|
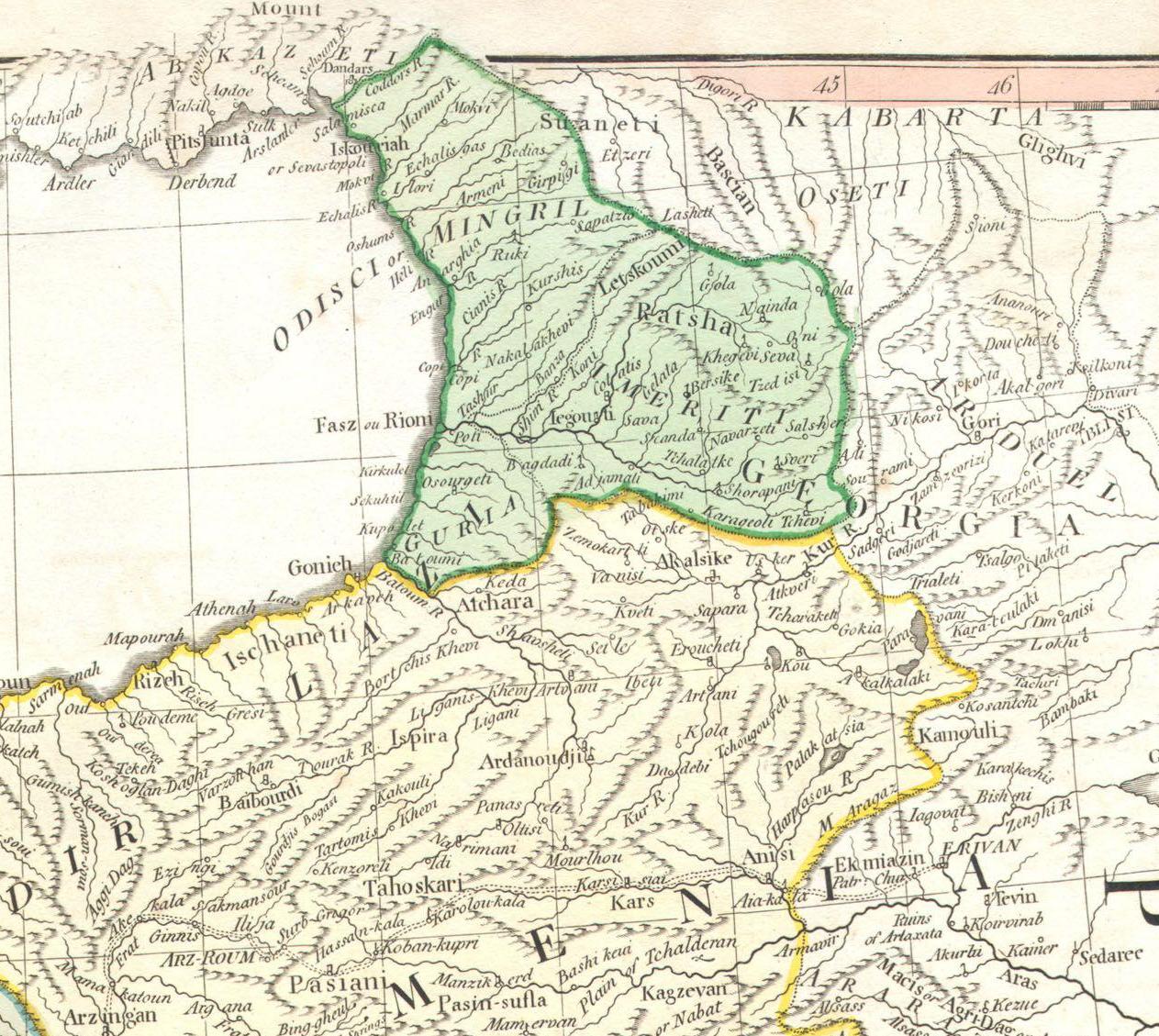
Klarjeti
Klarjeti ( ka, კლარჯეთი ) was a province of ancient and medieval Georgia, which is now part of Turkey's Artvin Province. Klarjeti, the neighboring province of Tao and several other smaller districts, constituted a larger region with shared history and culture conventionally known as Tao-Klarjeti. Early history Klarjeti, traversed by the Chorokhi (Çoruh), stretched from the Arsiani Range westwards, towards the Black Sea, and was centred in the key fortified trading town of Artanuji (now Ardanuç). It was bordered by Shavsheti and Nigali on the north, and Tao on the south. The region roughly corresponds to Cholarzene ( grc, Χολαρζηνή, Καταρζηνή) of Classical sources and probably to Kaţarza or Quturza of the earlier Urartian records.Toumanoff, Cyril (1967). ''Studies in Christian Caucasian History'', p. 442. Georgetown University Press. Klarjeti was one of the south-westernmost provinces of the Kingdom of Iberia, which appeared on the Cauca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumbat I Of Klarjeti
Sumbat I ( ka, სუმბატ I) (died 899) was a Georgian prince of the Bagratid dynasty of Tao-Klarjeti and hereditary ruler of Klarjeti from c. 870 until his death. A son of Adarnase II of Tao-Klarjeti, Sumbat received the province of Klarjeti as an appanage where he ruled with the title of ''mampali'', which seems to have passed on to Sumbat and his progeny after the extinction of the line of Guaram Mampali. He also bore the Byzantine title of patrician (, ανθύπατος πατρίκιος). Sumbat had a residence at Artanuji (modern Ardanuç, Turkey), which towards the end of the 9th century began to develop into a thriving trading centre. Hence comes his territorial epithet Artanujeli (არტანუჯელი), i.e., "of Artanuji". Sumbat is referred to as "the Great" by Constantine Porphyrogenitus, author of ''De Administrando Imperio'', where his name is rendered as Symbatius. Apart from Klarjeti, Sumbat must also have possessed Adjara and Nigali, since th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tao (historical Region)
Tao ( ka, ტაო) is a historical Georgian district and part of historic Tao-Klarjeti region, today part of the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey. Its name derives from the ancient proto-Georgian inhabitants of this area, known as Taochi. History Antiquity The history of Tao could be traced to the emergence of the tribal confederation of Diauchi (Taochi, Tayk, Taochoi, Tao) at 12–8th century BC. Diauchi was engaged in war with the powerful kingdom of Urartu, and the inscriptions of the Urartu kings Menua ( 810–786 BC) and Argishti ( 786–764) reveal the wealth and power of this kingdom, which was possibly proto-Georgian speaking.A. G. Sagona. ''Archaeology at the North-East Anatolian Frontier'', p. 30. In the 8th century BC, Diauchi was destroyed by the neighboring Colchis and Urartu and part of its territory was annexed by the Colchis. In the 4th-3rd centuries BC region was organized into a province of the Iberian Kingdom. The region was bitterly contested by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tao-Klarjeti (historical Region)
