|
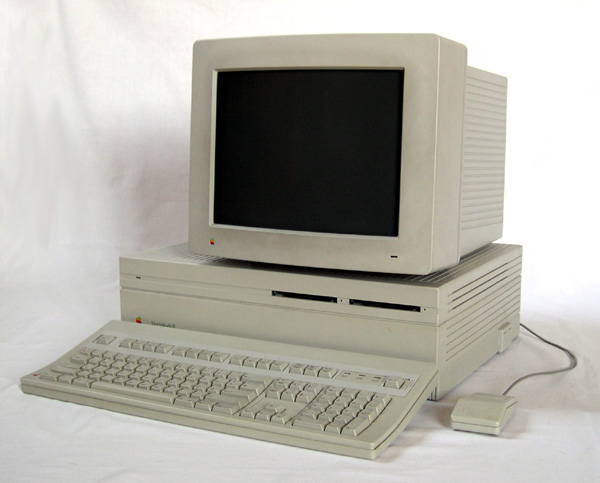
Korg Z1
The Korg Z1 is a physical modelling sound synthesiser released in 1997. Touted as a polyphonic Prophecy, the Z1 implements 13 synthesis types, all derived from the original OASYS synthesizer. Overview The Korg Z1 uses the same Multi-Oscillator Synthesis System (MOSS) tone generator found in the Korg Prophecy. The MOSS tone generator is a direct descendant of the later abandoned Korg OASYS (Open-Architecture SYnthesis System) development platform. Later implementations of the MOSS tone generator were available as optional expansion boards for the Korg Trinity and Triton workstations. Options *ADAT I/O An ADAT expansion available providing 48 kHz digital output, as well as word clock input. *DSPB-Z1 expansion board A DSP board that adds 6 voices of polyphony to the Z1, totaling in 18 voices of polyphony. *ZMC-01 card A blank RAM PCMCIA card *ZSC-01 card A PCMCIA card containing 256 programs, 32 multisets and 15 arpeggio patterns. Synthesis Algorithms The MOSS system, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribbon Controller
A ribbon or riband is a thin band of material, typically cloth but also plastic or sometimes metal, used primarily as decorative binding and tying. Cloth ribbons are made of natural materials such as silk, cotton, and jute and of synthetic materials, such as polyester, nylon, and polypropylene. Ribbon is used for useful, ornamental, and symbolic purposes. Cultures around the world use ribbon in their hair, around the body, and as ornament on non-human animals, buildings, and packaging. Some popular fabrics used to make ribbons are satin, organza, sheer, silk, velvet, and grosgrain. Etymology The word ribbon comes from Middle English ''ribban'' or ''riban'' from Old French ''ruban'', which is probably of Germanic origin. Cloth Along with that of tapes, fringes, and other smallwares, the manufacture of cloth ribbons forms a special department of the textile industries. The essential feature of a ribbon loom is the simultaneous weaving in one loom frame of two or more webs, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Architecture
Open architecture is a type of computer architecture or software architecture intended to make adding, upgrading, and swapping components with other computers easy. For example, the IBM PC, Amiga 500 and Apple IIe have an open architecture supporting plug-in cards, whereas the Apple IIc computer has a closed architecture. Open architecture systems may use a standardized system bus such as S-100, PCI or ISA or they may incorporate a proprietary bus standard such as that used on the Apple II, with up to a dozen slots that allow multiple hardware manufacturers to produce add-ons, and for the user to freely install them. By contrast, closed architectures, if they are expandable at all, have one or two "expansion ports" using a proprietary connector design that may require a license fee from the manufacturer, or enhancements may only be installable by technicians with specialized tools or training. Computer platforms may include systems with both open and closed architectures. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synclavier
The Synclavier is an early digital synthesizer, polyphonic digital sampling system, and music workstation manufactured by New England Digital Corporation of Norwich, Vermont. It was produced in various forms from the late 1970s into the early 1990s. The instrument has been used by prominent musicians. History The original design and development of the Synclavier prototype occurred at Dartmouth College with the collaboration of Jon Appleton, Professor of Digital Electronics, Sydney A. Alonso, and Cameron Jones, a software programmer and student at Dartmouth's Thayer School of Engineering. Synclavier I First released in 1977–78, it proved to be highly influential among both electronic music composers and music producers, including Mike Thorne, an early adopter from the commercial world, due to its versatility, its cutting-edge technology, and distinctive sounds. The early Synclavier I used FM synthesis, re-licensed from Yamaha, and was sold mostly to universities. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamaha DX7
The Yamaha DX7 is a synthesizer manufactured by the Yamaha Corporation from 1983 to 1989. It was the first successful digital synthesizer and is one of the best-selling synthesizers in history, selling more than 200,000 units. In the early 1980s, the synthesizer market was dominated by analog synthesizers. Frequency modulation synthesis, FM synthesis, a means of generating sounds via frequency modulation, was developed by John Chowning at Stanford University, California. FM synthesis created brighter, "glassier" sounds, and could better imitate acoustic sounds such as brass. Yamaha licensed the technology to create the DX7, combining it with very-large-scale integration chips to lower manufacturing costs. With its complex menus and lack of conventional controls, few learned to program the DX7 in depth. However, its preset sounds became staples of 1980s pop music, used by artists including A-ha, Kenny Loggins, Kool & the Gang, Whitney Houston, Chicago (band), Chicago, Phil Collin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
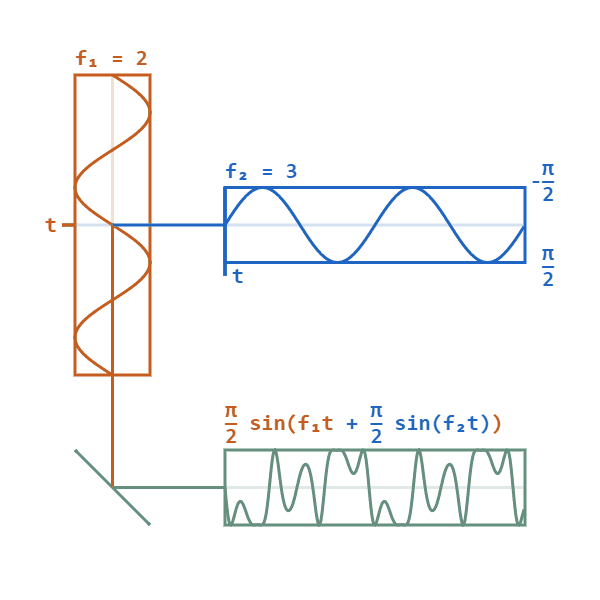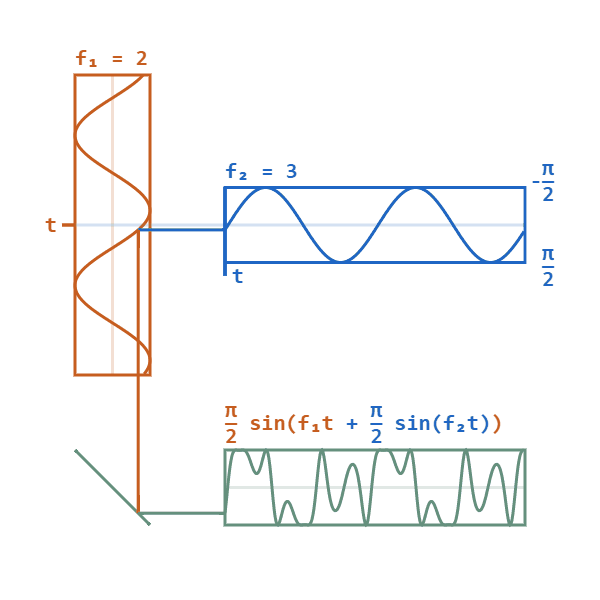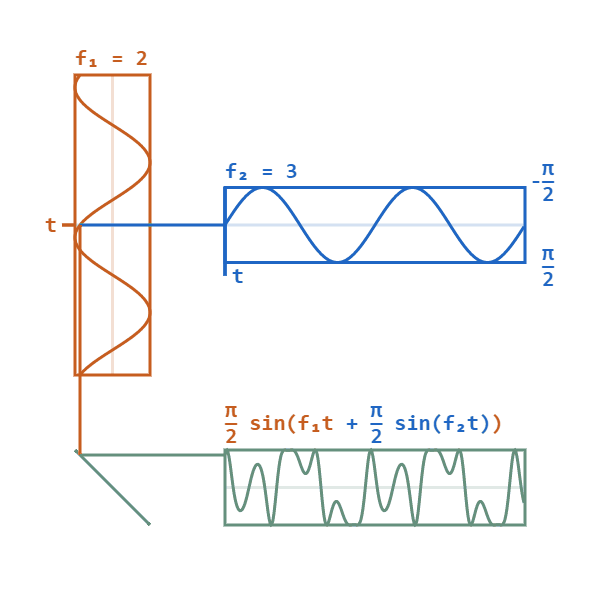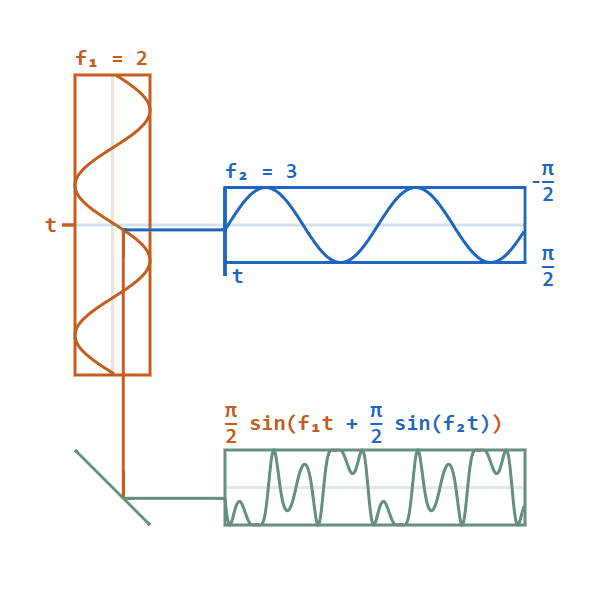
Frequency Modulation Synthesis
Frequency modulation synthesis (or FM synthesis) is a form of sound synthesis whereby the frequency of a waveform is changed by modulating its frequency with a modulator. The frequency of an oscillator is altered "in accordance with the amplitude of a modulating signal". FM synthesis can create both harmonic and inharmonic sounds. To synthesize harmonic sounds, the modulating signal must have a harmonic relationship to the original carrier signal. As the amount of frequency modulation increases, the sound grows progressively complex. Through the use of modulators with frequencies that are non-integer multiples of the carrier signal (i.e. inharmonic), inharmonic bell-like and percussive spectra can be created. FM synthesis using analog oscillators may result in pitch instability. However, FM synthesis can also be implemented digitally, which is more stable and became standard practice. Digital FM synthesis (implemented as phase modulation) was the basis of several musical instru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Modulation
Phase modulation (PM) is a modulation pattern for conditioning communication signals for transmission. It encodes a message signal as variations in the instantaneous phase of a carrier wave. Phase modulation is one of the two principal forms of angle modulation, together with frequency modulation. In phase modulation, the instantaneous amplitude of the baseband signal modifies the phase of the carrier signal keeping its amplitude and frequency constant. The phase of a carrier signal is modulated to follow the changing signal level (amplitude) of the message signal. The peak amplitude and the frequency of the carrier signal are maintained constant, but as the amplitude of the message signal changes, the phase of the carrier changes correspondingly. Phase modulation is widely used for transmitting radio waves and is an integral part of many digital transmission coding schemes that underlie a wide range of technologies like Wi-Fi, GSM and satellite television. It is also used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
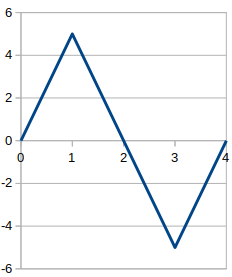
Triangle Wave
A triangular wave or triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape. It is a periodic, piecewise linear, continuous real function. Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics. However, the higher harmonics roll-off, roll off much faster than in a square wave (proportional to the inverse square of the harmonic number as opposed to just the inverse). Definitions Definition A triangle wave of period ''p'' that spans the range [0,1] is defined as: x(t)= 2 \left, \frac - \left \lfloor \frac + \frac \right \rfloor \ where \lfloor\,\ \rfloor is the Floor and ceiling functions, floor function. This can be seen to be the absolute value of a shifted sawtooth wave. For a triangle wave spanning the range the expression becomes: x(t)= 2 \left , 2 \left ( \frac - \left \lfloor + \right \rfloor \right) \right , - 1. A more general equation for a triangle wave with amplitude a and period p using the modulo operation and absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Wave
A pulse wave or pulse train is a type of non-sinusoidal waveform that includes square waves (duty cycle of 50%) and similarly periodic but asymmetrical waves (duty cycles other than 50%). It is a term used in synthesizer programming, and is a typical waveform available on many synthesizers. The exact shape of the wave is determined by the duty cycle or pulse width of the oscillator output. In many synthesizers, the duty cycle can be modulated (pulse-width modulation) for a more dynamic timbre.Reid, Gordon (February 2000). Synth Secrets: Modulation, ''SoundOnSound.com''. Retrieved May 4, 2018. The pulse wave is also known as the rectangular wave, the periodic version of the rectangular function. The average level of a rectangular wave is also given by the duty cycle, therefore by varying the on and off periods and then averaging these said periods, it is possible to represent any value between the two limiting levels. This is the basis of pulse-width modulation. Frequency-do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawtooth Wave
The sawtooth wave (or saw wave) is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based on its resemblance to the teeth of a plain-toothed saw with a zero rake angle. A single sawtooth, or an intermittently triggered sawtooth, is called a ramp waveform. The convention is that a sawtooth wave ramps upward and then sharply drops. In a reverse (or inverse) sawtooth wave, the wave ramps downward and then sharply rises. It can also be considered the extreme case of an asymmetric triangle wave. The equivalent piecewise linear functions x(t) = t - \lfloor t \rfloor x(t) = t \bmod 1 based on the floor function of time ''t'' is an example of a sawtooth wave with period 1. A more general form, in the range −1 to 1, and with period ''p'', is 2\left( - \left\lfloor + \right\rfloor\right) This sawtooth function has the same phase as the sine function. While a square wave is constructed from only odd harmonics, a sawtooth wave's sound is harsh and clear and its spectrum contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Modeling Synthesizer
An analog modeling synthesizer is a synthesizer that generates the sounds of traditional analog synthesizers using digital signal processing, DSP components and software algorithms. Analog modeling synthesizers simulate the behavior of the original electronic circuitry in order to digitally replicate their tone. This method of synthesis is also referred to as ''virtual analog'' or VA. Analog modeling synthesizers can be more reliable than their true analog counterparts since the oscillator pitch is ultimately maintained by a digital clock, and the digital hardware is typically less susceptible to temperature changes. While analog synthesizers need an oscillator circuit for each voice of polyphony, analog modeling synthesizers do not face this problem. This means that many of them, especially the more modern models, can produce as many polyphonic voices as the CPU on which they run can handle. Modeling synths also provide patch storage capabilities and MIDI support not found on mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Modeling Synthesis
Physical may refer to: *Physical examination In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patien ..., a regular overall check-up with a doctor * ''Physical'' (Olivia Newton-John album), 1981 ** "Physical" (Olivia Newton-John song) * ''Physical'' (Gabe Gurnsey album) * "Physical" (Alcazar song) (2004) * "Physical" (Enrique Iglesias song) (2014) * "Physical" (Dua Lipa song) (2020) *"Physical (You're So)", a 1980 song by Adam & the Ants, the B side to " Dog Eat Dog" * ''Physical'' (TV series), an American television series See also {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillators
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term ''vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesirable phenomenon in proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |