|
Known Unknowns
"Known Unknowns" is the seventh episode of the sixth season of ''House'' and 117th overall. It aired on November 9, 2009. The team tries to diagnose a teenage girl while House is away at a medical conference with Wilson and Cuddy. At the conference House finds something out about Cuddy. Plot After a wild night out, a teenage girl named Jordan ( Anna Attanasio) is brought to Princeton Plainsboro with severely swollen appendages. The team must work to diagnose Jordan, who is less than honest about what happened the night she fell ill. House suspects she is suffering from rhabdomyolysis and the fall caused crushed muscles which released toxins that caused swollen joints. But the CT shows no signs of trauma, so House goes in and gets Jordan to pretend to play the drums. Her hands are very weak. House notes that her chart shows low potassium, and rhabdo elevates potassium levels, meaning her potassium had to be extremely low the previous night. This means she can't have climbed stairs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House (TV Series)
''House'' (also called ''House, M.D.'') is an American medical drama television series that originally ran on the Fox network for eight seasons, from November 16, 2004, to May 21, 2012. The series' main character is Dr. Gregory House (Hugh Laurie), an unconventional, misanthropic medical genius who, despite his dependence on pain medication, leads a team of diagnosticians at the fictional Princeton–Plainsboro Teaching Hospital (PPTH) in New Jersey. The series' premise originated with Paul Attanasio, while David Shore, who is credited as creator, was primarily responsible for the conception of the title character. The series' executive producers included Shore, Attanasio, Attanasio's business partner Katie Jacobs, and film director Bryan Singer. It was filmed largely in a neighborhood and business district in Los Angeles County's Westside called Century City. The show received high critical acclaim, and was consistently one of the highest rated series in the United States. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, it is a paramedian symmetrical structure of two halves (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter located in the forebrain which is superior to the midbrain, near the center of the brain, with nerve fibers projecting out to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not all oysters are in the superfamily Ostreoidea. Some types of oysters are commonly consumed (cooked or raw), and in some locales are regarded as a delicacy. Some types of pearl oysters are harvested for the pearl produced within the mantle. Windowpane oysters are harvested for their translucent shells, which are used to make various kinds of decorative objects. Etymology The word ''oyster'' comes from Old French , and first appeared in English during the 14th century. The French derived from the Latin , the feminine form of , which is the latinisation of the Ancient Greek () 'oyster'. Compare () 'bone'. Types True oysters True oysters are members of the family Ostreidae. This family includes the edible oysters, which mainly belong t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
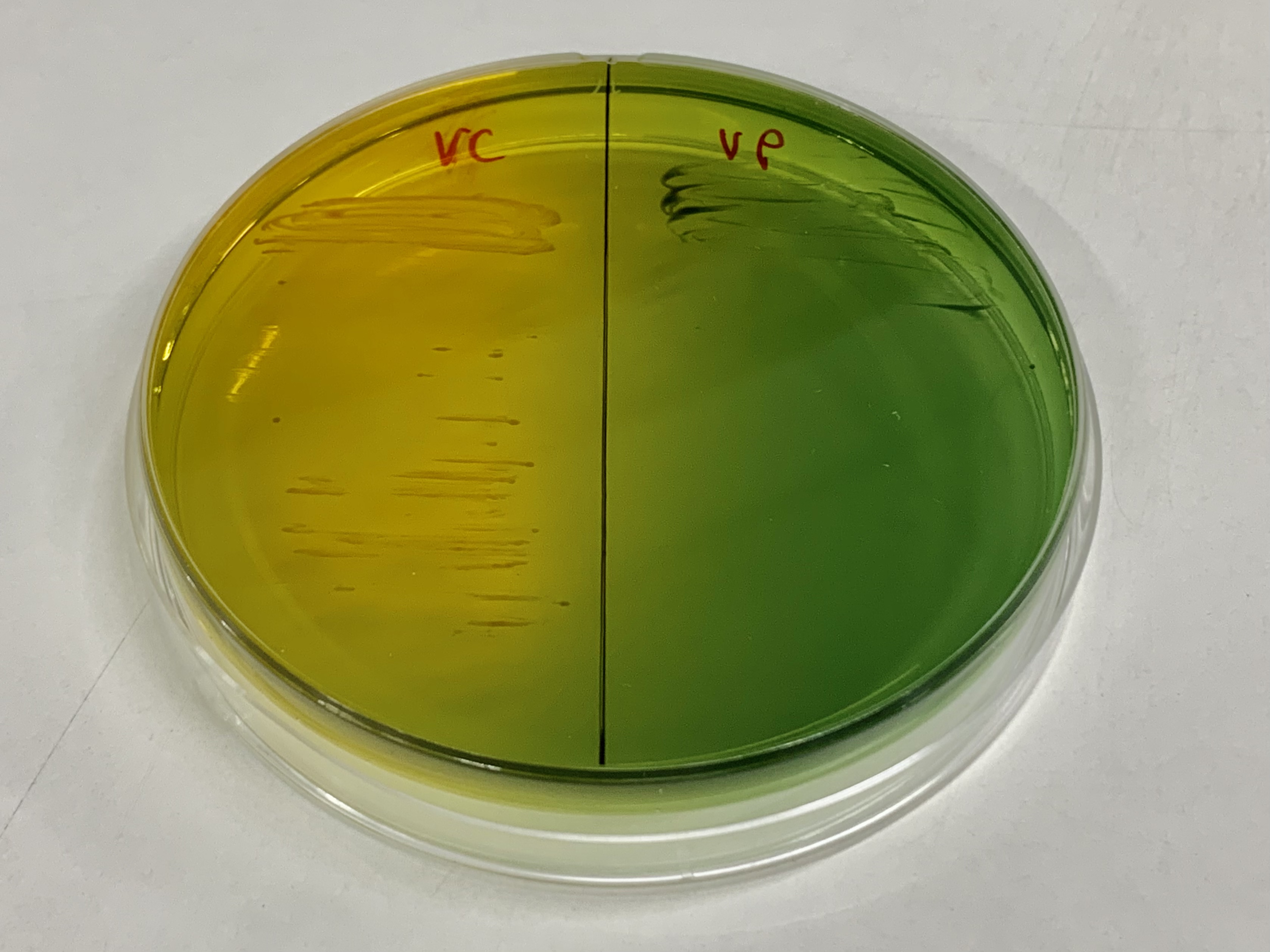
Vibrio
''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive in fresh water, ''Vibrio'' spp. are commonly found in various salt water environments. ''Vibrio'' spp. are facultative anaerobes that test positive for oxidase and do not form spores. All members of the genus are motile. They are able to have polar or lateral flagellum with or without sheaths. ''Vibrio'' species typically possess two chromosomes, which is unusual for bacteria. Each chromosome has a distinct and independent origin of replication, and are conserved together over time in the genus. Recent phylogenies have been constructed based on a suite of genes (multilocus sequence analysis). O. F. Müller (1773, 1786) described eight species of the genus ''Vibrio'' (included in Infusoria), three of which were spirilliforms. Some of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio Vulnificus
''Vibrio vulnificus'' is a species of Gram-negative, motile, curved rod-shaped (bacillus), pathogenic bacteria of the genus ''Vibrio''. Present in marine environments such as estuaries, brackish ponds, or coastal areas, ''V. vulnificus'' is related to '' ''V. cholerae'''', the causative agent of cholera. At least one strain of ''V. vulnificus'' is bioluminescent. Infection with ''V. vulnificus'' leads to rapidly expanding cellulitis or sepsis. It was first isolated as a source of disease in 1976. Signs and symptoms ''Vibrio vulnificus'' is an extremely virulent bacterium that can cause three types of infections: * Acute gastroenteritis from eating raw or undercooked shellfish: ''V. vulnificus'' causes an infection often incurred after eating seafood, especially raw or undercooked oysters. It does not alter the appearance, taste, or odor of oysters. Symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. * Necrotizing wound infections can occur in injured skin exposed to contam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make other illicit drug, illicit opioids. There are numerous methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual administration, sublingual; via inhalation; intramuscular, injection into a muscle; by Subcutaneous injection, injection under the skin; intravenously; Intrathecally, injection into the space around the spinal cord; transdermal; or via rectal administration, rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patient-controlled Analgesia
Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) is any method of allowing a person in pain to administer their own pain relief. The infusion is programmable by the prescriber. If it is programmed and functioning as intended, the machine is unlikely to deliver an overdose of medication. Providers must always observe the first administration of any PCA medication which has not already been administered by the provider to respond to allergic reactions. Routes of administration Oral The most common form of patient-controlled analgesia is self-administration of oral over-the-counter or prescription painkillers. For example, if a headache does not resolve with a small dose of an oral analgesic, more may be taken. As pain is a combination of tissue damage and emotional state, being in control means reducing the emotional component of pain. Intravenous In a hospital setting, an intravenous PCA (IV PCA) refers to an electronically controlled infusion pump that delivers an amount of analgesic whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminal Illness
Terminal illness or end-stage disease is a disease that cannot be cured or adequately treated and is expected to result in the death of the patient. This term is more commonly used for progressive diseases such as cancer, dementia or advanced heart disease than for injury. In popular use, it indicates a disease that will progress until death with near absolute certainty, regardless of treatment. A patient who has such an illness may be referred to as a terminal patient, terminally ill or simply as being terminal. There is no standardized life expectancy for a patient to be considered terminal, although it is generally months or less. Life expectancy for terminal patients is a rough estimate given by the physician based on previous data and does not always reflect true longevity. An illness which is lifelong but not fatal is a chronic condition. Terminal patients have options for disease management after diagnosis. Examples include caregiving, continued treatment, palliative and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euthanasia
Euthanasia (from el, εὐθανασία 'good death': εὖ, ''eu'' 'well, good' + θάνατος, ''thanatos'' 'death') is the practice of intentionally ending life to eliminate pain and suffering. Different countries have different euthanasia laws. The British House of Lords select committee on medical ethics defines euthanasia as "a deliberate intervention undertaken with the express intention of ending a life, to relieve intractable suffering". In the Netherlands and Belgium, euthanasia is understood as "termination of life by a doctor at the request of a patient". The Dutch law, however, does not use the term 'euthanasia' but includes the concept under the broader definition of "assisted suicide and termination of life on request". Euthanasia is categorized in different ways, which include voluntary, non-voluntary, or involuntary. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The term "rickettsia" has nothing to do with rickets (which is a deficiency disease resulting from lack of vitamin D); the bacterial genus ''Rickettsia'' instead was named after Howard Taylor Ricketts, in honor of his pioneering work on tick-borne spotted fever. Properly, ''Rickettsia'' is the name of a single genus, but the informal term "rickettsia", plural "rickettsias", usually not capitalised, commonly applies to any members of the order Rickettsiales. Being obligate intracellular bacteria, rickettsias depend on entry, growth, and replication within the cytoplasm of living eukaryotic host cells (typically endothelial cells). Accordingly, ''Rickettsia'' species cannot grow in artificial nutrient culture; they must be grown either in tissue or embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amobarbital
Amobarbital (formerly known as amylobarbitone or sodium amytal as the soluble sodium salt) is a drug that is a barbiturate derivative. It has sedative- hypnotic properties. It is a white crystalline powder with no odor and a slightly bitter taste. It was first synthesized in Germany in 1923. It is considered a short to intermediate acting barbiturate. If amobarbital is taken for extended periods of time, physiological and psychological dependence can develop. Amobarbital withdrawal mimics delirium tremens and may be life-threatening. Amobarbital was manufactured by Eli Lilly and Company in the US under the brand name Amytal in bright blue bullet shaped capsules (known as Pulvules) or pink tablets (known as Diskets) containing 50, 100, or 200 milligrams of the drug. The drug was also manufactured generically. Amobarbital was widely misused, known as "Blue Heavens" on the street. Amytal, as well as Tuinal, a combination drug containing equal quantities of secobarbital and amob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |