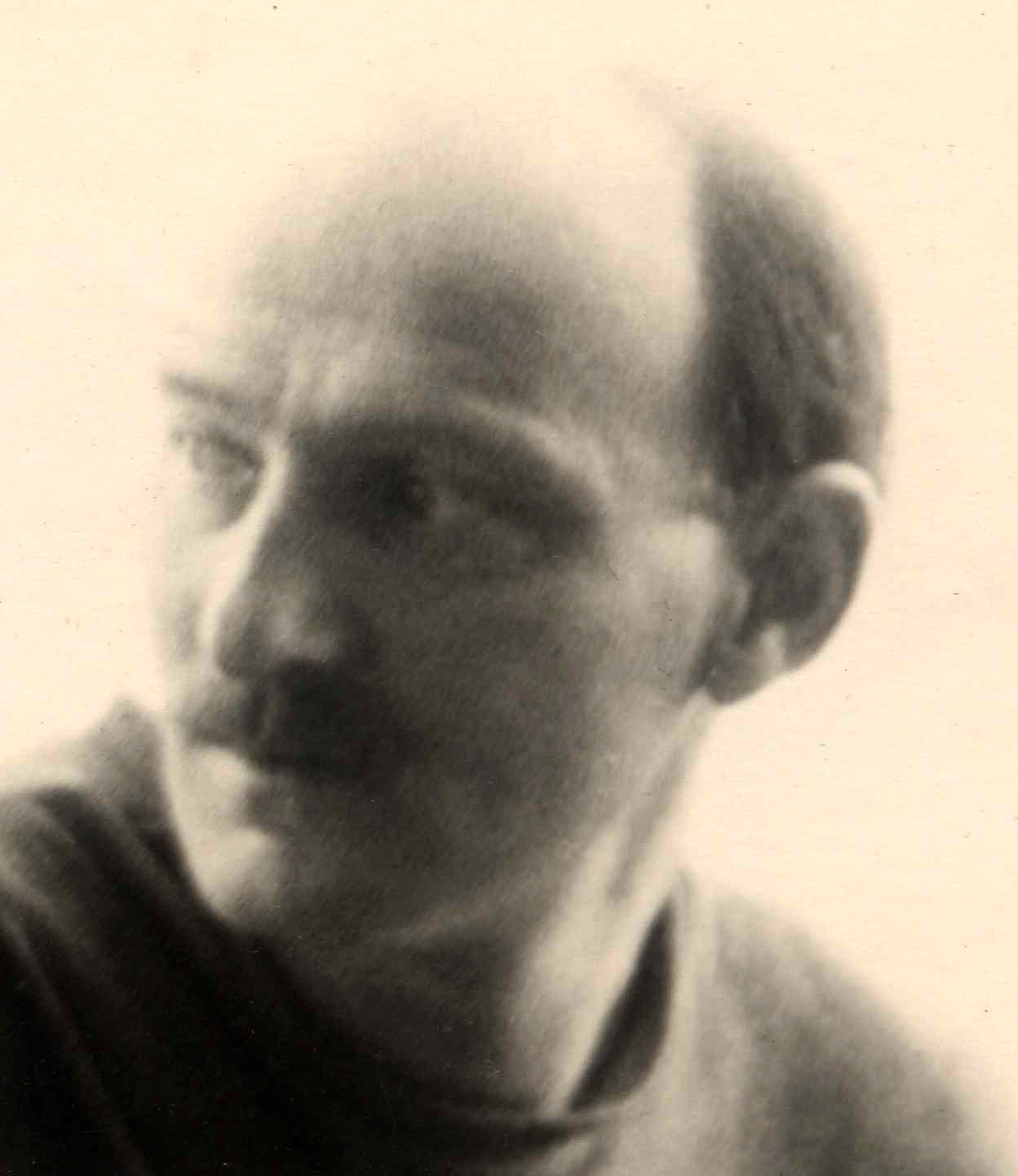|
Kronid Lyubarsky
Kronid Arkadyevich Lyubarsky (russian: Крони́д Арка́дьевич Люба́рский; 4 April 1934 – 23 May 1996) was a Russian journalist, dissident, human rights activist and political prisoner. Early career Born in the city of Pskov, USSR, on April 4, 1934, Lyubarsky graduated from the Moscow State University in 1956 and worked as an astrophysicist at the All-Union Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of the USSR Academy of Sciences. His academic work included studies on meteors and space biology. He was also working in the Soviet program of interplanetary exploration of Mars. He authored several books on astrobiology and translated scientific works into Russian, including books by Fred Hoyle. Dissident activity In the mid-1960s, Lyubarsky became active in the civil rights movement and became a contributing editor of various samizdat publications. These included the ''Chronicle of Current Events'' which circulated between April 1968 and August 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyudmila Alexeyeva
Lyudmila Mikhaylovna Alexeyeva (russian: Людми́ла Миха́йловна Алексе́ева, ; 20 July 1927 – 8 December 2018) was a Russian historian and human-rights activist who was a founding member in 1976 of the Moscow Helsinki Watch Group and one of the last Soviet dissidents active in post-Soviet Russia. Biography Soviet period In April 1968, Alexeyeva was expelled from the Communist Party and fired from her job at the publishing house. Nonetheless, she continued her activities in defense of human rights. From 1968 to 1972 she worked clandestinely as a typist for the first underground bulletin '' The Chronicle of Current Events'' devoted to human rights violations in the USSR. In February 1977, Alexeyeva fled from the USSR to the United States following a crackdown against members of ''The Chronicle'' by Soviet authorities. In the US Alexeyeva continued to advocate for human rights improvements in Russia and worked on a freelance basis for Radio Free Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Rights In Russia
Human rights in Russia have routinely been criticized by international organizations and independent domestic media outlets. Some of the most commonly cited violations include deaths in custody, the widespread and systematic use of torture by security forces and prison guards, hazing rituals (known as ''dedovshchina'', meaning "reign of grandfathers") in the Russian Army, widespread violations of children's rights, violence and discrimination against ethnic minorities, and the killing of journalists. (As of 9 July 2009). As a successor state of the Soviet Union, the Russian Federation remains bound by the same human rights agreements that were signed and ratified by its predecessor, such as the international covenants on civil and political rights as well as economic, social, and cultural rights. In the late 1990s, Russia also ratified the European Convention on Human Rights (with reservations) and from 1998 onwards the European Court of Human Rights in Strasbourg became a last ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Day Of Remembrance Of The Victims Of Political Repressions
The Remembrance Day for the Victims of Political Repression (russian: День памяти жертв политических репрессий) is an annual day when victims of political repression in the Soviet Union are remembered and mourned across the Russian Federation. Origins The day has been observed since 30 October 1991. It was established by the Supreme Soviet of Russia on 18 October 1991, the same day as that body passed the "Law on the Rehabilitation of the Victims of Political Repression", a key piece of legislation still in force. (The Memorial (society) has estimated that 12 million people qualified for rehabilitation under the terms of that act.) 30 October is an official date in the calendar of the Russian Federation. In 2007 President Putin visited the Butovo firing range on 30 October. Ten years later it was the day on which President Putin and Patriarch Kirill inaugurated the new Wall of Sorrow. This new use continues to be criticised by some Russia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Initiative Group For The Defense Of Human Rights In The USSR
