|
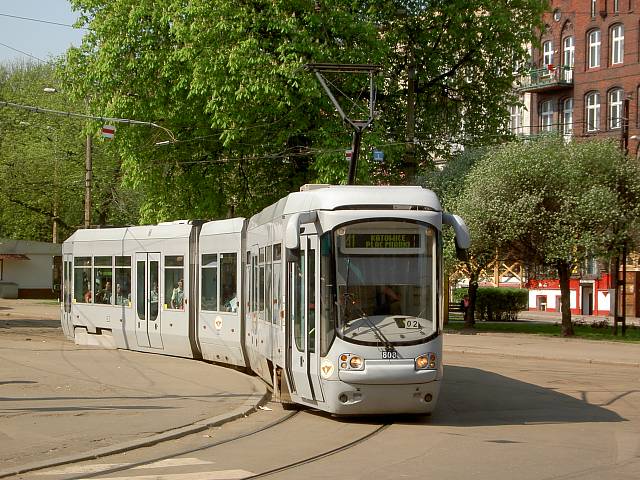
Konstal 102N
Konstal 102N was an electric tram built by Konstal in Chorzów between 1969 and 1970, replacing the Konstal 13N. History Konstal 102N was directly descended from the older 13N produced by Konstal between 1959 and 1969, but, unlike 13N, it was an articulated tram - basically two 13N cars connected by a pivot. Most of the electrical equipment remained unchanged; the body of the tram is where the most dramatic changes were visible. The streamlined design of 13N was replaced by a more boxy shape which made for excellent visibility - unfortunately in daytime only. The large windscreen was tilted is such a way that at night-time it reflected light directly into the driver's eyes making the 102N difficult to drive after dark. This issue was ultimately to prove the downfall of the 102N, as after producing just 42 units the company decided to abandon the 102N project, and in 1970 reverted to the 13N look for the newer 102Na model. Konstal 802N While most of the tram networks in Polan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trams In Warsaw
The Warsaw tram network is a The figure given in the source is of single track, it is assumed that the length of all routes (nearly all of them being double track) is about half that figure. tram system serving a third of Warsaw, Poland, and serving half the city's population. It operates 726 cars, and is the second-largest system in the country (after the Silesian system) There are about 25 regular lines, forming a part of the city's integrated public transport system organized by the Warsaw Transport Authority. Since 1994 the system is operated by the municipally-owned company Tramwaje Warszawskie sp. z.o.o. History Horse tram The history of tram transport in Warsaw dates back to 1866 when a long horse tram line was built to transport goods and passengers between the Vienna Railway Station and the Petersburg and Terespol railway stations across the Vistula River. This was in order to circumvent limitations imposed by Russian authorities, which prevented the constr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal
Alstom Konstal is a company based in Chorzów, Poland producing rail vehicles, in particular metro cars and trams, as well as components for trains. In 1864, the plant was founded as part of the Royal Steelworks in Chorzów and in 1917, it was excluded from its structures as a separate enterprise. During World War II, the factory belonged to the ''Reichswerke Hermann Göring'' produced for the needs of the army of the Third Reich, while during the Communist Period, as the Chorzów Steel Structures Factory Konstal, it was the main supplier of trams for Poland. In 1995, the company's shares were transferred to the National Investment Funds, after which the plant began cooperation with the Linke-Hofmann-Busch factory belonging to the French Alstom concern. In 1997, the company was bought out by Alstom, and a year later, simultaneously with the change of its name to Alstom, the Polish factory adopted its current name. History Origins and beginnings of activity In 1864, the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorzów
Chorzów ( ; ; german: link=no, Königshütte ; szl, Chorzōw) is a city in the Silesia region of southern Poland, near Katowice. Chorzów is one of the central cities of the Upper Silesian Metropolitan Union – a metropolis with a population of 2 million. It is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Rawa River (a tributary of the Vistula). Administratively, Chorzów is in the Silesian Voivodeship since 1999, previously Katowice Voivodeship, and before then, the Silesian Voivodeship. Chorzów is one of the cities of the 2.7 million conurbation – the Katowice urban area and within a greater Silesian metropolitan area with the population of about 5,294,000 people. The population within the city limits is 105,628 as of December 2021. History City name The city of Chorzów was formed in 1934–1939 by a merger of 4 adjacent cities: Chorzów, Królewska Huta, Nowe Hajduki and Hajduki Wielkie. The name of the oldest settlement ''Chorzów'' was applied to the amalgamated c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal 13N
