|
Kirkmabreck
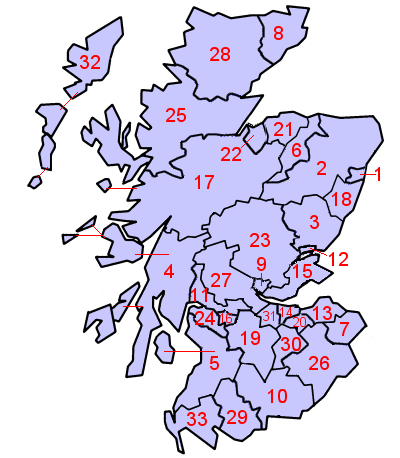
Kirkmabreck is a civil parish in the historic county of Kirkcudbrightshire in the Dumfries and Galloway council area, Scotland. Situated in the historic Stewartry of Kirkcudbright, and centred on the small town of Creetown on the east bank of the River Cree, it stretches north to the parishes of Minnigaff and Girthon, and west to Anwoth. Kirkmabreck also includes the small settlement of Carsluith, dominated by the eponymous castle which is in the care of Historic Scotland. It covers approximately 25,000 acres. Kirkmabreck was one of two parishes from Kirkcudbrightshire which were included in the Wigtown District which existed from 1975 to 1996, and as such forms part of the Wigtown lieutenancy area rather than the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright lieutenancy. Apart from Carsluith Castle, the other antiquities of note in the parish are at Cairnholy, also managed by Historic Scotland, the stone circle at Glenquicken and cup and ring marked stones and castle at Barholm. Thomas Brown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stewartry Of Kirkcudbright
Kirkcudbrightshire ( ), or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative county used for local government. Since 1975, the area has formed part of Dumfries and Galloway for local government purposes. Kirkcudbrightshire continues to be used as a registration county for land registration. A lower-tier district called Stewartry covered the majority of the historic county from 1975 to 1996. The area of Stewartry district is still used as a lieutenancy area. Dumfries and Galloway Council also has a Stewartry area committee. Kirkcudbrightshire forms the eastern part of the medieval lordship of Galloway, which retained a degree of autonomy until it was fully absorbed by Scotland in the 13th century. In 1369, the part of Galloway east of the River Cree was placed under the control of a steward based in Kirkcudbright and so t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkcudbrightshire
Kirkcudbrightshire ( ), or the County of Kirkcudbright or the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright is one of the historic counties of Scotland, covering an area in the south-west of the country. Until 1975, Kirkcudbrightshire was an administrative county used for local government. Since 1975, the area has formed part of Dumfries and Galloway for local government purposes. Kirkcudbrightshire continues to be used as a registration county for land registration. A lower-tier district called Stewartry covered the majority of the historic county from 1975 to 1996. The area of Stewartry district is still used as a lieutenancy area. Dumfries and Galloway Council also has a Stewartry area committee. Kirkcudbrightshire forms the eastern part of the medieval lordship of Galloway, which retained a degree of autonomy until it was fully absorbed by Scotland in the 13th century. In 1369, the part of Galloway east of the River Cree was placed under the control of a steward based in Kirkcudbright and so t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Brown (philosopher)
Thomas Brown (9 January 17782 April 1820) was a Scotland, Scottish philosopher and poet. Biography Early life Brown was born at Kirkmabreck, Kirkcudbrightshire, the son of Rev. Samuel Brown (died 1779) (minister of Kirkmabreck and Kirkdale) and Mary Smith. Their son was a wide reader and an eager student. Educated at several schools in London, he went to the University of Edinburgh in 1792, where he attended Dugald Stewart's moral philosophy class, but does not appear to have completed his course. After studying law for a time he took up medicine; his graduation thesis ''De Somno'' was well received. But his strength lay in metaphysics, metaphysical analysis. Career Brown set an answer to the objections raised against the appointment of John Leslie (physicist), Sir John Leslie to the mathematical professorship (1805). Leslie, a follower of David Hume, was attacked by the clerical party as a sceptic and an infidel, and Brown took the opportunity to defend Hume's doctrine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creetown