The Initiative or Action Group for the Defense of Human Rights in the USSR (russian: Инициати́вная гру́ппа по защи́те прав челове́ка в СССР) was the first civic organization of the Soviet human rights movement. Founded in 1969 by 15 dissidents, the unsanctioned group functioned for over six years as a public platform for Soviet dissidents concerned with violations of human rights in the Soviet Union. The main work of the group consisted in documenting abuses and preparing appeals. The letters focused on persecution of people for their convictions in the USSR, with particular attention being given to the use of punitive psychiatry and to political prisoners. Unusually for the dissident movement at the time, the appeals were directed to international organizations such as the UN Commission on Human Rights. The documents of the Initiative Group were circulated in ''samizdat'', and published by the Western press, as well as being broadcas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Central Prison
Vladimir Prison, popularly known as Vladimir Central (russian: Владимирский централ), is a prison in Vladimir, Russia. It is the largest prison in Russia, with a capacity of 1220 detainees, and is operated by the Federal Penitentiary Service as a maximum-security prison with most inmates serving a minimum of ten years to life sentences. History Vladimir Prison was established by the Russian Empire in 1783 by decree of Empress Catherine II, located about 160 kilometres (100 mi) northeast of Moscow. In 1906, it became known as Vladimir Central and contained political prisoners. At the beginning of 1921, shortly after the rise of the Bolsheviks to power, Vladimir Central became the first of several special-purpose prisons intended to house far-left opponents of the regime. Vladimir Central was later part of the system of "special camps and prisons" organized on the basis of the USSR Council of Ministers resolution No. 416-159 of February 21, 1948 "On the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordovia
The Republic of Mordovia (russian: Респу́блика Мордо́вия, r=Respublika Mordoviya, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə mɐrˈdovʲɪjə; mdf, Мордовия Республиксь, ''Mordovija Respublikś''; myv, Мордовия Республикась, ''Mordovija Respublikaś'') is a republic of Russia, located in Eastern Europe. Its capital is the city of Saransk. As of the 2010 Census, the population of the republic was 834,755. Ethnic Russians (53.1%) and Mordvins (39.8%) account for the majority of the population. History Early history The earliest archaeological signs of modern humans in the area of Mordovia are from the Neolithic era. Mordvins are mentioned in written sources from the 6th century. Later, Mordvins were under the influence of both Volga Bulgaria and the Kievan Rus. Mordvin princes sometimes raided Muroma and Volga Bulgaria and often despoiled each other's holdings. Mongol rule The Mongols conquered vast areas of Eastern Europe in the 13th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-Soviet Agitation And Propaganda
Anti-Soviet agitation and propaganda (ASA) (russian: антисове́тская агита́ция и пропага́нда (АСА)) was a criminal offence in the Soviet Union. To begin with the term was interchangeably used with counter-revolutionary agitation. The latter term was in use immediately after the first Russian Revolution in February 1917. The offence was codified in criminal law in the 1920s, and revised in the 1950s in two articles of the RSFSR Criminal Code. The offence was widely used against Soviet dissidents. Stalin era The new Criminal Codes of the 1920s introduced the offence of ''anti-Soviet agitation and propaganda'' as one of the many forms of counter-revolutionary activity grouped together under Article 58 of the Russian RSFSR Penal Code. The article was put in force on 25 February 1927 and remained in force throughout the period of Stalinism. Article 58:10, "propaganda and agitation that called to overturn or undermining of the Soviet regime", was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicle Of Current Events
