|
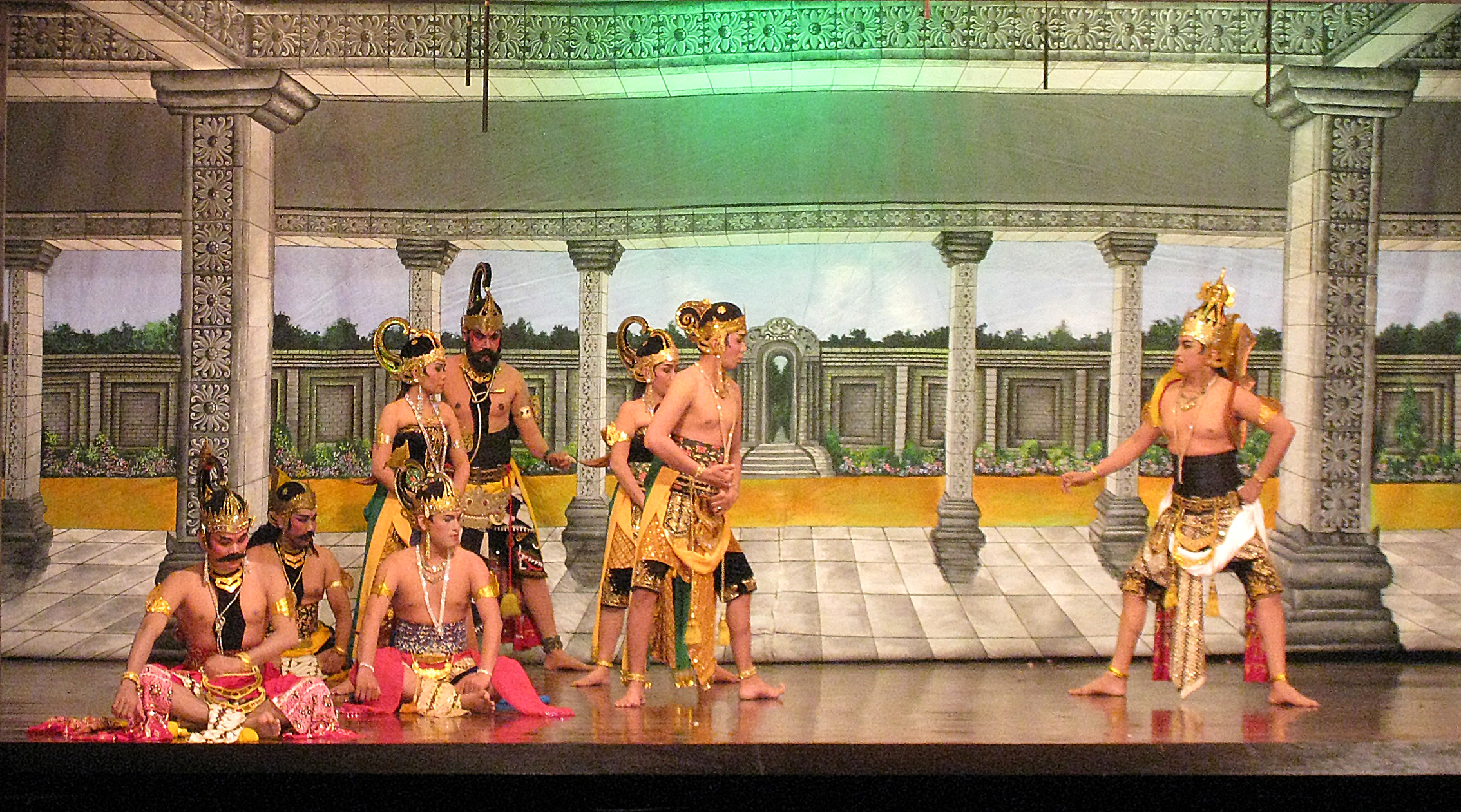
Komedi Stambul
''Komedi Stambul'' (or simply ''Stambul''), spelled ''Komedie Stamboel'' during the Dutch colonial era, is a form of trans-ethnic Indonesian folk theatre developed lately 19th-century to the mid 20th-century. The theatre originated in Dutch East Indies (modern-day Indonesia). ''Stambul'' drew inspiration from a variety of styles including Malay, Western, and Chinese opera as well as Middle Eastern music and operetta. See also *''Toneel ''Toneel'' (Dutch word for: "theatre") is a genre of theatrical drama performance developed in early 20th-century Dutch East Indies (modern-day Indonesia). Compared to earlier native musical dramas, such as the Malay ''bangsawan'' and ''Kome ...'' References {{Indonesian drama and theatre Indonesian culture Theatre in Indonesia Traditional drama and theatre of Indonesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture Of Indonesia
The culture of Indonesia has been shaped by long interaction between original indigenous customs and multiple foreign influences. Indonesia is centrally-located along ancient trading routes between the Far East, South Asia and the Middle East, resulting in many cultural practices being strongly influenced by a multitude of religions, including Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, and Islam, all strong in the major trading cities. The result is a complex cultural mixture, often different from the original indigenous cultures. Examples of the fusion of Islam with Hinduism include Javanese Abangan belief. Balinese dances have stories about ancient Buddhist and Hindu kingdoms, while Islamic art forms and architecture are present in Sumatra, especially in the Minangkabau and Aceh regions. Traditional art, music and sport are combined in a martial art form called Pencak Silat. The Western world has influenced Indonesia in science, technology and modern entertainment suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors or actresses, to present the experience of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a stage. The performers may communicate this experience to the audience through combinations of gesture, speech, song, music, and dance. Elements of art, such as painted scenery and stagecraft such as lighting are used to enhance the physicality, presence and immediacy of the experience. The specific place of the performance is also named by the word "theatre" as derived from the Ancient Greek θέατρον (théatron, "a place for viewing"), itself from θεάομαι (theáomai, "to see", "to watch", "to observe"). Modern Western theatre comes, in large measure, from the theatre of ancient Greece, from which it borrows technical terminology, classification into genres, and many of its themes, stock characters, and plot elements. Theatre artist Patrice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East Indies
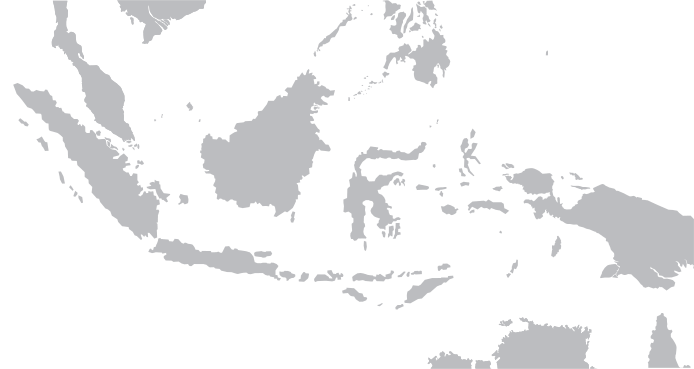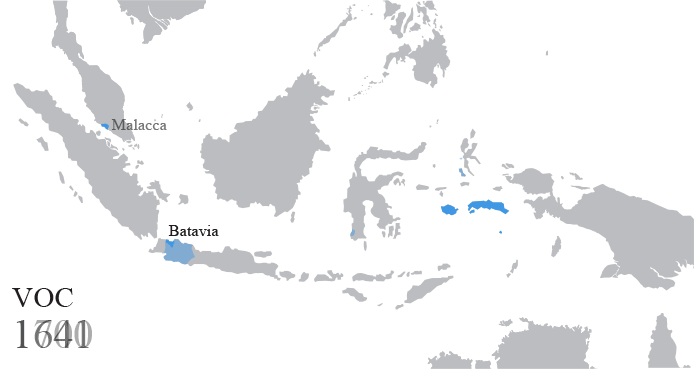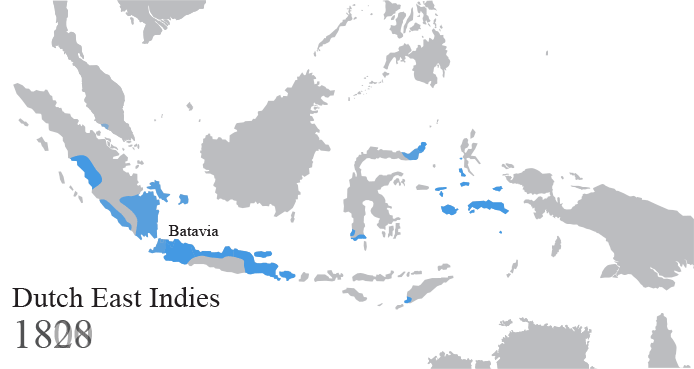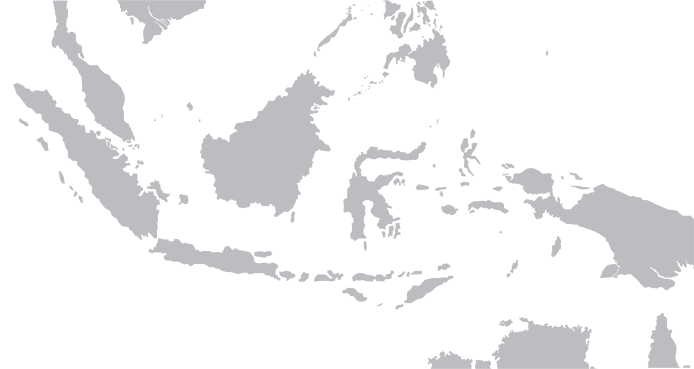
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangsawan
''Bangsawan'' ( Jawi: بڠساون) is a type of traditional Malay opera or theatre performed by a troupe, and accompanied by music and sometimes dances. The ''bangsawan'' theatrical performance encompasses music, dance and drama. It is widely spread in the Malay cultural realm in Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore and Brunei. The artform is indigenous in Malay Peninsula, Riau Islands, Sumatra and coastal Borneo. Etymology In the Malay language, ''bangsawan'' means "nobleman". ''Bangsa'' means "nation", "race", from the Sanskrit word ''vamsa'' which means "family", "dynasty". The suffix -''wan'' comes from the Sanskrit suffix -''vant''. A person is called bangsawan if he is descended from royal family (kings, princes, etc.). The theatre is called ''bangsawan'' because it is most often depicting the legends and stories of Malay nobles that took place in ''istana'' (Malay palaces and courts). There was another category of noblemen in Indonesia, precisely in Java, called ''priyayi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor. Although musical theatre is closely related to opera, the two are considered to be distinct from one another. Opera is a key part of the Western classical music tradition. Originally understood as an entirely sung piece, in contrast to a play with songs, opera has come to include numerous genres, including some that include spoken dialogue such as '' Singspiel'' and '' Opéra comique''. In traditional number opera, singers employ two styles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Opera
Traditional Chinese opera (), or ''Xiqu'', is a form of musical theatre in China with roots going back to the early periods in China. It is an amalgamation of various art forms that existed in ancient China, and evolved gradually over more than a thousand years, reaching its mature form in the 13th century, during the Song dynasty (960–1279). Early forms of Chinese theater are simple, but over time various art forms such as music, song and dance, martial arts, acrobatics, costume and make-up art, as well as literary art forms were incorporated to form traditional Chinese opera. Performers had to practice for many years to gain an understanding of the roles. Exaggerated features and colors made it easier for the audience to identify the roles portrayed. There are over a hundred regional branches of traditional Chinese opera today. In the 20th century the Peking opera emerged in popularity and has come to known as the "national theatre" of China, but other genres like Yue opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Eastern Music
The various nations of the region include the Arabic-speaking countries of the Middle East, the Iranian traditions of Persia, the Jewish music of Israel and the diaspora, Armenian music, Kurdish music, Azeri Music, the varied traditions of Cypriot music, the music of Turkey, traditional Assyrian music, Coptic ritual music in Egypt as well as other genres of Egyptian music in general, and the Andalusian (Muslim Spain) music very much alive in the greater Middle East (North Africa), all maintain their own traditions. It is widely regarded that some Middle-Eastern musical styles have influenced Central Asia, as well as Spain, and the Balkans. Throughout the region, religion has been a common factor in uniting peoples of different languages, cultures and nations. The predominance of Islam allowed a great deal of Arabic, and Byzantine influence to spread through the region rapidly from the 7th century onward. The Arabic scale is strongly melodic, based on various maqamat (sing. maq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operetta
Operetta is a form of theatre and a genre of light opera. It includes spoken dialogue, songs, and dances. It is lighter than opera in terms of its music, orchestral size, length of the work, and at face value, subject matter. Apart from its shorter length, the operetta is usually of a light and amusing character. It sometimes also includes satirical commentaries. "Operetta" is the Italian diminutive of "opera" and was used originally to describe a shorter, perhaps less ambitious work than an opera. Operetta provides an alternative to operatic performances in an accessible form targeting a different audience. Operetta became a recognizable form in the mid-19th century in France, and its popularity led to the development of many national styles of operetta. Distinctive styles emerged across countries including Austria-Hungary, Germany, England, Spain, the Philippines, Mexico, Cuba, and the United States. Through the transfer of operetta among different countries, cultural cosmop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toneel
''Toneel'' (Dutch word for: "theatre") is a genre of theatrical drama performance developed in early 20th-century Dutch East Indies (modern-day Indonesia). Compared to earlier native musical dramas, such as the Malay ''bangsawan'' and ''Komedie Stamboel'', ''toneel'' adapted more European stylings, with an emphasis on spoken dialogue and a reduction in the amount of music used during the performance; thus the genre is called ''toneel'', an adaptation of the Dutch word for theatre. One of the notable ''toneel'' troupe is Dardanella that gain popularity in East Indies back in 1920s. The play is presented in Malay and often featured themes and adaptations derived from popular Hollywood productions for the stage, including '' The Mark of Zorro'', ''The Three Musketeers'' and '' The Thief of Bagdad''. The ''toneel'' drama later influenced the development of film industry in the Dutch East Indies, and also influenced native Indonesian musical dramatic forms such as sandiwara, le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesian Culture
The culture of Indonesia has been shaped by long interaction between original indigenous customs and multiple foreign influences. Indonesia is centrally-located along ancient trading routes between the Far East, South Asia and the Middle East, resulting in many cultural practices being strongly influenced by a multitude of eastern religions, religions, including Buddhism, Christianity, Confucianism, Hinduism, and Islam, all strong in the major trading cities. The result is a complex cultural mixture, often different from the original indigenous cultures. Examples of the fusion of Islam with Hinduism include Javanese Abangan belief. Balinese dances have stories about ancient Buddhist and Hindu Monarchy, kingdoms, while Islamic art forms and architecture are present in Sumatra, especially in the Minangkabau people, Minangkabau and Aceh regions. Traditional art, music and sport are combined in a martial art form called Pencak Silat. The Western world has influenced Indonesia in sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theatre In Indonesia
''Indonesian theatre'' is a type of art in the form of drama performances that are staged on a stage, with a distinct Indonesian nuance or background. In general, theatre is an art that emphasizes the performing arts that are displayed in front of a large crowd. In other words, theater is a form of visualisation of a drama that is staged on the stage and watched by the audience. Indonesian theatre includes the performing arts of traditional theater and modern theatre located in the territory of Indonesia (also called Nusantara). Some examples of Indonesian theater are Arja, Wayang, Wayang wong, Lenong, Ludruk, Janger, Randai and others. Theatre in Indonesia can also be referred to as regional or ethnic theatre, because it originates and develops from 1,300 ethnic cultures in Indonesia. History Theatre performances in Indonesia have been going on for thousands of years. Most of Indonesia's oldest theatre forms are linked directly to local literary traditions (oral and written) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