Creetown (, sometimes ) is a small seaside town in the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright, in Galloway in the Dumfries and Galloway council area in south-west Scotland. Its population is about 750 people. It is situated near the head of Wigtown Bay, west of Castle Douglas. The town was originally named Ferrytown of Cree (Scottish Gaelic: ''Port Aiseig a' Chrìch'') as it formed one end of a ferry route that took pilgrims across the River Cree estuary to the shrine of St Ninian at Whithorn. This is why the local football team, formed in 1895, are known as "The Ferrytoun". Creetown was formerly served by the Portpatrick and Wigtownshire Railway. The granite quarries in the vicinity constituted the leading industry from about 1830 to 1900, the stone for the Liverpool docks and other public works having been obtained from them. The village dates from 1785, and became a burgh of barony in 1792. Sir Walter Scott laid part of the scene of the novel ''Guy Mannering'' in this neighbourhood. Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wigtown Area
Wigtown is a lieutenancy area in south-west Scotland and a committee area of Dumfries and Galloway Council. From 1975 until 1996 it was also a local government district. It closely resembles the historic county of Wigtownshire, covering the whole area of that county but also including the two parishes of Kirkmabreck and Minnigaff from the historic county of Kirkcudbrightshire. History Wigtown district was created on 16 May 1975 under the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1973, which established a two-tier structure of local government across Scotland comprising upper-tier regions and lower-tier districts. Wigtown district was one of four districts created within the region of Dumfries and Galloway. The district covered all of the former administrative county of Wigtownshire plus the parishes of Kirkmabreck and Minnigaff from Kirkcudbrightshire. The 1973 Act named the new district as " Merrick" after the mountain which formed the new district's highest point, but the name was chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cairnholy
Cairnholy (or Cairn Holy) is the site of two Neolithic chambered tombs of the Clyde type. It is located 4 kilometres east of the village of Carsluith in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland (). The tombs are scheduled monuments in the care of Historic Scotland. The name Cairnholy represents Gaelic ''*Càrn na h-ulaidhe'' ‘cairn of the stone tomb’. Description The Cairnholy tombs are situated on a hillside overlooking Wigtown Bay. They are situated next to Cairnholy Farm. The site can be accessed at the end of a minor road about 1 kilometre from the A75 road. The two tombs lie within 150 metres of each other.Cairn Holy Chambered Cairns Historic Scotland, accessed 6 February 2014 Both tombs lie open to the sky as most of their original covering stones have been taken in the past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumfries And Galloway
Dumfries and Galloway ( sco, Dumfries an Gallowa; gd, Dùn Phrìs is Gall-Ghaidhealaibh) is one of 32 unitary council areas of Scotland and is located in the western Southern Uplands. It covers the counties of Scotland, historic counties of Dumfriesshire, Kirkcudbrightshire, and Wigtownshire, the latter two of which are collectively known as Galloway. The administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Dumfries. The second largest town is Stranraer, on the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel coast, some to the west of Dumfries. Following the 1975 reorganisation of local government in Scotland, the three counties were joined to form a single regions and districts of Scotland, region of Dumfries and Galloway, with four districts within it. The districts were abolished in 1996, since when Dumfries and Galloway has been a unitary local authority. For lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy purposes, the area is divided into three lieutenancy a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Scotland
Historic Scotland ( gd, Alba Aosmhor) was an executive agency of the Scottish Office and later the Scottish Government from 1991 to 2015, responsible for safeguarding Scotland's built heritage, and promoting its understanding and enjoyment. Under the terms of a Bill of the Scottish Parliament published on 3 March 2014, Historic Scotland was dissolved and its functions were transferred to Historic Environment Scotland (HES) on 1 October 2015. HES also took over the functions of the Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland. Role Historic Scotland was a successor organisation to the Ancient Monuments Division of the Ministry of Works and the Scottish Development Department. It was created as an agency in 1991 and was attached to the Scottish Executive Education Department, which embraces all aspects of the cultural heritage, in May 1999. As part of the Scottish Government, Historic Scotland was directly accountable to the Scottish Ministers. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drove Road
A drovers' road, drove ''roador droveway is a route for droving livestock on foot from one place to another, such as to market or between summer and winter pasture (see transhumance). Many drovers' roads were ancient routes of unknown age; others are known to date back to medieval or more recent times. Description Drovers' roads are often wider than other roads, able to accommodate large herds or flocks. Packhorse ways were quite narrow as the horses moved in single file, whereas drove roads were at least and up to wide.Addison (1980), Pp. 70-78. In the United Kingdom, where many original drovers' roads have been converted into single carriageway metalled roads, unusually wide verges often give an indication of the road's origin. In Wales, the start of many droveways, drovers' roads are often recognisable by being deeply set into the countryside, with high earth walls or hedges. The most characteristic feature of these roads is the occasional sharp turn in the road, which p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
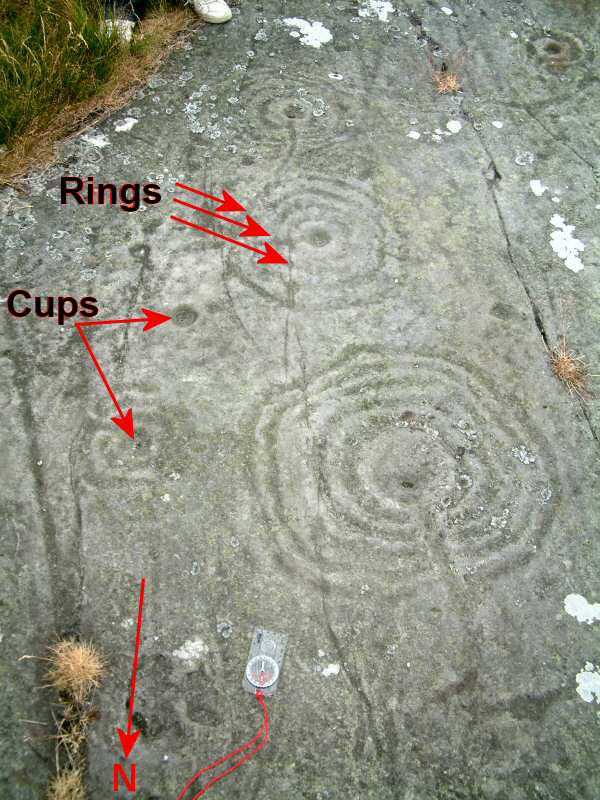
Cup And Ring Mark
Cup and ring marks or cup marks are a form of prehistoric art found in the Atlantic seaboard of Europe (Ireland, Wales, Northern England, Scotland, France (Brittany), Portugal, and Spain ( Galicia) – and in Mediterranean Europe – Italy (in Alpine valleys and Sardinia), Azerbaijan and Greece (Thessaly and Irakleia (Cyclades)), as well as in Scandinavia (Denmark, Sweden, Norway and Finland) and in Switzerland (at Caschenna in Grisons). Similar forms are also found throughout the world including Australia, Gabon, Greece, Hawaii, India ( Daraki-Chattan), Israel, Mexico, Mozambique and the Americas. The oldest known forms are found from the Fertile Crescent to India. They consist of a concave depression, no more than a few centimetres across, pecked into a rock surface and often surrounded by concentric circles also etched into the stone. Sometimes a linear channel called a gutter leads out from the middle. The decoration occurs as a petroglyph on natural boulders and outcrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenquicken Stone Circle
Glenquicken stone circle or Billy Diamond's Bridge stone circle () is an oval stone circle with a central pillar, two miles east of Creetown, Dumfries and Galloway. The outer ring is formed of 29 stones. Aubrey Burl has called it "the finest of all centre-stone circles." It is a scheduled monument. Two other circles to the north-west were marked on the Six-inch First Edition Ordnance Survey map. Alexander Thom planned these in 1939, but they are no longer visible. See also *Stone circles in the British Isles and Brittany *List of stone circles A stone circle is a monument of stones arranged in a circle or ellipse. Such monuments have been constructed in many parts of the world throughout history for many different reasons. The best known tradition of stone circle construction occurred ac ... * Scheduled monuments in Dumfries and Galloway References {{Stone circles in Dumfries and Galloway Stone circles in Dumfries and Galloway Scheduled Ancient Monuments in Dumfries and G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenancy Areas Of Scotland
The lieutenancy areas of Scotland are the areas used for the ceremonial lord-lieutenants, the monarch's representatives, in Scotland. The lord-lieutenants' titles chosen by the monarch and his legal advisers are mainly based on placenames of the traditional counties of Scotland. In 1794 permanent lieutenancies were established by Royal Warrant. By the Militia Act 1797 (37 Geo.3, C.103), the lieutenants appointed "for the Counties, Stewartries, Cities, and Places" were given powers to raise and command County Militia Units. While in their lieutenancies, lord lieutenants are among the few individuals in Scotland officially permitted to fly a banner of the Royal Arms of Scotland, the "Lion Rampant" as it is more commonly known. Lieutenancy areas are different from the current local government council areas and their committee areas. They also differ from other subdivisions of Scotland including sheriffdoms and former regions and districts. The Lord Provosts of Aberdeen, Dunde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)