''A Chronicle of Current Events'' (russian: Хро́ника теку́щих собы́тий, ''Khronika tekushchikh sobytiy'') was one of the longest-running ''samizdat'' periodicals of the post-Stalin USSR. This unofficial newsletter reported violations of civil rights and judicial procedure by the Soviet government and responses to those violations by citizens across the Soviet Union. Appearing first in April 1968, it soon became the main voice of the Soviet human rights movement, inside the country and abroad. During the 15 years of its existence the ''Chronicle'' covered 424 political trials, in which 753 people were convicted. Not one of the accused was acquitted. In addition, 164 people were declared insane and sent for indefinite periods of compulsory treatment in psychiatric hospitals. In 1973 the novelist and literary critic Lydia Chukovskaya wrote Despite constant harassment by the Soviet authorities more than sixty issues of the ''Chronicle'' were compiled and publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samizdat
Samizdat (russian: самиздат, lit=self-publishing, links=no) was a form of dissident activity across the Eastern Bloc in which individuals reproduced censored and underground makeshift publications, often by hand, and passed the documents from reader to reader. The practice of manual reproduction was widespread, because most typewriters and printing devices required official registration and permission to access. This was a grassroots practice used to evade official Soviet censorship. Name origin and variations Etymologically, the word ''samizdat'' derives from ''sam'' (, "self, by oneself") and ''izdat'' (, an abbreviation of , , "publishing house"), and thus means "self-published". The Ukrainian language has a similar term: ''samvydav'' (самвидав), from ''sam'', "self", and ''vydavnytstvo'', "publishing house". A Russian poet Nikolay Glazkov coined a version of the term as a pun in the 1940s when he typed copies of his poems and included the note ''Samsebyaizd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (magazine)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature'' cover the full ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fred Hoyle
Sir Fred Hoyle FRS (24 June 1915 – 20 August 2001) was an English astronomer who formulated the theory of stellar nucleosynthesis and was one of the authors of the influential B2FH paper. He also held controversial stances on other scientific matters—in particular his rejection of the "Big Bang" theory (a term coined by him on BBC Radio) in favor of the " Steady State" hypothesis, and his promotion of panspermia as the origin of life on Earth. He also wrote science fiction novels, short stories and radio plays, and co-authored twelve books with his son, Geoffrey Hoyle. He spent most of his working life at the Institute of Astronomy at Cambridge and served as its director for six years. Biography Early life and career Hoyle was born near Bingley in Gilstead, West Riding of Yorkshire, England. His father, Ben Hoyle, who was a violinist and worked in the wool trade in Bradford, served as a machine gunner in the First World War. His mother, Mabel Pickard, had studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos and Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a large impact feature. Days and seasons on Mars are comparable to those of Earth, as the planets have a similar rotation period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_83.jpg)