The Konstal 13N was an electric tram built by Konstal in Chorzów between 1959 and 1969 and used in Warsaw until 2012. The design borrowed heavily from the PCC-derived ČKD Tatra T1. History After 1945, the tram networks in most Polish cities relied on small, slow, and outdated Konstal N trams. The N-class trams were intended as a temporary measure to quickly improve the disastrous state of public transport in the aftermath of World War II, and were in fact based on a wartime German design, but all attempts at designing a better tram in Poland ended in failure. In 1955, two Tatra T1 trams were bought by the Warsaw Transport Authority. In 1956, these were sent to the Konstal works in Chorzów for analysis, and formed the basis for the first Konstal prototype called ''11N''. The prototype was then modernized with a redesigned interior, Belgian ACEC electrical equipment, different wheels, and transmission. In 1959, the prototype was put into production as the ''13N''. Passenge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal 102Na
Alstom Konstal is a company based in Chorzów, Poland producing rail vehicles, in particular metro cars and trams, as well as components for trains. In 1864, the plant was founded as part of the Royal Steelworks in Chorzów and in 1917, it was excluded from its structures as a separate enterprise. During World War II, the factory belonged to the ''Reichswerke Hermann Göring'' produced for the needs of the army of the Third Reich, while during the Communist Period, as the Chorzów Steel Structures Factory Konstal, it was the main supplier of trams for Poland. In 1995, the company's shares were transferred to the National Investment Funds, after which the plant began cooperation with the Linke-Hofmann-Busch factory belonging to the French Alstom concern. In 1997, the company was bought out by Alstom, and a year later, simultaneously with the change of its name to Alstom, the Polish factory adopted its current name. History Origins and beginnings of activity In 1864, the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with approximately 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except those in Russia, Finland, and Uzbekistan. The distance between the inside edges of the rails is defined to be 1435 mm except in the United States and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in U.S. customary/Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches" which is equivalent to 1435.1mm. History As railways developed and expanded, one of the key issues was the track gauge (the distance, or width, between the inner sides of the rails) to be used. Different railways used different gauges, and where rails of different gauge met – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Konstal 803N
Alstom Konstal is a company based in Chorzów, Poland producing rail vehicles, in particular metro cars and trams, as well as components for trains. In 1864, the plant was founded as part of the Royal Steelworks in Chorzów and in 1917, it was excluded from its structures as a separate enterprise. During World War II, the factory belonged to the ''Reichswerke Hermann Göring'' produced for the needs of the army of the Third Reich, while during the Communist Period, as the Chorzów Steel Structures Factory Konstal, it was the main supplier of trams for Poland. In 1995, the company's shares were transferred to the National Investment Funds, after which the plant began cooperation with the Linke-Hofmann-Busch factory belonging to the French Alstom concern. In 1997, the company was bought out by Alstom, and a year later, simultaneously with the change of its name to Alstom, the Polish factory adopted its current name. History Origins and beginnings of activity In 1864, the P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trams In Kraków
The Kraków tram system is a tram system in Kraków, Poland. The tramway has been in operation since 1882, and is currently operated by (MPK Kraków). There are 22 ordinary, 2 fast, and 3 night tram lines with a total line length of . , the total route length of the tramway was , including a tram tunnel with two underground stops.Budowa podziemnego tunelu dla linii Krakowskiego Szybkiego Tramwaju , "Construction of Kraków Fast Tram tunnel" (Polish) History 
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trams In Poznań
The Poznań tram system is a tramway operated by (MPK Poznań; ''Public Transport Company in Poznań Ltd.''). It currently has 20 daytime lines, one night line, and one tourist line served by historical vehicles. The tram system consists of about of route, operating on track. With a few exceptions the tramlines operate on double tracks rail. In local Poznań dialect trams are called ''bimby'' (pl.), ''bimba'' (sing). History Horse trams (1880-1898) The idea of trams in Poznań was brought to fruition by two businessmen from Berlin: Otto Reymer and Otto Masch. After receiving concessions from the town authorities on 30 July 1880 they began running a horse tram in Poznań. On the next day the first regular line transported passengers from the main train station via ul. Św. Marcin/St. Martin Str., ul. Rycerska/Ritter Str. (today ul. Ratajczaka), Pl. Wilhelmowski/Wilhelms Platz (currently Plac Wolności) to Rynek/Ring (currently Stary Rynek en, Old Market). The route was soon l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trams In Wrocław
The Wrocław tram system ( pl, Tramwaje we Wrocławiu) is the tram system in Wrocław, Poland. Having first opened for service on 10 July 1877 with horsecars, it is the third oldest tramway in Poland (after Warsaw and Szczecin). The system uses . and is operated by ''Miejskie Przedsiębiorstwo Komunikacyjne we Wrocławiu (MPK Wrocław)''. The network consists of 23 lines with a total track length of and line length of , six depots and 20 loops. Network Below is a table of permanent routes as of the 6 June 2022 schedule: There are plans for future lines to the Popowice and Maślice districts. The 3.8 km Popowice segment is planned to follow the Długa, Starogroblowa and Popowicka streets. The Maślicka line will start at the Municipal Stadium (Stadion Miejski) and continue to the intersection of Maślicka street with Główna and Królewiecka. Rolling stock Currently 7 types of trams are operating in Wrocław: Konstal 105Na, Protram 204 WrAs, Protram 205 WrAs, Škoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
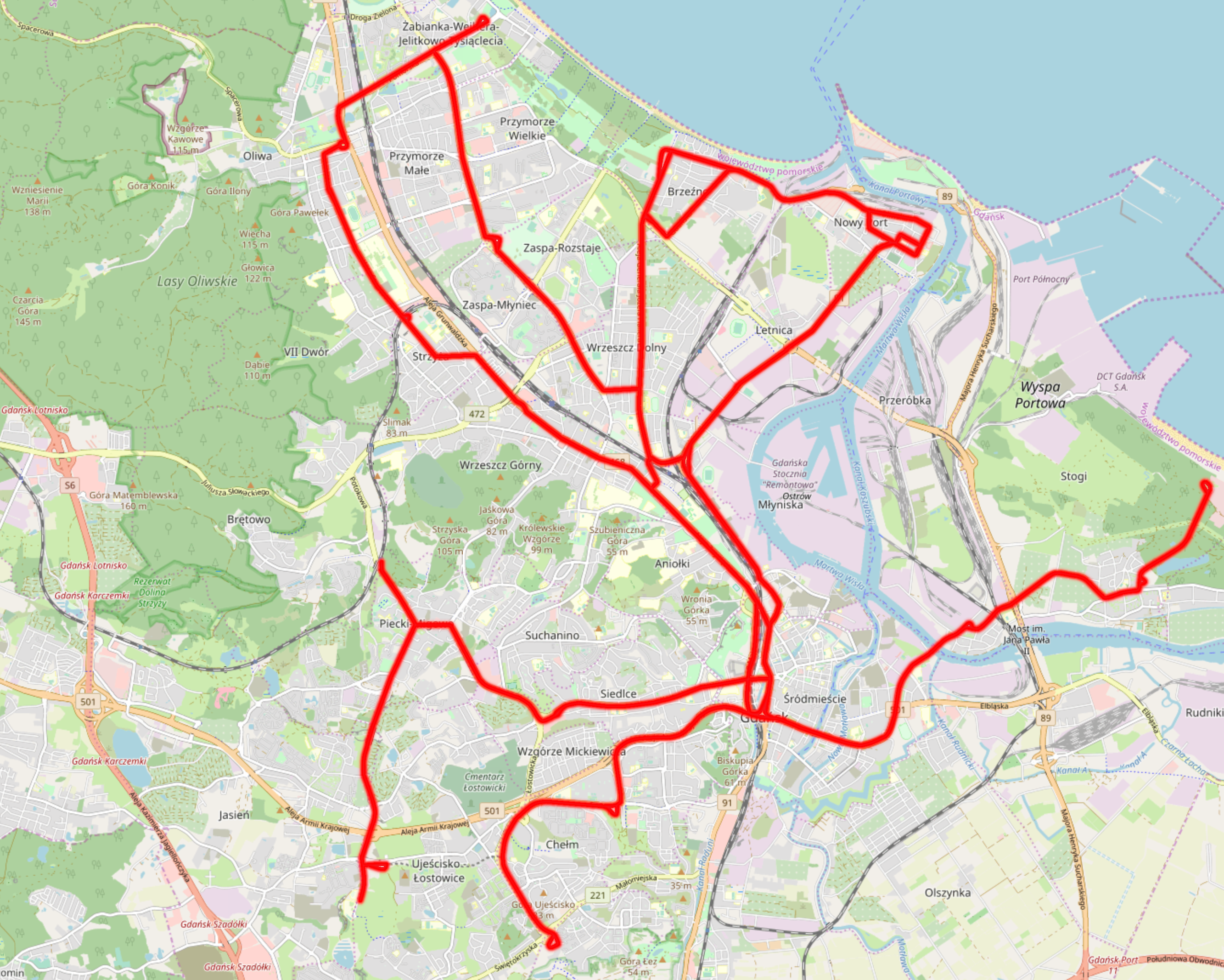
Trams In Gdańsk
The Gdańsk tram system is a tram network in Gdańsk, Poland that has been in operation since 1873. The tramway is operated by (GAiT) and managed by the (ZTM Gdańsk). There are 11 lines with a total line length of . The system operates on track. Background The route length of the tramway network is . The total track length is . The trams are powered using direct current at 600 V. Network characteristics The entire network is located within the administrative borders of the city of Gdańsk. The tracks are separated from road traffic at 85% of their length. Most of the network is double track. There are single track sections in the Brzeźno and Nowy Port districts functioning as balloon loops. The tramway network primarily covers the Dolny Taras and Śródmieście, and also links Wyspa Portowa and Siedlce. In 2007, the network was expanded to Chełm, and in 2012, it was expanded to Łostowice and Orunia Górna via Ujeścisko. In 2015 trams started running to Piecki-Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesian Interurbans
Silesian Trams ( pl, Tramwaje Konurbacji Śląskiej) is one of the largest tram systems in the world and the largest and longest tram system in Poland, located entirely within the Silesian Voivodeship. Started as a part of the German Empire in 1894, the system currently has 677 stops across 29 lines and serves the region’s population inhabited by more than two million people. Silesian Trams is at the heart of a region known for its dense historical and current industrialisation (coal, coke (fuel), coke, steel and other industries). Due to the deindustrialization since the 1990s and subsequent lack of investment, several branches were decommissioned in waves. The system runs on a mixture of Street running, on-street track shared with other traffic and reserved track sections segregated from other traffic. The network is spread over more than 50 kilometres (east-west axis) and covers thirteen towns in the Upper Silesia metropolitan area of southern Poland: Katowice, the capital t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |