can direct RNA folding, protect structural stability for messenger RNA (mRNA), provide recognition sites for RNA binding proteins, and serve as a substrate for enzymatic reactions. Formation and stability The formation of a stem-loop structure is dependent on the stability of the resulting helix and loop regions. The first prerequisite is the presence of a sequence that can fold back on itself to form a paired double helix. The stability of this helix is determined by its length, the number of mismatches or bulges it co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes. It is encoded by all codons starting with GU (GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG). History and etymology Valine was first isolated from casein in 1901 by Hermann Emil Fischer. The name valine comes from valeric acid, which in turn is named after the plant valerian due to the presence of the acid in the roots of the plant. Nomenclature According to IUPAC, carbon atoms forming valine are numbered sequentially s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |