Oscillators on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in
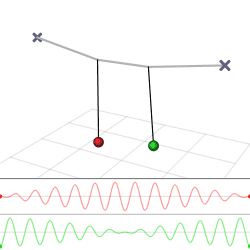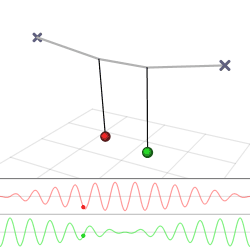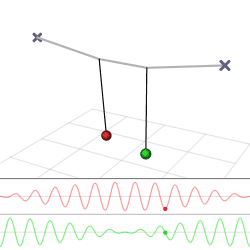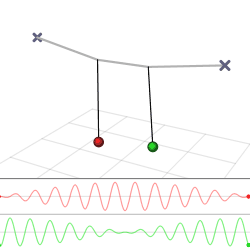
 The harmonic oscillator and the systems it models have a single degree of freedom. More complicated systems have more degrees of freedom, for example, two masses and three springs (each mass being attached to fixed points and to each other). In such cases, the behavior of each variable influences that of the others. This leads to a ''coupling'' of the oscillations of the individual degrees of freedom. For example, two pendulum clocks (of identical frequency) mounted on a common wall will tend to synchronise. This
The harmonic oscillator and the systems it models have a single degree of freedom. More complicated systems have more degrees of freedom, for example, two masses and three springs (each mass being attached to fixed points and to each other). In such cases, the behavior of each variable influences that of the others. This leads to a ''coupling'' of the oscillations of the individual degrees of freedom. For example, two pendulum clocks (of identical frequency) mounted on a common wall will tend to synchronise. This
 Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and event (philosophy), events that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various me ...
, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum
A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so that it can swing freely. When a pendulum is displaced sideways from its resting, equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward th ...
and alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current which periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time in contrast to direct current (DC) which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in whic ...
. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms.
Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics anal ...
, predator–prey
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
population cycles in ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
, geothermal geysers in geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other Astronomical object, astronomical objects, the features or rock (geology), rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology ...
, vibration of strings in guitar
The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected string ...
and other string instrument
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner.
Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the s ...
s, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
. The term ''vibration
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. The word comes from Latin ''vibrationem'' ("shaking, brandishing"). The oscillations may be periodic, such as the motion of a pendulum—or random, su ...
'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation.
Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, may be an undesirable phenomenon in process control and control theory
Control theory is a field of mathematics that deals with the control system, control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the application of system inputs to drive ...
(e.g. in sliding mode control), where the aim is convergence to stable state. In these cases it is called chattering or flapping, as in valve chatter, and route flapping.
Simple harmonic
The simplest mechanical oscillating system is a weight attached to alinear
Linearity is the property of a mathematical relationship ('' function'') that can be graphically represented as a straight line. Linearity is closely related to '' proportionality''. Examples in physics include rectilinear motion, the linear ...
spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a h ...
subject to only weight and tension. Such a system may be approximated on an air table or ice surface. The system is in an equilibrium state when the spring is static. If the system is displaced from the equilibrium, there is a net ''restoring force'' on the mass, tending to bring it back to equilibrium. However, in moving the mass back to the equilibrium position, it has acquired momentum which keeps it moving beyond that position, establishing a new restoring force in the opposite sense. If a constant force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a ...
such as gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stro ...
is added to the system, the point of equilibrium is shifted. The time taken for an oscillation to occur is often referred to as the oscillatory ''period''.
The systems where the restoring force on a body is directly proportional to its displacement, such as the dynamics of the spring-mass system, are described mathematically by the simple harmonic oscillator
In mechanics and physics, simple harmonic motion (sometimes abbreviated ) is a special type of periodic motion of a body resulting from a dynamic equilibrium between an inertial force, proportional to the acceleration of the body away from th ...
and the regular periodic motion is known as simple harmonic motion. In the spring-mass system, oscillations occur because, at the static equilibrium displacement, the mass has kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acce ...
which is converted into potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors.
Common types of potential energy include the gravitational potenti ...
stored in the spring at the extremes of its path. The spring-mass system illustrates some common features of oscillation, namely the existence of an equilibrium and the presence of a restoring force which grows stronger the further the system deviates from equilibrium.
In the case of the spring-mass system, Hooke's law
In physics, Hooke's law is an empirical law which states that the force () needed to extend or compress a spring by some distance () scales linearly with respect to that distance—that is, where is a constant factor characteristic of t ...
states that the restoring force of a spring is:
By using Newton's second law
Newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. These laws can be paraphrased as follows:
# A body remains at rest, or in mo ...
, the differential equation can be derived:
where
The solution to this differential equation produces a sinusoidal position function:
where is the frequency of the oscillation, is the amplitude, and is the phase shift of the function. These are determined by the initial conditions of the system. Because cosine oscillates between 1 and −1 infinitely, our spring-mass system would oscillate between the positive and negative amplitude forever without friction.
Two-dimensional oscillators
In two or three dimensions, harmonic oscillators behave similarly to one dimension. The simplest example of this is anisotropic
Isotropy is uniformity in all orientations; it is derived . Precise definitions depend on the subject area. Exceptions, or inequalities, are frequently indicated by the prefix ' or ', hence '' anisotropy''. ''Anisotropy'' is also used to describ ...
oscillator, where the restoring force is proportional to the displacement from equilibrium with the same restorative constant in all directions.
This produces a similar solution, but now there is a different equation for every direction.
Anisotropic oscillators
With anisotropic oscillators, different directions have different constants of restoring forces. The solution is similar to isotropic oscillators, but there is a different frequency in each direction. Varying the frequencies relative to each other can produce interesting results. For example, if the frequency in one direction is twice that of another, a figure eight pattern is produced. If the ratio of frequencies is irrational, the motion is quasiperiodic. This motion is periodic on each axis, but is not periodic with respect to r, and will never repeat.Damped oscillations
All real-world oscillator systems are thermodynamically irreversible. This means there are dissipative processes such asfriction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of ...
or electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallel ...
which continually convert some of the energy stored in the oscillator into heat in the environment. This is called damping. Thus, oscillations tend to decay with time unless there is some net source of energy into the system. The simplest description of this decay process can be illustrated by oscillation decay of the harmonic oscillator.
Damped oscillators are created when a resistive force is introduced, which is dependent on the first derivative of the position, or in this case velocity. The differential equation created by Newton's second law adds in this resistive force with an arbitrary constant . This example assumes a linear dependence on velocity.
This equation can be rewritten as before:
where .
This produces the general solution:
where .
The exponential term outside of the parenthesis is the decay function and is the damping coefficient. There are 3 categories of damped oscillators: under-damped, where ; over-damped, where ; and critically damped, where .
Driven oscillations
In addition, an oscillating system may be subject to some external force, as when an AC circuit is connected to an outside power source. In this case the oscillation is said to be '' driven''. The simplest example of this is a spring-mass system with a sinusoidal driving force. where This gives the solution: where and The second term of is the transient solution to the differential equation. The transient solution can be found by using the initial conditions of the system. Some systems can be excited by energy transfer from the environment. This transfer typically occurs where systems are embedded in some fluid flow. For example, the phenomenon of flutter inaerodynamics
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dy ...
occurs when an arbitrarily small displacement of an aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or by using the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in ...
wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is e ...
(from its equilibrium) results in an increase in the angle of attack of the wing on the air flow and a consequential increase in lift coefficient, leading to a still greater displacement. At sufficiently large displacements, the stiffness
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force.
The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Calculations
The stiffness, k, of a ...
of the wing dominates to provide the restoring force that enables an oscillation.
Resonance
Resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied periodic force (or a Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an oscil ...
occurs in a damped driven oscillator when ω = ω0, that is, when the driving frequency is equal to the natural frequency of the system. When this occurs, the denominator of the amplitude is minimized, which maximizes the amplitude of the oscillations.
Coupled oscillations

 The harmonic oscillator and the systems it models have a single degree of freedom. More complicated systems have more degrees of freedom, for example, two masses and three springs (each mass being attached to fixed points and to each other). In such cases, the behavior of each variable influences that of the others. This leads to a ''coupling'' of the oscillations of the individual degrees of freedom. For example, two pendulum clocks (of identical frequency) mounted on a common wall will tend to synchronise. This
The harmonic oscillator and the systems it models have a single degree of freedom. More complicated systems have more degrees of freedom, for example, two masses and three springs (each mass being attached to fixed points and to each other). In such cases, the behavior of each variable influences that of the others. This leads to a ''coupling'' of the oscillations of the individual degrees of freedom. For example, two pendulum clocks (of identical frequency) mounted on a common wall will tend to synchronise. This phenomenon
A phenomenon ( : phenomena) is an observable event. The term came into its modern philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be directly observed. Kant was heavily influenced by Gottfrie ...
was first observed by Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists o ...
in 1665. The apparent motions of the compound oscillations typically appears very complicated but a more economic, computationally simpler and conceptually deeper description is given by resolving the motion into normal modes.
The simplest form of coupled oscillators is a 3 spring, 2 mass system, where masses and spring constants are the same. This problem begins with deriving Newton's second law for both masses.
The equations are then generalized into matrix form.
where , , and
The values of and can be substituted into the matrices.
These matrices can now be plugged into the general solution.
The determinant of this matrix yields a quadratic equation.
Depending on the starting point of the masses, this system has 2 possible frequencies (or a combination of the two). If the masses are started with their displacements in the same direction, the frequency is that of a single mass system, because the middle spring is never extended. If the two masses are started in opposite directions, the second, faster frequency is the frequency of the system.
More special cases are the coupled oscillators where energy alternates between two forms of oscillation. Well-known is the Wilberforce pendulum, where the oscillation alternates between the elongation of a vertical spring and the rotation of an object at the end of that spring.
Coupled oscillators are a common description of two related, but different phenomena. One case is where both oscillations affect each other mutually, which usually leads to the occurrence of a single, entrained oscillation state, where both oscillate with a ''compromise frequency''. Another case is where one external oscillation affects an internal oscillation, but is not affected by this. In this case the regions of synchronization, known as Arnold Tongues, can lead to highly complex phenomena as for instance chaotic dynamics.
Small oscillation approximation
In physics, a system with a set of conservative forces and an equilibrium point can be approximated as a harmonic oscillator near equilibrium. An example of this is the Lennard-Jones potential, where the potential is given by: