|
Kosmos 1686
Kosmos 1686 (russian: Космос 1686 meaning ''Cosmos 1686''), also known as TKS-4, was a heavily modified TKS spacecraft which docked unmanned to the Soviet space station Salyut 7 as part of tests to attach scientific expansion modules to stations in Earth orbit. The module which docked to the station was the FGB component of a TKS vehicle launched on September 27, 1985, and was designed to test systems planned for use on the Mir Core Module. The spacecraft docked with Salyut 7 on October 2, 1985, during the long-duration stay of the cosmonauts of its fifth principal expedition, which arrived on Soyuz T-14. It was the last flown TKS spacecraft. Notable features * The spacecraft's VA capsule was greatly modified to carry instruments – the retrorocket and parachute packages were replaced by scientific equipment, including an infrared telescope and the Ozon spectrometer. * The combined Salyut 7-Kosmos 1686 complex massed 43 tons, with Kosmos 1686 delivering 4500 kg of ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut 7
Salyut 7 (russian: Салют-7; en, Salute 7) (a.k.a. DOS-6, short for Durable Orbital Station) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including 12 crewed and 15 uncrewed launches in total. Supporting spacecraft included the Soyuz T, Progress (spacecraft), Progress, and TKS spacecraft. It was part of the Soviet Union, Soviet Salyut programme, and launched on 19 April 1982 on a Proton (rocket), Proton rocket from Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 200, Site 200/40 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome in the Soviet Union. Salyut 7 was part of the transition from monolithic to modular space stations, acting as a testbed for docking of additional modules and expanded station operations. It was the eighth space station of any kind launched. Salyut 7 was the last of both the second generation of DOS-series spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Core Module
''Mir'' (russian: Мир lit. ''Peace'' or ''World''), DOS-7, was the first module of the Soviet/Russian ''Mir'' space station complex, in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001. Generally referred to as either the core module or base block, the module was launched on 20 February 1986 on a Proton-K rocket from LC-200/39 at the Baikonur Cosmodrome. The spacecraft was generally similar in design to the two previous Soviet orbital stations, Salyut 6 and Salyut 7, however possessed a revolutionary addition in the form of a multiple docking node at the forward end of the module. This, in addition to the docking port at the rear of the spacecraft, allowed five additional modules ( ''Kvant''-1 (1987), ''Kvant''-2 (1989), ''Kristall'' (1990), ''Spektr'' (1995) and ''Priroda'' (1996)) to be docked directly to DOS-7, greatly expanding the station's capabilities. Designed as a 'habitat' or 'living' module, DOS-7 possessed less scientific apparatus than its predecessors (lacking, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos Satellites
The cosmos (, ) is another name for the Universe. Using the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity. The cosmos, and understandings of the reasons for its existence and significance, are studied in cosmologya broad discipline covering scientific, religious or philosophical aspects of the cosmos and its nature. Religious and philosophical approaches may include the cosmos among spiritual entities or other matters deemed to exist outside the physical universe. Etymology The philosopher Pythagoras first used the term ''kosmos'' ( grc, κόσμος, Latinized ''kósmos'') for the order of the universe. Greek κόσμος "order, good order, orderly arrangement" is a word with several main senses rooted in those notions. The verb κοσμεῖν (''κοσμεῖν'') meant generally "to dispose, prepare", but especially "to order and arrange (troops for battle), to set (an army) in array"; also "to establish (a government or regime)" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salyut Program
The ''Salyut'' programme (russian: Салют, , meaning "salute" or "fireworks") was the first space station programme, undertaken by the Soviet Union. It involved a series of four crewed scientific research space stations and two crewed military reconnaissance space stations over a period of 15 years, from 1971 to 1986. Two other ''Salyut'' launches failed. In one respect, ''Salyut'' had the task of carrying out long-term research into the problems of living in space and a variety of astronomical, biological and Earth-resources experiments, and on the other hand the USSR used this civilian programme as a cover for the highly secretive military ''Almaz'' stations, which flew under the ''Salyut'' designation. ''Salyut'' 1, the first station in the programme, became the world's first crewed space station. ''Salyut'' flights broke several spaceflight records, including several mission-duration records, and achieved the first orbital handover of a space station from one crew t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitan Bermudez
Capitan and Kapitan are equivalents of the English Captain in other European languages. Capitan, Capitano, and Kapitan may also refer to: Places in the United States * Capitan, Louisiana, an unincorporated community *Capitan, New Mexico, a village *Capitan Mountains, New Mexico People *George Kapitan, who wrote for Timely in the Golden Age of Comic Books. *Tomis Kapitan, an American philosopher and Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus at Northern Illinois University. Arts and entertainment *''Der Kapitän'' or ''The Captain'' (film), a 1971 German comedy * ''Der Kapitän'' (TV series), a German series *''Le Capitan'', a novel by Michel Zevaco Other uses *Kapitän, a shortened version of several ranks in the German navy *Kapitan, another name for Opperhoofd, a Dutch colonial governor *Opel Kapitän, a luxury car manufactured from 1938 to 1970 *Capitan (tequila), a brand of tequila produced by Barton Brands *Capitan Records, a record label set up by US musician Chris Brokaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
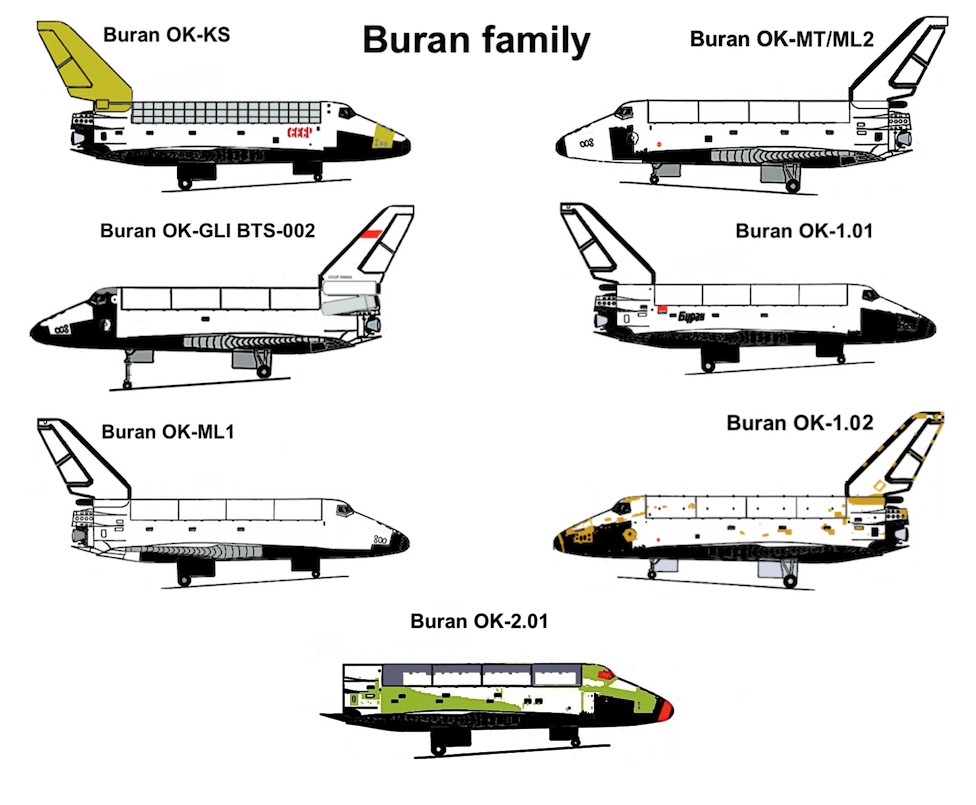
Buran Program
The ''Buran'' program (russian: Буран, , "Snowstorm", "Blizzard"), also known as the "VKK Space Orbiter program" (russian: ВКК «Воздушно-Космический Корабль», lit=Air and Space Ship), was a Soviet Union, Soviet and later Russian reusable spacecraft project that began in 1974 at the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute in Moscow and was formally suspended in 1993. In addition to being the designation for the whole Soviet/Russian reusable spacecraft project, ''Buran'' was also the name given to Buran (spacecraft), Orbiter K1, which completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988 and was the only Soviet reusable spacecraft to be launched into space. The ''Buran''-class orbiters used the expendable Energia (rocket), Energia rocket as a launch vehicle. Unlike the Space Shuttle, Buran had a capability of flying uncrewed missions, as well as performing fully automated landings. The Buran program was started by the Soviet Union as a response to the United St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buran (spacecraft)
''Buran'' (russian: Буран, , meaning "Snowstorm" or "Blizzard"; GRAU index serial number: 11F35 1K, construction number: 1.01) was the first spaceplane to be produced as part of the Soviet/Russian Buran program. Besides describing the first operational Soviet/Russian shuttle orbiter, "Buran" was also the designation for the entire Soviet/Russian spaceplane project and its orbiters, which were known as "Buran-class orbiters". Buran completed one uncrewed spaceflight in 1988, and was destroyed in the 2002 collapse of its storage hangar. The Buran-class orbiters used the expendable Energia rocket, a class of super heavy-lift launch vehicle. It is named after the Asian wind. Construction The construction of the Buran spacecraft began in 1980, and by 1984 the first full-scale orbiter was rolled out. Over 1000 companies all over the Soviet Union were involved in construction and development. The Buran spacecraft was made to be launched on the Soviet Union's super-heavy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VA Capsule
The Vozvraschaemyi Apparat (russian: Возвращаемый Аппарат, lit=Return Vehicle, GRAU index 11F74), or VA spacecraft, was a Soviet crew capsule, intended to serve as a crewed launch and reentry vehicle. Initially designed for the LK-1 human lunar flyby spacecraft for one of the Soviet crewed lunar programs, then the LK-700 redesign, it was later repurposed for the Almaz military space station program. The VA capsule on display at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum was labeled as ''Merkur'', following a mistranslation of the original documentation – while incorrect, the name is being used in the West for the VA spacecraft and capsule. The VA spacecraft was capable of independent flight – up to 31 hours in its last incarnation – it needed however to be combined with additional hardware (containing propulsion and storage) to achieve a longer flight duration. Three different such usage scenarios for the VA spacecraft were planned: Initially the LK- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soyuz T-14
Soyuz T-14 (russian: Союз Т-14, ''Union T-14'') was the ninth expedition to Salyut 7. The mission relieved Soyuz T-13, whose crew had performed unprecedented repairs aboard the previously-dead station. Crew Backup crew Mission parameters * Mass: * Perigee: * Apogee: * Inclination: 51.6° * Period: 88.7 minutes Mission highlights Soyuz T-14 demonstrated the wisdom of maintaining a Soyuz at Salyut 7 as an emergency medical evacuation vehicle: the mission commander Vasyutin fell ill which forced an early termination of the planned 6-month mission. The main goals of the mission was to receive Cosmos 1686, a modified TKS, and conduct spacewalks with application to future space stations. The first goal was achieved on October 2. Cosmos 1686 contained of freight, including large items like a girder to be assembled outside Salyut 7, and the Kristallizator materials processing apparatus. However, the crew of Soyuz T-14 were unable to achieve their second goal. By late Octob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station is an artificial satellite (i.e. a type of orbital spaceflight). Stations must have docking ports to allow other spacecraft to dock to transfer crew and supplies. The purpose of maintaining an orbital outpost varies depending on the program. Space stations have most often been launched for scientific purposes, but military launches have also occurred. Space stations have harboured so far the only long-duration direct human presence in space. After the first station Salyut 1 (1971) and its tragic Soyuz 11 crew, space stations have been operated consecutively since Skylab (1973), having allowed a progression of long-duration direct human presence in space. Stations have been occupied by consecutive crews since 1987 with the Salyut successor M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome
The Baikonur Cosmodrome ( kk, Байқоңыр ғарыш айлағы, translit=Baiqoñyr ğaryş ailağy, ; russian: Космодром Байконур, translit=Kosmodrom Baykonur, ) is a spaceport in an area of southern Kazakhstan leased to Russia. The Cosmodrome is the world's first spaceport for orbital and human launches and the largest (in area) operational Spaceport, space launch facility. All crewed Russian spaceflights are launched from Baikonur. The spaceport is in the Kazakh Steppe, desert steppe of Baikonur, about east of the Aral Sea and north of the river Syr Darya. It is near the Tyuratam railway station and is about above sea level. The spaceport is currently leased by the Government of Kazakhstan, Kazakh Government to the Russian Federation until 2050 and is managed jointly by the Roscosmos State Corporation, Roscosmos and the Russian Aerospace Forces. The shape of the area leased is an ellipse, measuring east–west by north–south, with the cosmodrome at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TKS Spacecraft
The TKS spacecraft (russian: Транспортный корабль снабжения, , ''Transport Supply Spacecraft'', GRAU index 11F72) was a Soviet spacecraft conceived in the late 1960s for resupply flights to the military Almaz space station. The spacecraft was designed for both crewed and autonomous uncrewed cargo resupply flights, but was never used operationally in its intended role – only four test missions were flown (including three that docked to Salyut space stations) during the program. The Functional Cargo Block (FGB) of the TKS spacecraft later formed the basis of several space station modules, including the Zarya FGB module on the International Space Station. The TKS spacecraft consisted of two spacecraft mated together, both of which could operate independently: * The VA spacecraft (known mistakenly in the West as the ''Merkur spacecraft''), which would have housed the cosmonauts during launch and reentry of a TKS spacecraft, while traveling to and fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |