|
Kirkpatrick Railway Station
Kirkpatrick railway station was a station which served the rural area around Kirkpatrick Fleming, north of Gretna in the Scottish county of Dumfries and Galloway. It was served by local trains on what is now known as the West Coast Main Line. The nearest station for Kirkpatrick Fleming is now at Gretna Green. History Opened by the Caledonian Railway, it became part of the London Midland and Scottish Railway during the Grouping of 1923 and was then closed by British Railways in 1960. The station had a number of sidings, a signal box on the western side controlling the level crossing, a pedestrian overbridge, weighing machine, and goods yard. Retrieved : 2012-11-08 Accident A rail crash that took place near Kirkpatrick at the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkpatrick Fleming
Kirkpatrick-Fleming (Scottish Gaelic: Cill Phàdraig) is a village and civil parish in Dumfries and Galloway, south-west Scotland. It is located between the Kirtle Water and the A74(M) motorway, the Solway Firth, and the Cumbrian hills are visible from the village. Kirkpatrick-Fleming is east of Annan, east of Dumfries, north-west of Gretna and north-west of Carlisle. Etymology The name is derived from the parish church, dedicated to St Patrick, and the Fleming family, the local landowners who resided at Redhall. The medieval parish church was given to Gisborough Priory in Cleveland by Robert de Brus, Lord of Annandale, around 1170, though this connection lapsed after 1330. The present church dates to the 18th century and is protected as a category B listed building. Railways The village was served by Kirkpatrick railway station on the old Caledonian Railway main line from 1847 to 1960. Today, the line is part of the West Coast Main Line. Bruce's Cave Bruce's Cave, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Closed In 1960
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer facil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Stations In Great Britain Opened In 1847
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
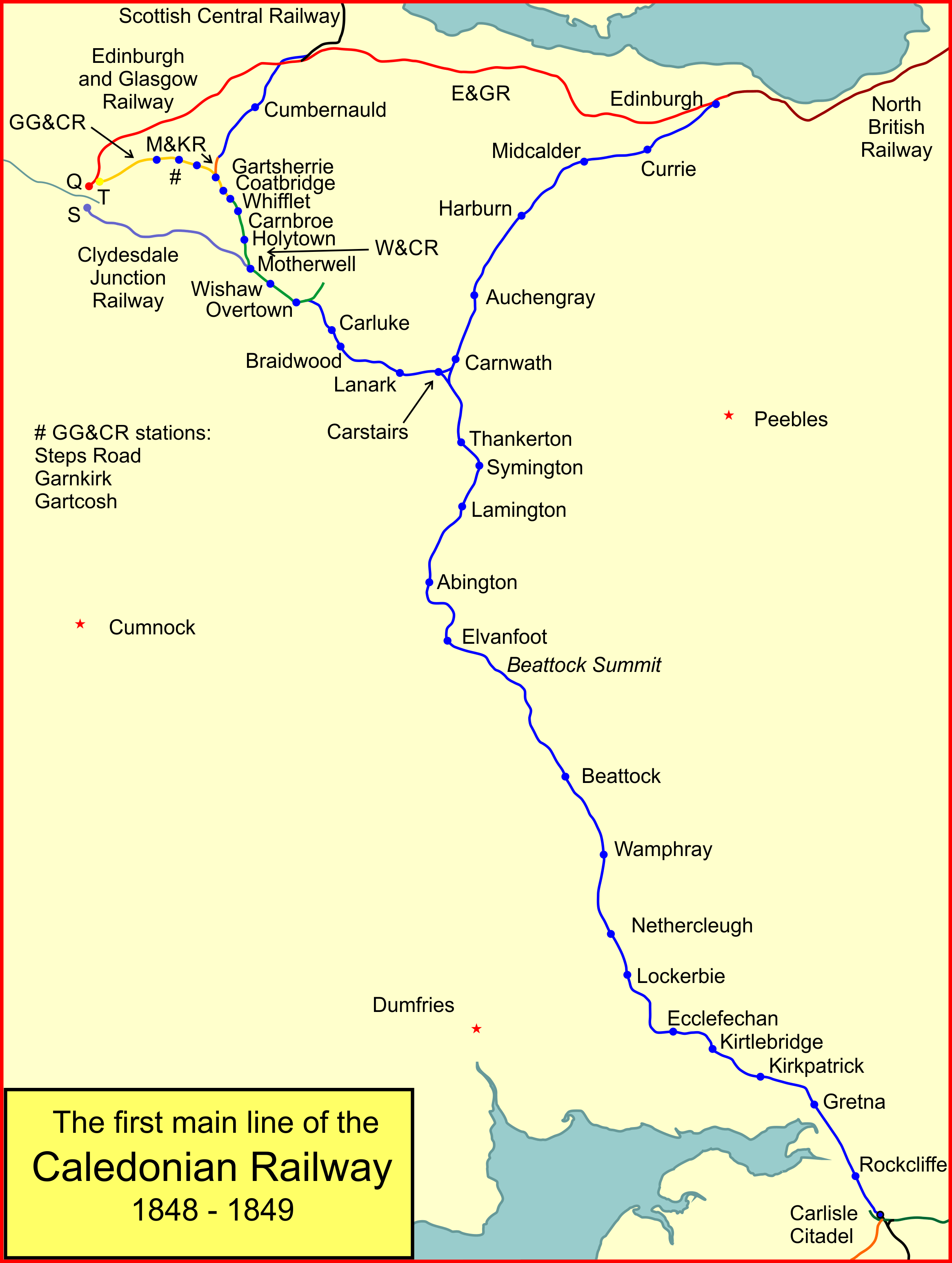
Caledonian Railway Main Line
The Caledonian Railway main line in Scotland connected Glasgow and Edinburgh with Carlisle, via Carstairs and Beattock. It was opened in 1847 by the Caledonian Railway. The approach to Glasgow used railways already built, primarily for mineral traffic; these were later by-passed by a more direct route. Today, the route forms the northern section of the West Coast Main Line, and was electrified in the early 1970s. Opening From 1830 onwards considerable attention was given to the means by which Glasgow and Edinburgh might be connected to London, and as English railways began to develop into a network, the urgency of making a railway accelerated. The difficult terrain of the Southern Uplands and Cumberland made the selection of a route controversial. After much difficulty, the Caledonian Railway was authorised to build a line via Beattock; this was known as the ''Annandale Route''. On 10 September 1847 the line was opened between Carlisle and Beattock. The station at Carlisle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gretna (Caledonian) Railway Station
Gretna railway station was a railway station close to Gretna Green in Scotland. The Caledonian Railway, however, built the station just south of Gretna Junction and the England/Scotland border, in Cumberland (now Cumbria Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. C ...). History The station opened on 9 September 1847. It closed on 10 September 1951. Very little remains of the station in 2008. The Caledonian Railway station was one of three serving Gretna, the others being: * Gretna built by Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway in 1848 (successor station open) * Gretna built by the Border Union Railway in 1861, closing in 1915. A short distance to the north on the Caledonian Railway are Quintinshill loops, the site of the rail crash in 1915. References Note ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintinshill Rail Disaster
The Quintinshill rail disaster was a multi-train rail crash which occurred on 22 May 1915 outside the Quintinshill signal box near Gretna Green in Dumfriesshire, Scotland, United Kingdom. It resulted in the deaths of over 200 people, and remains the worst rail disaster in British history. The Quintinshill signal box controlled two passing loops, one on each side of the double-track Caledonian Main Line linking Glasgow and Carlisle (now part of the West Coast Main Line). At the time of the accident, both passing loops were occupied with goods trains and a northbound local passenger train was standing on the southbound main line. The first collision occurred when a southbound troop train travelling from to Liverpool collided with the stationary local train. A minute later the wreckage was struck by a northbound sleeping car express train travelling from London Euston to Glasgow Central. Gas from the Pintsch gas lighting system of the old wooden carriages of the troop train ign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies dubbed the " Big Four". This was intended to move the railways away from internal competition, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway during and after the Great War of 1914–1918. The provisions of the Act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands and the rivalry between the South Eastern Railway and the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway at Hastings were two examples of such local competition. During the First World War the railways were under st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfries And Galloway
Dumfries and Galloway ( sco, Dumfries an Gallowa; gd, Dùn Phrìs is Gall-Ghaidhealaibh) is one of 32 unitary council areas of Scotland and is located in the western Southern Uplands. It covers the counties of Scotland, historic counties of Dumfriesshire, Kirkcudbrightshire, and Wigtownshire, the latter two of which are collectively known as Galloway. The administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Dumfries. The second largest town is Stranraer, on the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel coast, some to the west of Dumfries. Following the 1975 reorganisation of local government in Scotland, the three counties were joined to form a single regions and districts of Scotland, region of Dumfries and Galloway, with four districts within it. The districts were abolished in 1996, since when Dumfries and Galloway has been a unitary local authority. For lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy purposes, the area is divided into three lieutenancy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gretna Green Railway Station
Gretna Green is a railway station on the Glasgow South Western Line, which runs between and via . The station, situated north-west of Carlisle, serves the town of Gretna and village of Gretna Green in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. It is owned by Network Rail and managed by ScotRail. History The station was opened by the Glasgow, Dumfries and Carlisle Railway on 23 August 1848 as ''Gretna''.Butt (1995), page 110 The Glasgow and South Western Railway renamed the station ''Gretna Green'' in April 1852. On 6 December 1965, the station was closed and the station building was subsequently sold. In 1975, the site of the station became the eastern end of a single line section to , as part of the route rationalisation carried out by British Rail, following the electrification of the West Coast Main Line. The station was reopened on 20 September 1993 by British Rail, with just one platform on the northern side of the line to the west of the previous station, coinciding with the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast Main Line
The West Coast Main Line (WCML) is one of the most important railway corridors in the United Kingdom, connecting the major cities of London and Glasgow with branches to Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester and Edinburgh. It is one of the busiest mixed-traffic railway routes in Europe, carrying a mixture of intercity rail, regional rail, commuter rail and rail freight traffic. The core route of the WCML runs from London to Glasgow for and was opened from 1837 to 1869. With additional lines deviating to Northampton, Birmingham, Manchester, Liverpool and Edinburgh, this totals a route mileage of . The Glasgow–Edinburgh via Carstairs line connects the WCML to Edinburgh, however the main London–Edinburgh route is the East Coast Main Line. Several sections of the WCML form part of the suburban railway systems in London, Coventry, Birmingham, Liverpool, Manchester and Glasgow, with many more smaller commuter stations, as well as providing links to more rural towns. It is one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)