|
Khazneh
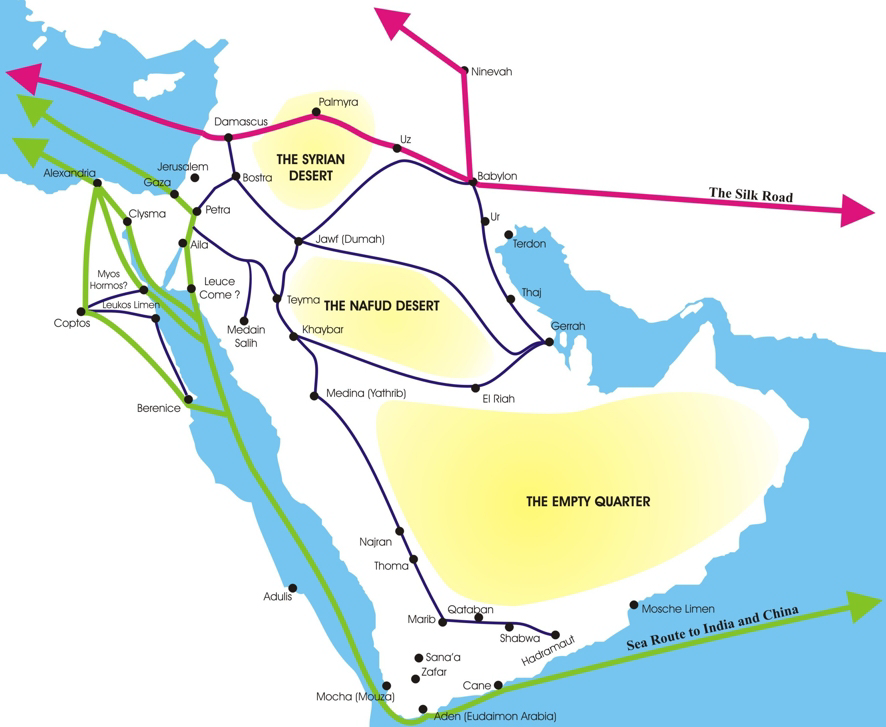
Al-Khazneh ( ar, الخزنة; "The Treasury") is one of the most elaborate temples in Petra, a city of the Nabatean Kingdom inhabited by the Arabs in ancient times. As with most of the other buildings in this ancient town, including the Monastery (Arabic: Ad Deir), this structure was carved out of a sandstone rock face. The structure is believed to have been the mausoleum of the Nabatean King Aretas IV in the 1st century AD. It is one of the most popular tourist attractions in both Jordan and the region. It became known as "Al-Khazneh", or The Treasury, in the early 19th century by the area's Bedouins as they had believed it contained treasures. Name Al-Khazneh means "The Treasury" in Arabic, a name derived from legends regarding the decorative stone urn high on the second level, which in reality is solid sandstone. One legend is that the Egyptian Pharaoh and some of his armies escaped the closing of the Red Sea, created the Khazneh by magic as a safe place for his treasury, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petra
Petra ( ar, ٱلْبَتْرَاء, Al-Batrāʾ; grc, Πέτρα, "Rock"), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu or Raqēmō is a historic and archaeological city in southern Jordan. It is adjacent to the mountain of Jabal Al-Madbah, in a basin surrounded by mountains forming the eastern flank of the Arabah valley running from the Dead Sea to the Gulf of Aqaba. The area around Petra has been inhabited from as early as 7000 BC, and the Nabataeans might have settled in what would become the capital city of their kingdom as early as the 4th century BC. Archaeological work has only discovered evidence of Nabataean presence dating back to the second century BC, by which time Petra had become their capital. The Nabataeans were nomadic Arabs who invested in Petra's proximity to the incense trade routes by establishing it as a major regional trading hub. The trading business gained the Nabataeans considerable revenue and Petra became the focus of their wealth. The Nabataea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petra
Petra ( ar, ٱلْبَتْرَاء, Al-Batrāʾ; grc, Πέτρα, "Rock", Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: ), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu or Raqēmō, is an historic and archaeological city in southern Jordan. It is adjacent to the mountain of Jebel al-Madhbah, Jabal Al-Madbah, in a Depression (geology), basin surrounded by mountains forming the eastern flank of the Arabah valley running from the Dead Sea to the Gulf of Aqaba. The area around Petra has been inhabited from as early as 7000 BC, and the Nabataeans might have settled in what would become the capital city of Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom as early as the 4th century BC. Archaeological work has only discovered evidence of Nabataean presence dating back to the second century BC, by which time Petra had become their capital. The Nabataeans were nomadic Arabs who invested in Petra's proximity to the incense trade routes by establishing it as a major regional trading hub. The trading business gained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Deir
Ad Deir ("The Monastery"; Arabic: الدير ), also spelled ad-Dayr and el-Deir, is a monumental building carved out of rock in the ancient Jordanian city of Petra. The Deir was probably carved out of the rock in the mid-first century AD. Arguably one of the most iconic monuments in the Petra Archaeological Park, the Monastery is located high in the hills northwest of the Petra city center. It is the second most commonly visited monument in Petra, after the Khazneh or "Treasury". The huge facade, the inner chamber and the other structures next to it or in the wider area around the Deir probably originally served a complex religious purpose, and was possibly repurposed as a church in the Byzantine period. Location The Monastery can be reached by ascending a nearly 800 step path (40 minute walking time) from the Basin. The Wadi Kharrubeh, the Lion's tomb, and small biclinia and grottos can be seen en route to the Monastery. From the Monastery, one can view the stunning valle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiana Jones And The Last Crusade
''Indiana Jones and the Last Crusade'' is a 1989 American action film, action-adventure film directed by Steven Spielberg, from a story co-written by executive producer George Lucas. It is the third installment in the Indiana Jones, ''Indiana Jones'' franchise and a sequel to ''Raiders of the Lost Ark'' (1981). Harrison Ford returned in Indiana Jones (character), the title role, while Henry Jones, Sr., his father is portrayed by Sean Connery. Other cast members featured include Alison Doody, Denholm Elliott, Julian Glover, River Phoenix, and John Rhys-Davies. In the film, set largely in 1938, Indiana searches for his father, a Holy Grail scholar, who has been kidnapped and held hostage by the Nazis while on a journey to find the Holy Grail. After the mixed reaction to ''Indiana Jones and the Temple of Doom'', Spielberg chose to lower the dark tone and graphic violence in the next installment. During the five years between ''The Temple of Doom'' and ''The Last Crusade'', he and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western List of islands in the Indian Ocean, Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Arabs in Turkey, Turkey, Arab Indonesians, Indonesia, and Iranian Arabs, Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both Arab identity, carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the northeast, Syria to the north, and the Palestinian West Bank, Israel, and the Dead Sea to the west. It has a coastline in its southwest on the Gulf of Aqaba's Red Sea, which separates Jordan from Egypt. Amman is Jordan's capital and largest city, as well as its economic, political, and cultural centre. Modern-day Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three stable kingdoms emerged there at the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their Kingdom with Petra as the capital. Later rulers of the Transjordan region include the Assyrian, Babylonian, Roman, Byzantine, Rashidun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type of tomb, or the tomb may be considered to be within the mausoleum. Overview The word ''mausoleum'' (from Greek μαυσωλείον) derives from the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus (near modern-day Bodrum in Turkey), the grave of King Mausolus, the Persian satrap of Caria, whose large tomb was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Historically, mausolea were, and still may be, large and impressive constructions for a deceased leader or other person of importance. However, smaller mausolea soon became popular with the gentry and nobility in many countries. In the Roman Empire, these were often in necropoles or along roadsides: the via Appia Antica retains the ruins of many private mausolea for kilometres outside Rome. Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabatean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea (), was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Red Sea coast into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several nomadic Bedouin tribes that roamed the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. Although the Nabataeans were initially embedded in Aramaic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabateans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic language, Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabian Peninsula, Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Petra, Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' ( grc, Ναβατηνή, translit=Nabatēnḗ) to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BCE,Taylor, Jane (2001). ''Petra and the Lost Kingdom of the Nabataeans''. London: I.B.Tauris. pp. 14, 17, 30, 31. . Retrieved 8 July 2016. with Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aretas IV
Aretas IV Philopatris (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢗𐢓𐢆 𐢊𐢛𐢞𐢞 𐢛𐢊𐢒 ''Ḥārīṯat Rāḥem-ʿammeh'', "Aretas, friend of his people") was the King of the Nabataeans from roughly 9 BC to AD 40. His daughter Phasaelis was married to, and divorced from, Herod Antipas. Herod then married his stepbrother's wife, Herodias. It was opposition to this marriage that led to the beheading of John the Baptist. After he received news of the divorce, Aretas invaded the territory of Herod Antipas and defeated his army. Rise to power Aretas came to power after the assassination of Obodas III, who was apparently poisoned. Josephus says that he was originally named Aeneas, but took "Aretas" as his throne name. An inscription from Petra suggests that he may have been a member of the royal family, as a descendant of Malichus I. The capital of his kingdom was a prosperous trading city, Petra, some 170 miles south of Amman. Petra is famous for the many monuments carved into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aretas IV Philopatris
Aretas IV Philopatris (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢗𐢓𐢆 𐢊𐢛𐢞𐢞 𐢛𐢊𐢒 ''Ḥārīṯat Rāḥem-ʿammeh'', "Aretas, friend of his people") was the King of the Nabataeans from roughly 9 BC to AD 40. His daughter Phasaelis was married to, and divorced from, Herod Antipas. Herod then married his stepbrother's wife, Herodias. It was opposition to this marriage that led to the beheading of John the Baptist. After he received news of the divorce, Aretas invaded the territory of Herod Antipas and defeated his army. Rise to power Aretas came to power after the assassination of Obodas III, who was apparently poisoned. Josephus says that he was originally named Aeneas, but took "Aretas" as his throne name. An inscription from Petra suggests that he may have been a member of the royal family, as a descendant of Malichus I. The capital of his kingdom was a prosperous trading city, Petra, some 170 miles south of Amman. Petra is famous for the many monuments carved into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpeg/1200px-Taj_Mahal_(Edited).jpeg)