Tao-Klarjeti ( ka, ტაო-კლარჯეთი, tr) is a Georgian historical and cultural region in north-eastern Turkey. The region is based around two river basins - Chorokhi and Kura (Mtkvari), and also partially includes the upper source of the Aras river. In modern usage it most often denotes the territory that was administrated or claimed by Georgian Democratic Republic but is nowadays part of Turkey due to the Soviet-Turkish deal in 1921. The term "Tao-Klarjeti" is based on the names of two most important provinces of the region — Tao and Klarjeti. The term is equivalent to “Zemo Kartli” (i.e., Upper Kartli or Upper Iberia) and is also a synonym for historical Meskheti. Cultural and historical heritage Many important Georgian cultural monuments from the middle ages are located on the territory of Tao-Klarjeti and many of them are preserved as ruins. Several monuments of medieval Georgian architecture – abandoned or converted churches, monasteries, bridg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bagrationi Dynasty
The Bagrationi dynasty (; ) is a royal dynasty which reigned in Georgia from the Middle Ages until the early 19th century, being among the oldest extant Christian ruling dynasties in the world. In modern usage, the name of the dynasty is sometimes Hellenized and referred to as the Georgian Bagratids, also known in English as the Bagrations. The origins of the dynasty are disputed. The early Georgian Bagratids gained the Principality of Iberia through dynastic marriage after succeeding the Chosroid dynasty at the end of the 8th century. In 888 Adarnase IV of Iberia restored the Georgian monarchy; various native polities then united into the Kingdom of Georgia, which prospered from the 11th to the 13th century. This period of time, particularly the reigns of David IV the Builder (1089–1125) and of his great-granddaughter Tamar the Great (1184–1213) inaugurated the Georgian Golden Age in the history of Georgia. Montgomery-Massingberd, Hugh. " Burke's Royal Families of the Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javakheti
Javakheti ( ka, ჯავახეთი ) or Javakhk ( hy, Ջավախք, ''Javakhk'') is a historical province in southern Georgia, corresponding to the modern municipalities of Akhalkalaki, Aspindza (partly), Ninotsminda, and partly to the Turkey's Ardahan Province. Historically, Javakheti borders were defined by the Kura River (Mtkvari) to the west, and the Shavsheti, Samsari and Nialiskuri mountains to the north, south and east, respectively. The principal economic activities in this region are subsistence agriculture, particularly potatoes and raising livestock. In 1995, the Akhalkalaki and Ninotsminda districts, comprising the historical territory of Javakheti, were merged with the neighboring land of Samtskhe to form a new administrative region, Samtskhe-Javakheti. As of January 2020, the total population of Samtskhe-Javakheti is 152,100 individuals. Armenians comprise the majority of Javakheti's population. According to the 2014 Georgian census, 93% (41,870) of the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Şavşat
Şavşat ( ka, შავშეთი, tr) is a town and district of Artvin Province in the Black Sea region, between the cities of Artvin and Kars on the border with Georgia at the far eastern end of Turkey. History According to Rayfield, in 790 BC, King Menua of Urartu invaded Shesheti in Kingdom of Diauehi, which is the Kartvelian province of Shavsheti. In 387 this land was a part of Marzpan Iberia (vassal of Iran). After this, in IX century it was one of the Georgian princedoms in the constellation of several polities which is conventionally known as Tao-Klarjeti in Georgian. The princedom of Shavsheti included today's districts of Şavşat, Borçka, and Murgul in Turkey and Lower Machakheli in Adjara (Georgia). The fortress above the town is primarily of Georgian construction and probably dates from the 9th century A.D., when it was rebuilt by Adarnase I of Iberia. The site has an impressive circuit wall with strategically placed towers and rooms, including two small chapel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chosroid Dynasty
The Chosroid dynasty (a Latinization of ''Khosro anni'', ka, ხოსრო ����ანები), also known as the Iberian Mihranids, were a dynasty of the kings and later the presiding princes of the early Georgian state of Iberia from the 4th to the 9th centuries. The family, of Iranian Mihranid origin, accepted Christianity as their official religion (or 319/326), and maneuvered between the Byzantine Empire and Sassanid Iran to retain a degree of independence. After the abolition of the Iberian kingship by the Sassanids c. 580, the dynasty survived in its two closely related, but sometimes competing princely branches—the elder Chosroid and the younger Guaramid—down to the early ninth century when they were succeeded by the Georgian Bagratids on the throne of Iberia. Origins The Chosroids were a branch of the Mihranid princely family, one of the Seven Great Houses of Iran, who were distantly related to the Sasanians, and whose two other branches were soon placed on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigali Valley
Nigali or the Nigali valley ( ka, ნიგალი, ნიგალის ხევი, ''nigalis khevi''), also known, through a subsequent metathesis, as Ligani (ლიგანი) or Livana (ლივანა; tr, Livâne)Toumanoff, Cyril (1963). ''Studies in Christian Caucasian History'', p. 439. Georgetown University Press. is a historical district on the lower course of the Çoruh or Chorokhi river, currently divided between Turkey and Georgia. History The land known as ''Nigal'' first appears as one of the districts of Colchis in the 7th-century Armenian geography attributed to Ananias of Shirak. Hewsen, Robert H. (1992), ''The Geography of Ananias of Širak: Ašxarhac'oyc', the Long and the Short Recensions'', p. 210. Reichert, In the 8th century, Nigali became part of an appanage of the Georgian Bagratid family. It was bounded by Adjara on the north-east, Shavsheti on the east, and Klarjeti on the south. The medieval Georgian sources also make mention of N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (country)
Georgia (, ; ) is a transcontinental country at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is part of the Caucasus region, bounded by the Black Sea to the west, by Russia to the north and northeast, by Turkey to the southwest, by Armenia to the south, and by Azerbaijan to the southeast. The country covers an area of , and has a population of 3.7 million people. Tbilisi is its capital as well as its largest city, home to roughly a third of the Georgian population. During the classical era, several independent kingdoms became established in what is now Georgia, such as Colchis and Iberia. In the early 4th century, ethnic Georgians officially adopted Christianity, which contributed to the spiritual and political unification of the early Georgian states. In the Middle Ages, the unified Kingdom of Georgia emerged and reached its Golden Age during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar in the 12th and early 13th centuries. Thereafter, the kingdom decl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ardanuç
Ardanuç ( ka, italic=yes, არტანუჯი, Artanuji; ) is a town and district in Artvin Province in Turkey's Black Sea region of Turkey, 32 km east of Artvin. The name Ardanuç derives from Lazuri language and Armenian ( lzz, Artanish-Uji; lit. "edge of Ardahan” in Lazuri and “Ard” meaning field in Armenian"). History The history of this area goes back to the settlement of the banks of the Çoruh River by the Hurri and Mitanni branches of the Hittites in 2000 BC. The first mention of Ardanuç was in a Urartu monument to the defeat of the local people in battle by King Sarduri II in 753 BC. Then in the 7th century BC the Saka or Scythians are known to have settled and they dominated Artanuj. From the 2nd century BC to the 4th century AD this region formed a part of Greater Armenia. The castle of Artanuj was built by Georgian king Vakhtang Gorgasali (5th century AD). The castle was besieged by Arab caliph Marwan II (688-750) Umayyad in 744 AD. and was resto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaramid Dynasty
The Guaramid dynasty or Guaramiani ( ka, გუარამიანი)The dynastic name "Guaramids" is a modern designation introduced by Professor Cyril Toumanoff based on Prince Vakhushti's reference to the dynasty as ''Guaramiani''. It is not universally accepted among the Georgian historians, but is commonly used in the English-language literature. was the younger branch of the Chosroid royal house of Iberia (Kartli, eastern Georgia). They ruled Iberia as Grand dukes (erismtavari) in the periods of 588–627, 684–748, and 779/780–786, and three of them were bestowed with the dignity of curopalates by the Byzantine imperial court. History This branch descended from Leo, son of the Iberian King Vakhtang I and his second wife, Helena, a relative of the Byzantine emperor (485/6). Leo and his brother Mihrdat were given the western portion of the Kingdom of Iberia, composed of the duchies of Klarjeti, Odzrkhe, and the western half of that of Tsunda, of which, however, they w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artvin Province
Artvin Province ( tr, ; ka, , ''Artvinis p’rovincia''; Laz: ართვინიშ დობადონა ''Artviniş dobadona'') is a province in Turkey, on the Black Sea coast in the northeastern corner of the country, on the border with Georgia. The provincial capital is the city of Artvin. Geography Artvin is an attractive area of steep valleys carved by the Çoruh River system, surrounded by high mountains of Kaçkar, Karçal and Yalnızçam (up to 3900 m) and forest with much national parkland including the Karagöl-Sahara, which contains the Şavşat and Borçka lakes. The weather in Artvin is very wet and mild at the coast, and as a result is heavily forested. This greenery runs from the top all the way down to the Black Sea coast. The rain turns to snow at higher altitudes, and the peaks are very cold in winter. The forests are home to brown bears and wolves. The Çoruh is now being dammed in 11 places for hydro-electric power, including the 249 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |