|
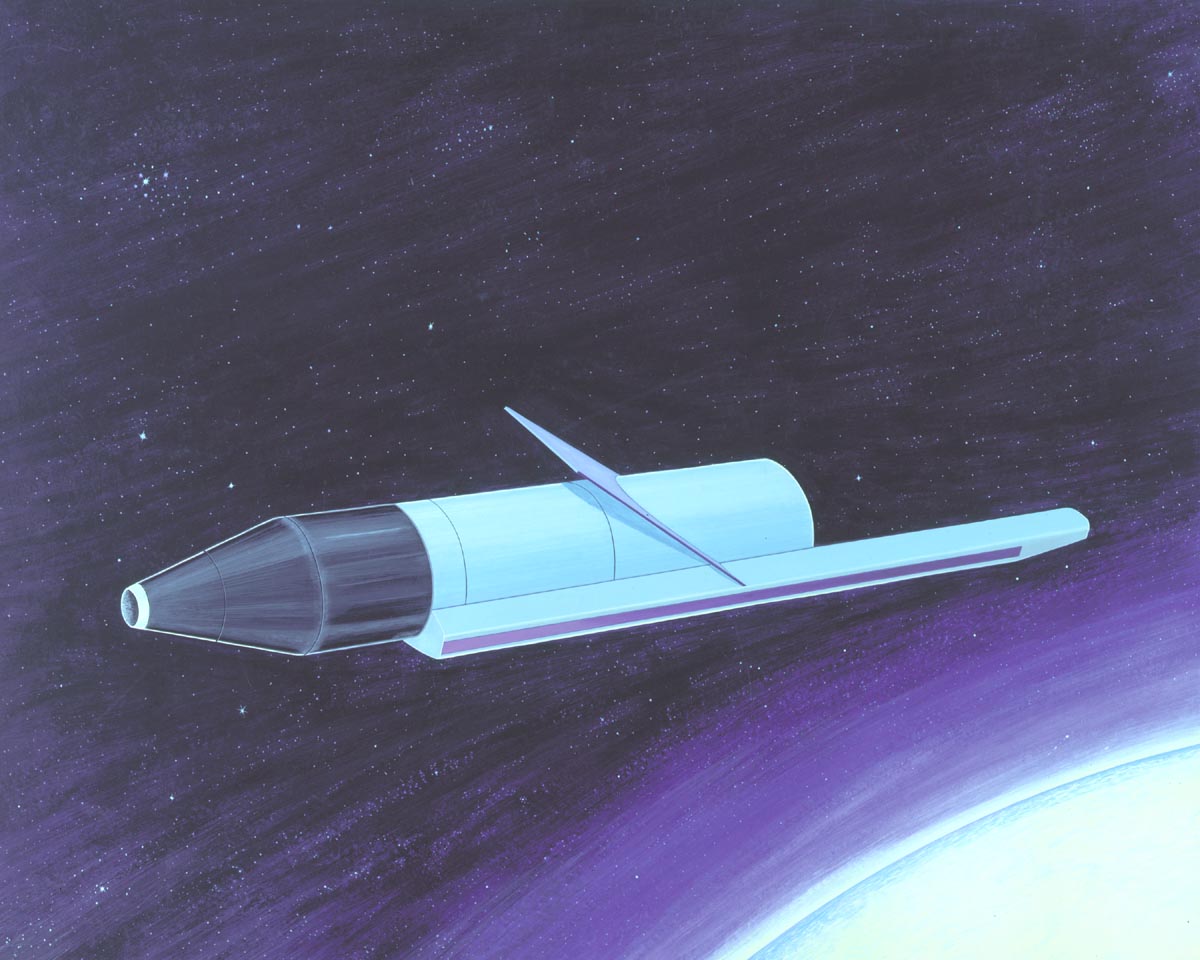
Kosmos 1402
Kosmos 1402 (russian: Космос 1402) was a Soviet spy satellite that malfunctioned, resulting in the uncontrolled re-entry of its nuclear reactor and its radioactive uranium fuel. Kosmos 1402 was launched on August 30, 1982, and re-entered the atmosphere on 23 January 1983. The fission reactor entered a few days later; on 7 February 1983. Kosmos 1402 was a RORSAT surveillance satellite that used radar for monitoring NATO vessels. The power source for the satellite was a BES-5 nuclear fission reactor, which used about of enriched uranium as a fuel source. The satellite operated in low Earth orbit, and the reactor was designed to eject to a higher parking orbit at the end of the satellite's mission, or in the event of a mishap. This ejection mechanism was implemented in the RORSAT satellites after a nuclear accident caused by a previous malfunction of Kosmos 954, five years earlier over Canada's Northwest Territories. In response to the Kosmos 954 mishap, RORSAT satellites we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US-A
Upravlyaemy Sputnik Aktivnyy (russian: Управляемый Спутник Активный for Controlled Active Satellite), or US-A, also known in the west as Radar Ocean Reconnaissance Satellite or RORSAT (GRAU index 17F16K), was a series of 33 Soviet reconnaissance satellites. Launched between 1967 and 1988 to monitor NATO and merchant vessels using radar, the satellites were powered by nuclear reactors. Because a return signal from an ordinary target illuminated by a radar transmitter diminishes as the inverse of the fourth power of the distance, for the surveillance radar to work effectively, US-A satellites had to be placed in low Earth orbit. Had they used large solar panels for power, the orbit would have rapidly decayed due to drag through the upper atmosphere. Further, the satellite would have been useless in the shadow of Earth. Hence the majority of the satellites carried type BES-5 nuclear reactors fuelled by uranium-235. Normally the nuclear reactor cores were e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World" of the Americas in the European perception of the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other definitions describe the Atlantic as extending southward to Antarctica). The Atlantic Ocean is divided in two parts, by the Equatorial Counter Current, with the North(ern) Atlantic Ocean and the South(ern) Atlantic Ocean split at about 8°N. Scientific explorations of the Atlant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1983 In The Soviet Union
The year 1983 saw both the official beginning of the Internet and the first mobile cellular telephone call. Events January * January 1 – The migration of the ARPANET to TCP/IP is officially completed (this is considered to be the beginning of the true Internet). * January 24 – Twenty-five members of the Red Brigades are sentenced to life imprisonment for the 1978 murder of Italian politician Aldo Moro. * January 25 ** High-ranking Nazi war criminal Klaus Barbie is arrested in Bolivia. ** IRAS is launched from Vandenberg AFB, to conduct the world's first all-sky infrared survey from space. February * February 2 – Giovanni Vigliotto goes on trial on charges of polygamy involving 105 women. * February 3 – Prime Minister of Australia Malcolm Fraser is granted a double dissolution of both houses of parliament, for elections on March 5, 1983. As Fraser is being granted the dissolution, Bill Hayden resigns as leader of the Australian Labor Party, and in the subseq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1982 In The Soviet Union
__NOTOC__ Year 198 (CXCVIII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sergius and Gallus (or, less frequently, year 951 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 198 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire *January 28 **Publius Septimius Geta, son of Septimius Severus, receives the title of Caesar. **Caracalla, son of Septimius Severus, is given the title of Augustus. China *Winter – Battle of Xiapi: The allied armies led by Cao Cao and Liu Bei defeat Lü Bu; afterward Cao Cao has him executed. By topic Religion * Marcus I succeeds Olympianus as Patriarch of Constantinople (until 211). Births * Lu Kai (or Jingfeng), Chinese official and general (d. 269) * Quan Cong, Chinese general and advisor (d. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconnaissance Satellites Of The Soviet Union
In military operations, reconnaissance or scouting is the exploration of an area by military forces to obtain information about enemy forces, terrain, and other activities. Examples of reconnaissance include patrolling by troops (skirmishers, long-range reconnaissance patrol, U.S. Army Rangers, cavalry scouts, or military intelligence specialists), ships or submarines, crewed or uncrewed reconnaissance aircraft, satellites, or by setting up observation posts. Espionage is usually considered to be different from reconnaissance, as it is performed by non-uniformed personnel operating behind enemy lines. Often called recce (British, Canadian and Australian English) or recon (American English), the word for this activity has at its root the associated verb ''reconnoitre'' or ''reconnoiter''. Etymology The word from the Middle French ''reconoissance''. Overview Reconnaissance conducted by ground forces includes special reconnaissance, armored reconnaissance, amphibious rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos Satellites
The cosmos (, ) is another name for the Universe. Using the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity. The cosmos, and understandings of the reasons for its existence and significance, are studied in cosmologya broad discipline covering scientific, religious or philosophical aspects of the cosmos and its nature. Religious and philosophical approaches may include the cosmos among spiritual entities or other matters deemed to exist outside the physical universe. Etymology The philosopher Pythagoras first used the term ''kosmos'' ( grc, κόσμος, Latinized ''kósmos'') for the order of the universe. Greek κόσμος "order, good order, orderly arrangement" is a word with several main senses rooted in those notions. The verb κοσμεῖν (''κοσμεῖν'') meant generally "to dispose, prepare", but especially "to order and arrange (troops for battle), to set (an army) in array"; also "to establish (a government or regime)" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellites Formerly Orbiting Earth
A satellite or artificial satellite is an object intentionally placed into orbit in outer space. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which is small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as a group, forming constellations. Because of the high launch cost to space, satellites are designed to be as lightweight and robust as possible. Most communication satellites are radio relay stations in orbit and carry dozens of transponders, each with a bandwidth of tens of megahertz. Satellites are placed from the surface to orbit by launch vehicles, high enough to avoid orbital decay by the atmosphere. Satellites can then change or maintain the orbit by propulsion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nuclear Power Systems In Space
This list of nuclear power systems in space includes nuclear power systems that were flown to space, or at least launched in an attempt to reach space. Such used nuclear power systems include: * radioisotope heater units (RHU) (usually produce heat by spontaneous decay of ) * radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTG) (usually produce heat by spontaneous decay of and convert it to electricity using a thermoelectric generator) * miniaturized fission reactors (usually produce heat by controlled fission of highly enriched and convert it to electricity using a thermionic converter) Systems never launched are not included here, see Nuclear power in space. Initial total power is provided as either electrical power (We) or thermal power (Wt), depending on the intended application. See also *Outer Space Treaty * List of high-altitude nuclear explosions *Nuclear power in space * List of artificial radiation belts * :Nuclear-powered robots References {{DEFAULTSORT:Nuclear p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Kosmos Satellites
This is a list of Kosmos (satellite), Kosmos satellites. Due to its size, the list has been split into groups of 250 satellites: * List of Kosmos satellites (1–250) * List of Kosmos satellites (251–500) * List of Kosmos satellites (501–750) * List of Kosmos satellites (751–1000) * List of Kosmos satellites (1001–1250) * List of Kosmos satellites (1251–1500) * List of Kosmos satellites (1501–1750) * List of Kosmos satellites (1751–2000) * List of Kosmos satellites (2001–2250) * List of Kosmos satellites (2251–2500) * List of Kosmos satellites (2501–2750) External links NSSDC Master Catalog Spacecraft Query FormTBS satelliteAstronautix.com {{DEFAULTSORT:Kosmos satellites Kosmos satellites, * Lists of satellites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos (satellite)
Kosmos (russian: Ко́смос, , meaning " (outer) space" or " Kosmos") is a designation given to many satellites operated by the Soviet Union and subsequently Russia. Kosmos 1, the first spacecraft to be given a Kosmos designation, was launched on 16 March 1962. History The first Soviet satellites orbiting Earth were named Sputnik, Polyot (starting in 1963), Elektron (in 1964), Proton (in 1965), and Molniya (in 1965), but most have been called Kosmos since Kosmos 1 on 16 March 1962. The program has included uncrewed tests of crewed spacecraft and satellites for scientific research and military purposes. , 2548 Kosmos satellites have been launched. The spacecraft do not form a single programme, but instead consist of almost all Soviet and Russian military satellites, as well as a number of scientific satellites, and spacecraft which failed during or immediately after launch, but still reached orbit. Most Soviet and subsequently Russian military satellites were given Kosm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 1818
Kosmos 1818 was a nuclear powered Soviet surveillance satellite in the RORSAT program, which monitored NATO vessels using radar. Kosmos 1818 was the first satellite to use the TOPAZ-1 fission reactor. In July 2008, the satellite was damaged, and leaked a trail of sodium coolant. Description Kosmos 1818 was launched on February 1, 1987 on a Tsyklon-2 rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome. It was put into an orbit about above the Earth's surface at an inclination of 65° and a period of 100.6 minutes. The satellite had a mission life of about five to six months. The satellite was powered by a TOPAZ nuclear reactor, TOPAZ 1 nuclear reactor. This was cooled by liquid sodium-potassium, NaK, metal, it used a high-temperature Neutron moderator, moderator containing hydrogen and highly enriched uranium fuel. It produced electricity using a thermionic converter. It had a Hall effect thruster, Plazma-2 SPT electric engine. Its mission was to search the oceans for naval and merchant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratosphere
The stratosphere () is the second layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, located above the troposphere and below the mesosphere. The stratosphere is an atmospheric layer composed of stratified temperature layers, with the warm layers of air high in the sky and the cool layers of air in the low sky, close to the planetary surface of the Earth. The increase of temperature with altitude is a result of the absorption of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation by the ozone layer. The temperature inversion is in contrast to the troposphere, near the Earth's surface, where temperature decreases with altitude. Between the troposphere and stratosphere is the tropopause border that demarcates the beginning of the temperature inversion. Near the equator, the lower edge of the stratosphere is as high as , at midlatitudes around , and at the poles about . Temperatures range from an average of near the tropopause to an average of near the mesosphere. Stratospheric temperatures also vary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |