|
Kp-index
The ''K''-index quantifies disturbances in the horizontal component of earth's magnetic field with an integer in the range 0–9 with 1 being calm and 5 or more indicating a geomagnetic storm. It is derived from the maximum fluctuations of horizontal components observed on a magnetometer during a three-hour interval. The label ''K'' comes from the German word ''Kennziffer'' meaning "''characteristic digit''". The ''K''-index was introduced by Julius Bartels in 1939. Calculation of ''K''-index The ''K''-scale is quasi-logarithmic. The conversion table from maximum fluctuation ''R'' (in units of nano teslas, nT) to ''K''-index, varies from observatory to observatory in such a way that the historical rate of occurrence of certain levels of ''K'' are about the same at all observatories. In practice this means that observatories at higher geomagnetic latitude require higher levels of fluctuation for a given ''K''-index. For example, at Godhavn, Greenland, a value of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Bartels
Julius Bartels (17 August 1899, Magdeburg – 6 March 1964) was a German geophysicist and statistician who made notable contributions to the physics of the Sun and Moon; to geomagnetism and meteorology; and to the physics of the ionosphere. He also made fundamental contributions to statistical methods for geophysics. Bartels was the first President of the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA). With Sydney Chapman, he wrote the influential book '' Geomagnetism''. Life and career Bartels was awarded his Ph.D. from Göttingen in 1923, then worked at the Potsdam magnetic observatory as a post-doctorate. In 1928, he was named professor at Eberswalde, teaching meteorology. He became full professor at Berlin University in 1936, and director of the Potsdam Geophysical Institute. From 1931 until the second year of World War II, he was also a research associate at the Carnegie Institution of Washington. He collaborated with Sydney Chapman to publish the two-volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
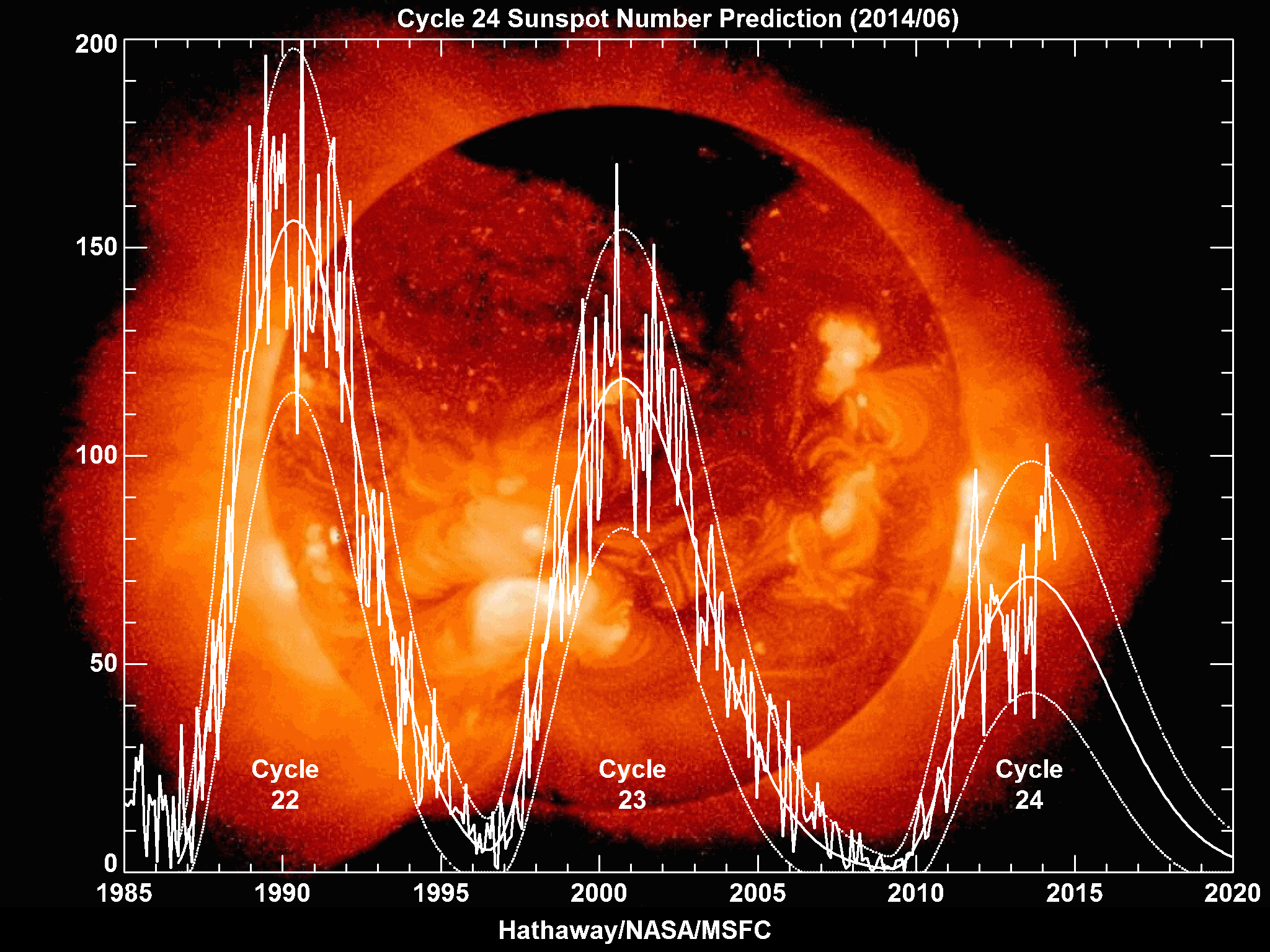
Solar Cycle 24
Solar cycle 24 is the most recently completed solar cycle, the 24th since 1755, when extensive recording of solar sunspot activity began.Kane, R.P. (2002).Some Implications Using the Group Sunspot Number Reconstruction. ''Solar Physics'' 205(2), 383-401. It began in December 2008 with a minimum smoothed sunspot number of 2.2, and ended in December 2019. Activity was minimal until early 2010. It reached its maximum in April 2014 with a 23 months smoothed sunspot number of 81.8. This maximum value was substantially lower than other recent solar cycles, down to a level which had not been seen since cycles Solar cycle 12, 12 to Solar cycle 15, 15 (1878-1923). Predictions Prior to the minimum between the end of Solar Cycle 23 and the beginning of Solar Cycle 24, two theories predicted how strong Solar Cycle 24 would be. One camp postulated that the Sun retained a long memory (Solar Cycle 24 would be active) while the other asserted that it had a short memory (quiet). Prior to 2006, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth's Magnetic Field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic field is generated by electric currents due to the motion of convection currents of a mixture of molten iron and nickel in Earth's outer core: these convection currents are caused by heat escaping from the core, a natural process called a geodynamo. The magnitude of Earth's magnetic field at its surface ranges from . As an approximation, it is represented by a field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 11° with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were an enormous bar magnet placed at that angle through the center of Earth. The North geomagnetic pole actually represents the South pole of Earth's magnetic field, and conversely the South geomagnetic pole corresponds to the north pole of Earth's magnetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Usable Frequency
In radio transmission maximum usable frequency (MUF) is the highest radio frequency that can be used for transmission between two points via reflection from the ionosphere (skywave or "skip" propagation) at a specified time, independent of transmitter power. This index is especially useful in regard to shortwave transmissions. In shortwave radio communication, a major mode of long distance propagation is for the radio waves to reflect off the ionized layers of the atmosphere and return diagonally back to Earth. In this way radio waves can travel beyond the horizon, around the curve of the Earth. However the refractive index of the ionosphere decreases with increasing frequency, so there is an upper limit to the frequency which can be used. Above this frequency the radio waves are not reflected by the ionosphere but are transmitted through it into space. The ionization of the atmosphere varies with time of day and season as well as with solar conditions, so the upper frequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionospheric Storm
Ionospheric storms are storms which contain varying densities of energised electrons produced from the sun. They are categorised into positive and negative storms, where positive storms have a high density of electrons and negative storms contain a lower density. The total electron content (TEC) is used to measure these densities, and is a key variable used in data to record and compare the intensities of ionospheric storms. ''Ionospheric storms are caused by geomagnetic storms.'' Ionospheric storm occurrences are strongly linked with sudden increases of solar wind speed, where solar wind brings energised electrons into the upper atmosphere of the Earth and contributes to increased TEC. Larger storms form global visibility of auroras. Auroras are most commonly seen in the arctic circle; however, large ionospheric storms allow for them to be visible in places such as the United States, United Kingdom, and Europe. The most intense ionospheric storm occurred in 1859, commonly named the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionosphere
The ionosphere () is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about to above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. History of discovery As early as 1839, the German mathematician and physicist Carl Friedrich Gauss postulated that an electrically conducting region of the atmosphere could account for observed variations of Earth's magnetic field. Sixty years later, Guglielmo Marconi received the first trans-Atlantic radio signal on December 12, 1901, in St. John's, Newfoundland (now in Canada) using a kite-supported antenna for reception. The transmitting station in Poldhu, Cornwall, used a spark-gap transmitter to produce a signal with a freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Frequency
High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the range of radio frequency electromagnetic waves (radio waves) between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten decameters (ten to one hundred meters). Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted medium frequency (MF), while the next band of higher frequencies is known as the very high frequency (VHF) band. The HF band is a major part of the shortwave band of frequencies, so communication at these frequencies is often called shortwave radio. Because radio waves in this band can be reflected back to Earth by the ionosphere layer in the atmosphere – a method known as "skip" or " skywave" propagation – these frequencies are suitable for long-distance communication across intercontinental distances and for mountainous terrains which prevent line-of-sight communications. The band is used by international shortwave broadcasting stations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honolulu, Hawaii
