|
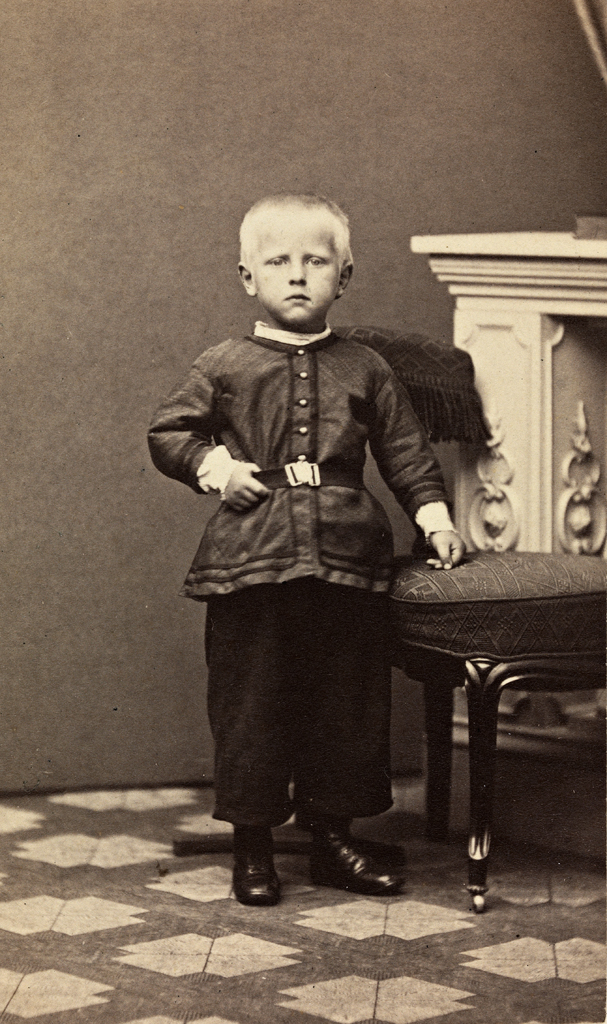
Komsomolskaya Pravda Islands
The Komsomolskaya Pravda Islands (russian: Острова Комсомольской Правды, ''Ostrova Komsomol'skoy Pravdy'') are an archipelago in the far north of the Russian Federation. The islands are uninhabited and are covered with tundra vegetation, shingle and ice. The climate in these islands and the surrounding waters is extremely severe with frequent gales and blizzards in the winter. The sea surrounding the archipelago is covered with fast ice most of the year and is obstructed by pack ice even in the summer. Etymology The island group was known as Saint Samuel Islands (named after Samuel the Confessor) before the 1917 Russian Revolution and then they were renamed after Komsomolskaya Pravda, being for a while the only island group in the world named after a newspaper. This situation lasted only until the Izvesti Tsik Islands were given their name after newspaper Izvestia. The original name of the islands, "Samuila", was retained for one of the islands of the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
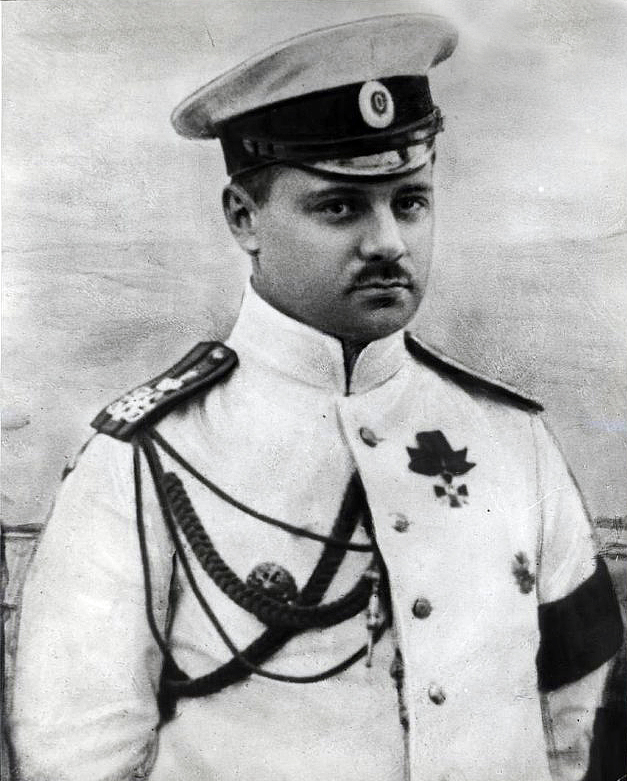
Boris Vilkitsky
Boris Andreyevich Vilkitsky (russian: Бори́с Андре́евич Вильки́цкий) (22 March (3 April N.S.) 1885, Pulkovo – 6 March 1961) was a Russian hydrographer and surveyor. He was the son of Andrey Ippolitovich Vilkitsky. Career Born in Pulkovo, Tsarskoselsky Uyezd (now part of Saint Petersburg), Vilkitsky graduated from the Naval Academy in Saint Petersburg in 1908. He participated in the Russo-Japanese War of 1904–1905. In 1913—1915 he led the Arctic hydrographic expedition on the ships ''"Taimyr"'' and ''"Vaigach"'' with the purpose of further exploration of the Northern Sea Route. In 1913, Vilkitsky's expedition discovered Emperor Nicholas II Land (russian: Земля Императора Николая II, ''Zemlya Imperatora Nikolaya II'') —later renamed 'Severnaya Zemlya', perhaps one of the most important Russian discoveries in the Arctic at the time. Other discoveries were an island that now bears his name ( Vilkitsky Island), as well as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiksi
Tiksi ( rus, Ти́кси, , ˈtʲiksʲɪ; sah, Тиксии, ''Tiksii'' – lit. ''a moorage place'') is an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) and the administrative center of Bulunsky District in the Sakha Republic, Russia, located on the shore of the Buor-Khaya Gulf of the Laptev Sea, southeast of the delta of the Lena River. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 5,063. Tiksi is the northernmost port of Russia. History In August 1901, Russian Arctic ship '' Zarya'' headed across the Laptev Sea, searching for the legendary Sannikov Land but was soon blocked by floating drift ice in the New Siberian Islands. During 1902, the attempts to reach Sannikov Land continued while ''Zarya'' was trapped in fast ice. Leaving the ship, Russian Arctic explorer Baron Eduard Toll and three companions vanished forever in November 1902 while traveling away from Bennett Island towards the south on loose ice floes. ''Zarya'' was finally moored close to Brusneva Island in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krasin (1917 Icebreaker)
The first icebreaker ''Krassin'', or ''Krasin'', (russian: Красин) was built for the Imperial Russian Navy as ''Svyatogor''. She had a long, distinguished career in rescue operations, as well as a pathfinder and explorer of the Northern Sea Route. She has been fully restored to operating condition and is now a museum ship in Saint Petersburg. History The icebreaker was built by Armstrong Whitworth in Newcastle upon Tyne under the supervision of Yevgeny Zamyatin. (updates articles by Myers published in '' Slavonic and East European Review'') The vessel was launched as the '' Svyatogor'' on 3 August 1916 and completed in February 1917. Up to the beginning of the 1950s she remained the most powerful icebreaker in the world. During the allied intervention against the Bolsheviks in Northern Russia (1918–19) she was scuttled by Bolshevik forces to block the port at Arkhangelsk. The Royal Navy raised her for use in the White Sea and later brought her to England. Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakut ASSR
The Yakut Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (russian: Якутская Автономная Советская Социалистическая Республика, ''Yakutskaya Avtonomnaya Sovetskaya Sotsialisticheskaya Respublika''; sah, Саха автономнай сэбиэскэй социалистическэй республиката, ''Sakha avtonomnay sebieskey sotsialistichyeskey ryespublikata''), Soviet Yakutia, or the Yakut ASSR (, ''Yakutskaya ASSR''), was an autonomous republic of the Russian SFSR within the Soviet Union. History It was created on April 27 1922, during the Yakut revolt, and was transformed into the Sakha Republic Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia),, is the largest republic of Russia, located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of roughly 1 million. Sakha comprises half of the area of its governing Far Eas ... in 1991. See also * First Secretary of the Yakut Communist Party Notes Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lena River
The Lena (russian: Ле́на, ; evn, Елюенэ, ''Eljune''; sah, Өлүөнэ, ''Ölüöne''; bua, Зүлхэ, ''Zülkhe''; mn, Зүлгэ, ''Zülge'') is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean (the other two being the Ob and the Yenisey). Permafrost underlies most of the catchment, 77% of which is continuous. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . The Lena is the eleventh-longest river in the world, and the longest river entirely within Russia. Course Originating at an elevation of at its source in the Baikal Mountains south of the Central Siberian Plateau, west of Lake Baikal, the Lena flows northeast across the Lena-Angara Plateau, being joined by the Kirenga, Vitim and Olyokma. From Yakutsk it enters the Central Yakutian Lowland and flows north until joined by its right-hand tributary the Aldan and its most important left-hand tributary, the Vilyuy. After that, it bends westward and northward, flowing between the K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Sea Route
The Northern Sea Route (NSR) (russian: Се́верный морско́й путь, ''Severnyy morskoy put'', shortened to Севморпуть, ''Sevmorput'') is a shipping route officially defined by Russian legislation as lying east of Novaya Zemlya and specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from the Kara Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait. To be more precise, The Northern Sea Route crosses the seas of the Arctic Ocean (Kara Sea, Laptev Sea, East Siberian Sea, and Chukchi Sea). Administratively, in the west the NSR is bounded by the western entrances to the Novaya Zemlya straits and by the meridian running north from Cape Zhelaniya, and in the east, in the Bering Strait, it is bounded by the parallel of 66 ° N and the meridian of 168 ° 58′37 ″ W. The entire route lies in Arctic waters and within Russia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). Parts are free of ice for only two months per year. The overall route on Russia's side of the Arctic between No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Directorate Of The Northern Sea Route
The Chief Directorate of the Northern Sea Route (russian: Главное Управление Северного Морского Пути , translit=Glavnoe upravlenie Severnogo morskogo puti), also known as Glavsevmorput or GUSMP (russian: ГУСМП), was a Soviet government organization in charge of the maritime Northern Sea Route, established in January 1932 and dissolved in 1964. History The organization traces its roots to AO Komseverput (russian: Комитет Северного морского пути , translit= Komitet Severnogo morskogo puti) or KSMP, a shipping company established by the Kolchak government in 1919 and subsequently nationalized by the Bolsheviks. In May 1931 AO Komseverput was reorganized into VO Glavkomseverput; the organization employed 35,000 men scattered all over Arctic, as well as a sizable staff in Moscow and in other mainland cities. A new office, Glavsevmorput, was established in December 1932 and absorbed VO Glavkomseverput in May 1933. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasili Pronchishchev
Vasili Vasilyevich Pronchishchev (russian: Василий Васильевич Прончищев) (1702–) was a Russian explorer. In 1718, Vasili Pronchishchev graduated from Moscow School of Mathematics and Navigation and was promoted to naval cadet. In 1733, he was promoted to the rank of lieutenant and appointed head of one of the units of the Second Kamchatka Expedition, the purpose of which was to map the shores of the Arctic Ocean from the mouth of the Lena to the mouth of the Yenisey. In 1735, Vasili Pronchishchev went down the Lena River (from Yakutsk) on his sloop ''Yakutsk'', doubled its delta, and stopped for wintering at the mouth of the Olenek River. Many members of the crew fell ill and died, mainly owing to scurvy. Despite the difficulties, in 1736, he reached the eastern shore of the Taymyr Peninsula and went north along its coastline. Finally Pronchishchev and his wife Maria (also referred to as Tatyana Feodorovna) succumbed to scurvy and died on the way back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fram (ship)
''Fram'' ("Forward") is a ship that was used in expeditions of the Arctic and Antarctic regions by the Norwegian explorers Fridtjof Nansen, Otto Sverdrup, Oscar Wisting, and Roald Amundsen between 1893 and 1912. It was designed and built by the Scottish-Norwegian shipwright Colin Archer for Fridtjof Nansen's 1893 Arctic expedition in which the plan was to freeze ''Fram'' into the Arctic ice sheet and float with it over the North Pole. ''Fram'' is preserved as a museum ship at the Fram Museum in Oslo, Norway. Construction Nansen's ambition was to explore the Arctic farther north than anyone else. To do that, he would have to deal with a problem that many sailing on the polar ocean had encountered before him: the freezing ice could crush a ship. Nansen's idea was to build a ship that could survive the pressure, not by pure strength, but because it would be of a shape designed to let the ice push the ship up, so it would "float" on top of the ice. ''Fram'' is a three-masted sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fridtjof Nansen
Fridtjof Wedel-Jarlsberg Nansen (; 10 October 186113 May 1930) was a Norwegian polymath and Nobel Peace Prize laureate. He gained prominence at various points in his life as an explorer, scientist, diplomat, and humanitarian. He led the team that made the first crossing of the Greenland interior in 1888, traversing the island on cross-country skis. He won international fame after reaching a record northern latitude of 86°14′ during his ''Fram'' expedition of 1893–1896. Although he retired from exploration after his return to Norway, his techniques of polar travel and his innovations in equipment and clothing influenced a generation of subsequent Arctic and Antarctic expeditions. Nansen studied zoology at the Royal Frederick University in Christiania and later worked as a curator at the University Museum of Bergen where his research on the central nervous system of lower marine creatures earned him a doctorate and helped establish neuron doctrine. Later, neuroscientist Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |