|
Julius Bartels
Julius Bartels (17 August 1899, Magdeburg – 6 March 1964) was a German geophysicist and statistician who made notable contributions to the physics of the Sun and Moon; to geomagnetism and meteorology; and to the physics of the ionosphere. He also made fundamental contributions to statistical methods for geophysics. Bartels was the first President of the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA). With Sydney Chapman, he wrote the influential book '' Geomagnetism''. Life and career Bartels was awarded his Ph.D. from Göttingen in 1923, then worked at the Potsdam magnetic observatory as a post-doctorate. In 1928, he was named professor at Eberswalde, teaching meteorology. He became full professor at Berlin University in 1936, and director of the Potsdam Geophysical Institute. From 1931 until the second year of World War II, he was also a research associate at the Carnegie Institution of Washington. He collaborated with Sydney Chapman to publish the two-volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-index
The ''K''-index quantifies disturbances in the horizontal component of earth's magnetic field with an integer in the range 0–9 with 1 being calm and 5 or more indicating a geomagnetic storm. It is derived from the maximum fluctuations of horizontal components observed on a magnetometer during a three-hour interval. The label ''K'' comes from the German word ''Kennziffer'' meaning "''characteristic digit''". The ''K''-index was introduced by Julius Bartels in 1939. Calculation of ''K''-index The ''K''-scale is quasi-logarithmic. The conversion table from maximum fluctuation ''R'' (in units of nano teslas, nT) to ''K''-index, varies from observatory to observatory in such a way that the historical rate of occurrence of certain levels of ''K'' are about the same at all observatories. In practice this means that observatories at higher geomagnetic latitude require higher levels of fluctuation for a given ''K''-index. For example, at Godhavn, Greenland, a value of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg
Magdeburg (; nds, label= Low Saxon, Meideborg ) is the capital and second-largest city of the German state Saxony-Anhalt. The city is situated at the Elbe river. Otto I, the first Holy Roman Emperor and founder of the Archdiocese of Magdeburg, was buried in the city's cathedral after his death. Magdeburg's version of German town law, known as Magdeburg rights, spread throughout Central and Eastern Europe. In the Late Middle Ages, Magdeburg was one of the largest and most prosperous German cities and a notable member of the Hanseatic League. One of the most notable people from the city is Otto von Guericke, famous for his experiments with the Magdeburg hemispheres. Magdeburg has been destroyed twice in its history. The Catholic League sacked Magdeburg in 1631, resulting in the death of 25,000 non-combatants, the largest loss of the Thirty Years' War. During the World War II the Allies bombed the city in 1945 and destroying much of it. After World War II the city b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnegie Institution Of Washington
The Carnegie Institution of Washington (the organization's legal name), known also for public purposes as the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS), is an organization in the United States established to fund and perform scientific research. The institution is headquartered in Washington, D.C. , the Institution's endowment was valued at $926.9 million. In 2018 the expenses for scientific programs and administration were $96.6 million.Eric Isaacs is president of the institution. Name More than 20 independent organizations were established through the philanthropy of Andrew Carnegie and now feature his surname. They perform work involving topics as diverse as art, education, international relations, international affairs, world peace, and scientific research. In 2007, the Carnegie Institution of Washington adopted the public name "Carnegie Institution for Science" to distinguish itself from other organizations established by and named for Andrew Carnegie. The Institution remai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Magnetism And Atmospheric Electricity
The ''Journal of Geophysical Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. It is the flagship journal of the American Geophysical Union. It contains original research on the physical, chemical, and biological processes that contribute to the understanding of the Earth, Sun, and Solar System. It has seven sections: A (Space Physics), B (Solid Earth), C (Oceans), D (Atmospheres), E (Planets), F (Earth Surface), and G (Biogeosciences). All current and back issues are available online for subscribers. History The journal was originally founded under the name ''Terrestrial Magnetism'' by the American Geophysical Union's president Louis Agricola Bauer in 1896. It was renamed to ''Terrestrial Magnetism and Atmospheric Electricity'' in 1899 and in 1948 it acquired its current name. In 1980, three specialized sections were established: ''A: Space Physics'', ''B: Solid Earth'', and ''C: Oceans''. Subsequently, further sections have been added: ''D: Atmospheres'' in 1984, ''E: Planets'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific interchange between East and West had been seriously interrupted. Sixty-seven countries participated in IGY projects, although one notable exception was the mainland People's Republic of China, which was protesting against the participation of the Republic of China ( Taiwan). East and West agreed to nominate the Belgian Marcel Nicolet as secretary general of the associated international organization. The IGY encompassed eleven Earth sciences: aurora and airglow, cosmic rays, geomagnetism, gravity, ionospheric physics, longitude and latitude determinations (precision mapping), meteorology, oceanography, seismology, and solar activity. The timing of the IGY was particularly suited for studying some of these phenomena, since it cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations included an orbital workshop, a solar observatory, Earth observation, and hundreds of experiments. Unable to be re-boosted by the Space Shuttle, which was not ready until 1981, Skylab's orbit eventually decayed, and it disintegrated in the atmosphere on July 11, 1979, scattering debris across the Indian Ocean and Western Australia. Overview Skylab was the only space station operated exclusively by the United States. A permanent station was planned starting in 1988, but funding for this was canceled and replaced with United States participation in an International Space Station in 1993. Skylab had a mass of with a Apollo command and service module (CSM) attached and included a workshop, a solar observatory, and several hundred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
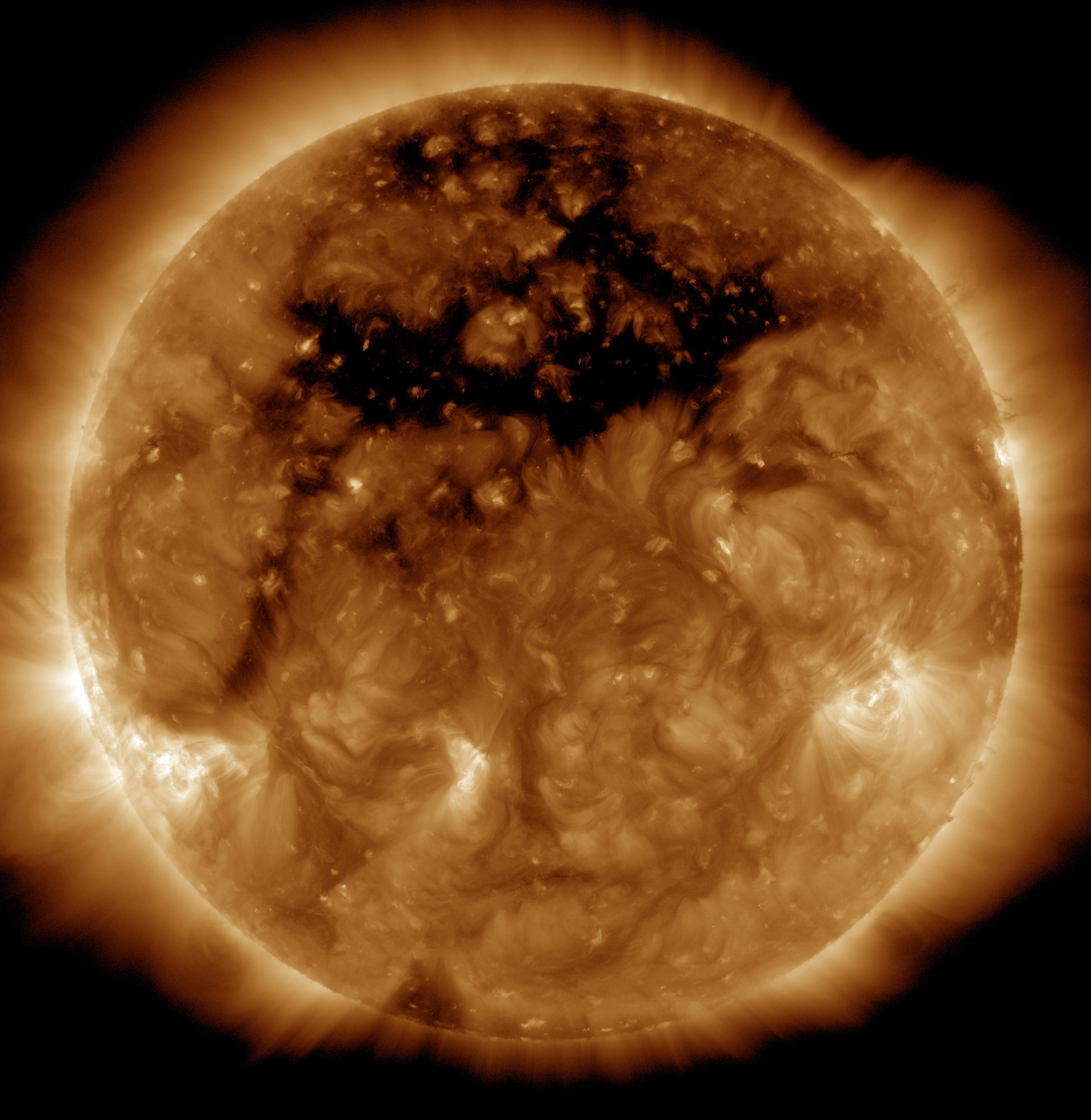
Coronal Holes
A coronal hole is a temporary region of relatively cool, less dense plasma in the solar corona where the Sun's magnetic field extends into interplanetary space as an open field.Freedman, Roger A., and William J. Kaufmann III. "Our Star, the Sun." Universe. 8th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman, 2008. 419–420. Print. Compared to the corona's usual closed magnetic field that arches between regions of opposite magnetic polarity, the open magnetic field of a coronal hole allows solar wind to escape into space at a much quicker rate. This results in decreased temperature and density of the plasma at the site of a coronal hole, as well as an increased speed in the average solar wind measured in interplanetary space. If streams of high-speed solar wind from coronal holes encounter the Earth, they can cause major displays of aurorae. Near solar minimum, when activity such as coronal mass ejections is less frequent, such streams are the main cause of geomagnetic storms and associated aurorae. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Geodesy And Geophysics
The International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG; french: Union géodésique et géophysique internationale, UGGI) is an international non-governmental organization dedicated to the scientific study of Earth and its space environment using geophysical and geodetic techniques. The IUGG was established in Brussels, Belgium in 1919. Some areas within its scope are environmental preservation, reduction of the effects of natural hazards, and mineral resources. The IUGG is a member of the International Science Council (ISC), which is composed of international scholarly and scientific institutions and national academies of sciences. Objectives IUGG's objectives are the promotion and coordination of studies related to Earth's physical, chemical and mathematical representation. This includes geometrical shape, internal structure, gravity and magnetic fields, seismicity, volcanism Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee On Space Research
The Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) was established on October 3, 1958 by the International Council for Scientific Unions (ICSU). Among COSPAR's objectives are the promotion of scientific research in space on an international level, with emphasis on the free exchange of results, information, and opinions, and providing a forum, open to all scientists, for the discussion of problems that may affect space research. These objectives are achieved through the organization of symposia, publication, and other means. COSPAR has created a number of research programmes on different topics, a few in cooperation with other scientific Unions. The long-term project COSPAR international reference atmosphere started in 1960; since then it has produced several editions of the high-atmosphere code CIRA. The code "IRI" of the URSI-COSPAR working group on the International Reference Ionosphere was first edited in 1978 and is yearly updated. General Assembly Every second year, COSPAR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Council For Science
The International Council for Science (ICSU, after its former name, International Council of Scientific Unions) was an international non-governmental organization devoted to international cooperation in the advancement of science. Its members were national scientific bodies and international scientific unions. In July 2018, the ICSU merged with the International Social Science Council (ISSC) to form the International Science Council (ISC). In 2017, the ICSU comprised 122 multi-disciplinary National Scientific Members, Associates and Observers representing 142 countries and 31 international, disciplinary Scientific Unions. ICSU also had 22 Scientific Associates. In July 2018, ICSU merged with the International Social Science Council (ISSC) to form the International Science Council (ISC) at a constituent general assembly in Paris. Mission and principles The ICSU's mission was to strengthen international science for the benefit of society. To do this, the ICSU mobilized the kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Planck Institute For Solar System Research
The Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (abbreviation: MPS; german: Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung) is a research institute in astronomy and astrophysics located in Göttingen, Germany, where it relocated in February 2014 from the nearby village of Lindau. The exploration of the Solar System is the central theme for research done at this institute. MPS is a part of the Max Planck Society, which operates 80 research facilities in Germany. Research MPS is organised in three departments: Sun and Heliosphere, Planets and Comets, and Solar and Stellar Interiors. In addition, since 2002 there is also an International Max Planck Research School. Subjects of research at the institute are the various objects within the solar system. A major area of study concerns the Sun, its atmosphere, the interplanetary medium as influenced by the solar wind, as well as the impact of solar particles and radiation on the planets. The second area of research involves the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)