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island of Oahu, and is the westernmost and southernmost major U.S. city. Honolulu is Hawaii's main gateway to the world. It is also a major hub for business, finance, hospitality, and military defense in both the state and Oceania. The city is characterized by a mix of various Asian, Western, and Pacific cultures, reflected in its diverse demography, cuisine, and traditions. ''Honolulu'' means "sheltered harbor" or "calm port" in Hawaiian; its old name, ''Kou'', roughly encompasses the area from Nuuanu Avenue to Alakea Street and from Hotel Street to Queen Street, which is the heart of the present downtown district. The city's desirability as a port accounts for its historical growth and importance in the Hawaiian archipelago and the broader Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-index
The ''K''-index quantifies disturbances in the horizontal component of earth's magnetic field with an integer in the range 0–9 with 1 being calm and 5 or more indicating a geomagnetic storm. It is derived from the maximum fluctuations of horizontal components observed on a magnetometer during a three-hour interval. The label ''K'' comes from the German word ''Kennziffer'' meaning "''characteristic digit''". The ''K''-index was introduced by Julius Bartels in 1939. Calculation of ''K''-index The ''K''-scale is quasi-logarithmic. The conversion table from maximum fluctuation ''R'' (in units of nano teslas, nT) to ''K''-index, varies from observatory to observatory in such a way that the historical rate of occurrence of certain levels of ''K'' are about the same at all observatories. In practice this means that observatories at higher geomagnetic latitude require higher levels of fluctuation for a given ''K''-index. For example, at Godhavn, Greenland, a value of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign (−1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language of mathematics, the set of integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold \mathbb. The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the natural numbers, \mathbb is countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , and are not. The integers form the smallest group and the smallest ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the integers are sometimes qualified as rational integers to distinguish them from the more general algebraic integers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godhavn
Qeqertarsuaq () is a port and town in Qeqertalik municipality, located on the south coast of Disko Island on the west coast of Greenland. Founded in 1773, the town is now home to a campus of the University of Copenhagen known as Arctic Station. ''Qeqertarsuaq'' is the Kalaallisut name for Disko Island and is also now used for several other islands on Greenland, including those formerly known as Upernavik and Herbert Island. Qeqertarsuaq means ‘the big island’ in Kalaallisut ( da, den store ø). In 2020, the town had 839 inhabitants. The remainder of the population of the island (less than 50 people) lives in the Kangerluk settlement, a few hours by boat to the northwest. Geography The total area of Disko Island and its satellite islands (mainly Qeqertarsuatsiaq Island northwest of the northern coast and Qeqertaq on the southwest coast at the mouth of Disko Fjord) is . Blæsedalen valley is to the north of the town. Kangerluk is the location where researchers found a 'g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |