|
Khudoyor Yusufbekov
Khudoyor Yusufbekovich Yusufbekov (russian: Худоер Юсуфбекович Юсуфбеков, tg, Худоёр Юсуфбеков; December 10, 1928 — November 27, 1990) was a Soviet scientist and organizer of scientific projects and institutes in Pamir. He was a leading scientist who made a significant contribution to the development of biological sciences, whose name is connected with a new direction of the development of plant growing in the arid mountain and highland territory of Pamir-Alay; a prominent specialist in the field of plant growing, plant introduction and pasture economy, meadow studies, phyto-amelioration, and botany, Yusufbekov was a practicing field researcher, figure of higher education, and professor. In 1968, he developed a system for fodder improvement in the Pamir and Alay valleys that was differentiated from the perspective of the ecological and geographical areas and high-altitude zones. He also implemented a system of arid fodder, and propo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand. Though villages are often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighborhoods. Villages are normally permanent, with fixed dwellings; however, transient villages can occur. Further, the dwellings of a village are fairly close to one another, not scattered broadly over the landscape, as a dispersed settlement. In the past, villages were a usual form of community for societies that practice subsistence agriculture, and also for some non-agricultural societies. In Great Britain, a hamlet earned the right to be called a village when it built a church. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
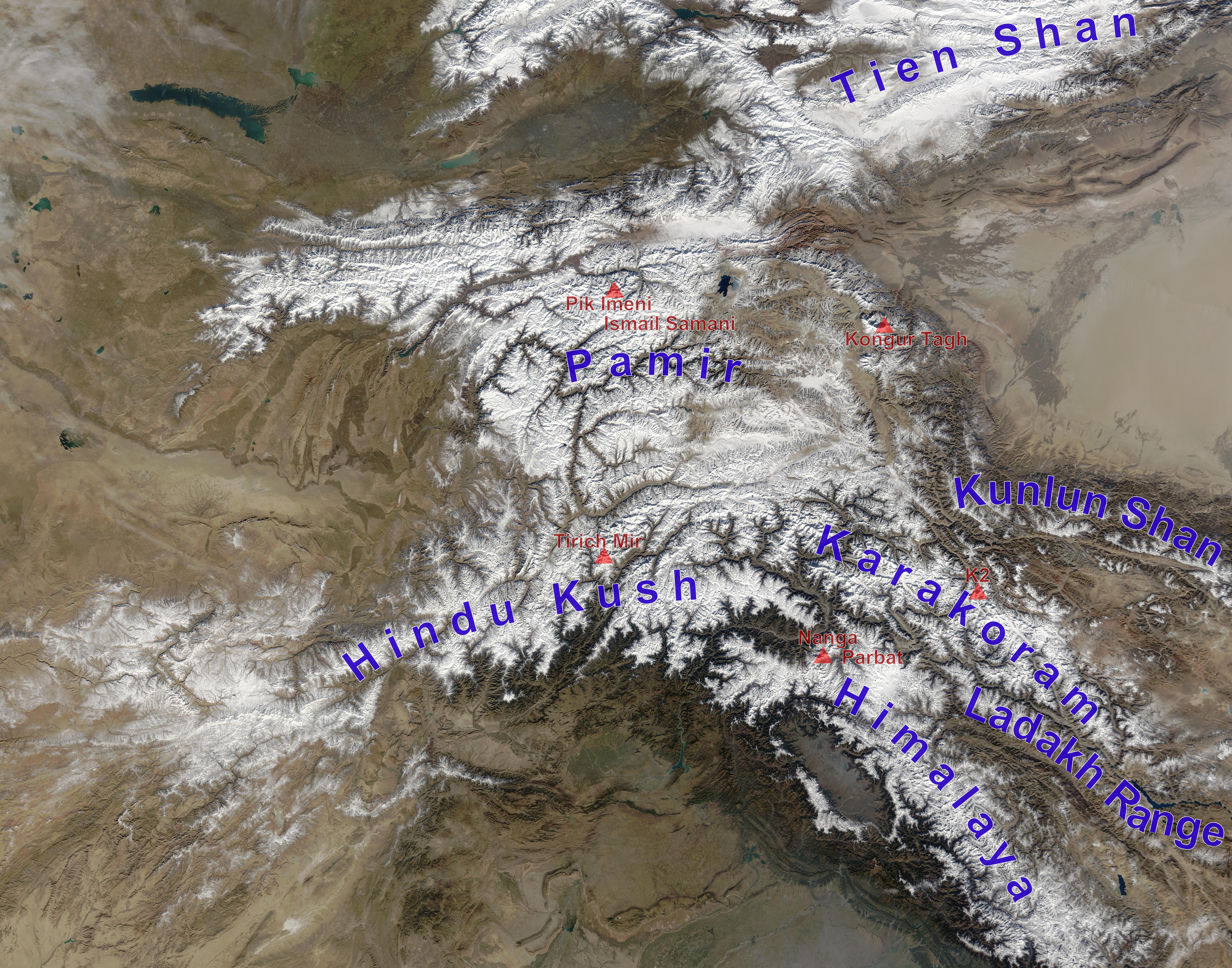
Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world's highest mountains. Much of the Pamir Mountains lie in the Gorno-Badakhshan Province of Tajikistan. To the south, they border the Hindu Kush mountains along Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in Badakhshan Province, Chitral District, Chitral and Gilgit-Baltistan regions of Pakistan. To the north, they join the Tian Shan mountains along the Alay Valley of Kyrgyzstan. To the east, they extend to the range that includes China's Kongur Tagh, in the "Eastern Pamirs", separated by the Yarkand River, Yarkand valley from the Kunlun Mountains. Name and etymology Since Victorian times, they have been known as the "Roof of the World", presumably a translation from Persian language, Persian. Names In other languages they are called: ps, , ; k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of Sciences
An academy of sciences is a type of learned society or academy (as special scientific institution) dedicated to sciences that may or may not be state funded. Some state funded academies are tuned into national or royal (in case of the United Kingdom i.e. Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge) as a form of honor. The other type of academies are '' Academy of Arts'' or combination of both (e.g., American Academy of Arts and Sciences). ''Academy of Letters'' is another related expression, encompassing literature. In non-English-speaking countries, the range of academic fields of the members of a national Academy of Science often includes scholarly disciplines which would not normally be classed as "science" in English. Many languages use a broad term for systematized learning which includes both natural sciences and social sciences and fields such as literary studies, linguistics, history, or art history. (Often these terms are calques from Latin ''scientia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academician
An academician is a full member of an artistic, literary, engineering, or scientific academy. In many countries, it is an honorific title used to denote a full member of an academy that has a strong influence on national scientific life. In systems such as the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, the title grants privileges and administrative responsibilities for funding allocation and research priorities. History Historically, the meaning for the title of ''Academician'' follows the traditions of the two most successful early scientific societies: either the Royal Society, where it was an honorary recognition by an independent body of peer reviewers and was meant to distinguish a person, while giving relatively little formal power, or the model of the French Academy of Sciences, which was much closer integrated with the government, provided with more state funding as an organization, and where the title of ''Academician'' implied in a lot more rights when it came to decision maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Sciences
Agricultural science (or agriscience for short) is a broad multidisciplinary field of biology that encompasses the parts of exact, natural, economic and social sciences that are used in the practice and understanding of agriculture. Professionals of the agricultural science are called agricultural scientists or agriculturists. History In the 18th century, Johann Friedrich Mayer conducted experiments on the use of gypsum (hydrated calcium sulphate) as a fertilizer.John Armstrong, Jesse Buel. ''A Treatise on Agriculture, The Present Condition of the Art Abroad and at Home, and the Theory and Practice of Husbandry. To which is Added, a Dissertation on the Kitchen and Garden.'' 1840. p. 45. In 1843, John Bennet Lawes and Joseph Henry Gilbert began a set of long-term field experiments at Rothamsted Research in England, some of which are still running as of 2018. In the United States, a scientific revolution in agriculture began with the Hatch Act of 1887, which used the term " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Planning
Urban planning, also known as town planning, city planning, regional planning, or rural planning, is a technical and political process that is focused on the development and design of land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportation, communications, and distribution networks and their accessibility. Traditionally, urban planning followed a top-down approach in master planning the physical layout of human settlements. The primary concern was the public welfare, which included considerations of efficiency, sanitation, protection and use of the environment, as well as effects of the master plans on the social and economic activities. Over time, urban planning has adopted a focus on the social and environmental bottom-lines that focus on planning as a tool to improve the health and well-being of people while maintaining sustainability standards. Sustainable development was added as one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most arid climates straddle the Equator; these regions include parts of Africa, Asia, South America, North America, and Australia. Change over time The distribution of aridity at any time is largely the result of the general circulation of the atmosphere. The latter does change significantly over time through climate change. For example, temperature increase by 1.5–2.1 percent across the Nile Basin over the next 30–40 years could change the region from semi-arid to arid, significantly reducing the land usable for agriculture. In addition, changes in land use can increase demands on soil water and thereby increase aridity. See also * Arid Forest Research Institute * Aridity index * Desert climate * Desiccation tolerance * Drought * Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-altitude
Altitude or height (also sometimes known as depth) is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometry, geographical survey, sport, or atmospheric pressure). Although the term ''altitude'' is commonly used to mean the height above sea level of a location, in geography the term elevation is often preferred for this usage. Vertical distance measurements in the "down" direction are commonly referred to as depth. In aviation In aviation, the term altitude can have several meanings, and is always qualified by explicitly adding a modifier (e.g. "true altitude"), or implicitly through the context of the communication. Parties exchanging altitude information must be clear which definition is being used. Aviation altitude is measured using either mean sea level (MSL) or local ground level (above ground level, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alay Valley
The Alay Valley ( ky, Алай өрөөнү, ) is a broad, dry valley running east–west across most of southern Osh Region, Kyrgyzstan. It spreads over a length of east–west. The valley extends in north–south direction with varying width of in the west, in the central part, and in the east. The altitude of the valley ranges from near Karamyk to at Toomurun Pass with an average altitude of about . The area of the valley is . The north side is the Alay Mountains which slope down to the Ferghana Valley. The south side is the Trans-Alay Range along the Tajikistan border, with Lenin Peak, (). The western or so is more hills than valley. On the east there is the low Tongmurun pass and then more valley leading to the Irkestam border crossing to China. The eastern Kyzyl-Suu ('Red River') flows from the Tongmurun rise past Irkestam toward Kashgar. The western Kyzyl-Suu flows west from the Tongmurun rise and drains most of the valley, flowing on the north side. It exits thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Improvement
Land development is the alteration of landscape in any number of ways such as: * Changing landforms from a natural or semi-natural state for a purpose such as agriculture or House, housing * subdivision (land), Subdividing real estate into Lot (real estate), lots, typically for the purpose of building homes * Real estate development or changing its purpose, for example by converting an unused factory complex into a condominium. Economic aspects In an economic context, land development is also sometimes advertised as land improvement or land amelioration. It refers to investment making land more usable by humans. For accounting purposes it refers to any variety of projects that increase the property value, value of the process . Most are depreciable, but some land improvements are not able to be depreciated because a useful life cannot be determined. Home building and containment are two of the most common and the oldest types of development. In an Urban development, urban context ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)