|
Khatso
The Khatso people (), commonly known as the "Mongols in Yunnan", is a Mongolic ethnic group, mainly distributed in Tonghai County in the Yunnan Province of southwestern China. The Khatso people are descendants of the army personnel of the Yuan dynasty. History Before the mid-13th century, Yunnan was held by many war-like independent states such as the Nanchao and Dali Kingdoms. The Mongol Empire under Möngke Khan conquered the Dali Kingdom in 1253. Until 1273, a Chinggisid prince received viceroyalty over the area. Kublai Khan appointed the first governor, Turkmen Sayid Ajall, in Yunnan in 1273. Yunnan and Hunan were main bases for Mongol military operations to Indo-China. It was called Yunnan district with Kunming as the headquarters during the Yuan. After the expulsion of the Mongols from China in 1368, the Ming Dynasty destroyed the Yuan loyalists in Yunnan under Basalawarmi in 1381 and occupied it. In 1381, "Ming Dynasty troops routed the Yuan army by the shore of the Baishui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sichuan Mongols
The Sichuan Mongols () are officially counted among the Mongolian nationality in China. However, they are a distinct ethno-linguistic group from all other Mongolic peoples. They call themselves Mongols and possess their own clothing, history and language. All other peoples in the region recognize them as Mongols (''Mengguzu''). The Sichuan Mongols' main religion is Tibetan Buddhism. A sizable temple remains in active use just behind the prince's house. Most temples and altars being destroyed during the Cultural Revolution but many of them were recovered afterwards. Most Sichuan Mongols are farmers or fishermen, leading quiet lives in their remote villages. They observe Buddhist festivals. Historically, the Mongols in Yongning were ruled by three chiefs, elevated to power by Kublai Khan in the 13th century. Before Communist rule, the Mongol monarch acted as a warlord over the whole region. When the Communists took over, they deposed him, not killing him so as not to make him a mart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolic Peoples
The Mongolic peoples are a collection of East Asian originated ethnic groups in East, North, South Asia and Eastern Europe, who speak Mongolic languages. Their ancestors are referred to as Proto-Mongols. The largest contemporary Mongolic ethnic group is the Mongols. Mongolic-speaking people, although distributed in a wide geographical area, show a high genetic affinity to each other, and display continuity with ancient Northeast Asians. List of ethnic groups Contemporary ethnic groups In addition, Mongolized Soyots live in Buryatia. Their population is 3600 people. A number of orientalists (Nanzatov, Baldaev and others) traditionally consider modern Soyots as a sub-ethnos within the Buryat people. Ethnic groups of Mongolian origin A large Mongolian component took part in the ethnic formation of the Hazaras, also called the Hazara Mongols. Even in the 16th century, according to Babur, the Mongolian language was widespread among the Hazaras, and a small part of them, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
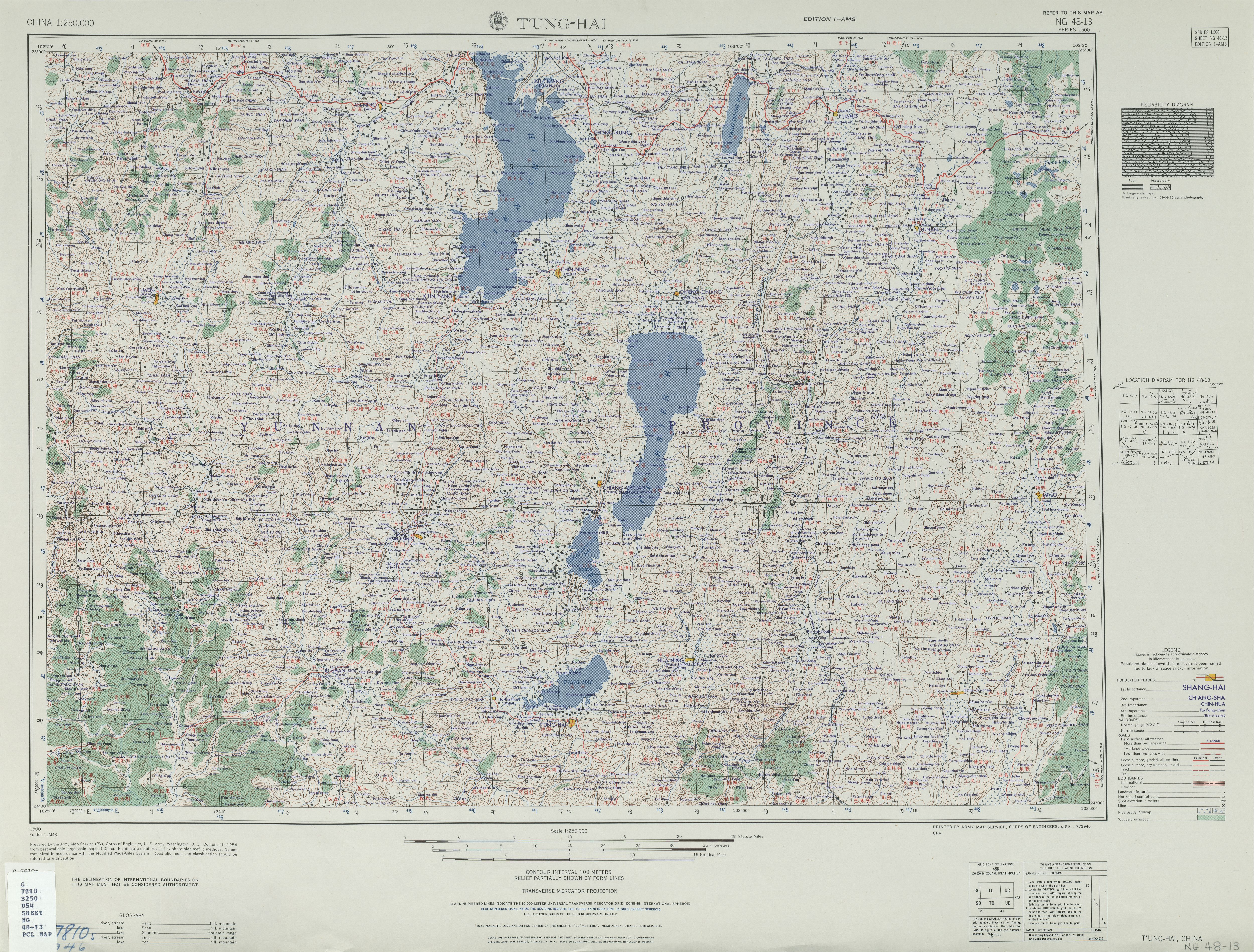
Tonghai County
Tonghai County () is located in Yuxi Prefecture-level City, Yunnan Province, China. Geography Tonghai County occupies the fertile valley of Qilu Lake, surrounded on all sides by mountains. The county seat is located on the south side of the lake, separated from the lake by a mile-wide strip of farmland. The county's southernmost part, including the Dagao Dai and Yi Ethnic Township and Lishan Yi Ethnic Township, is separated from the rest of the county by mountains; it is outside of the Qilu Lake basin, and is drained into the Qu River instead. In 1970, a powerful earthquake struck the area. History The area around Qilu Lake has been inhabited since at least the Neolithic period. In the Tang dynasty it was the base of a general. For many centuries it was the political, economic and military center of southern Yunnan. Soon after the formation of PRC, the area of today's Tonghai County was organized as two counties: Tonghai and Hexi (in the western part of today's Tonghai Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katso Language
Katso, also known as Kazhuo (autonyms: ', '; ), is a Loloish language of Xingmeng Township (兴蒙乡), Tonghai County, Yunnan, China. The speakers are officially classified as ethnic Mongols, although they speak a Loloish The Loloish languages, also known as Yi in China and occasionally Ngwi or Nisoic, are a family of fifty to a hundred Sino-Tibetan languages spoken primarily in the Yunnan province of China. They are most closely related to Burmese and its relat ... language. Katso speakers call themselves ' (卡卓) or ' (嘎卓) (''Kazhuoyu Yanjiu''). Lama (2012) lists the following sound changes from Proto-Loloish as Kazhuoish innovations. * *x- > s- * *mr- > z- References Further reading * Donlay, Chris. A Grammar of Khatso. De Gruyter Mouton, 2019. {{Lolo-Burmese languages Loloish languages Languages of China ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basalawarmi
Basalawarmi ( xng, ᠪᠠᠵᠠᠯᠠᠸᠠᠷᠮᠠᠢ, , died January 6, 1382), commonly known by his hereditary noble title, the Prince of Liang, was a Yuan dynasty prince and loyalist who fought against the ascendant Ming dynasty in China proper. He was a descendant of Khökhechi, the fifth son of Kublai Khan.Zhang, Tingyu et al.History of Ming.vol.124 Before the fall of the Yuan Before the Yuan dynasty's fall in 1368, Basalawarmi had been the Yuan Viceroy of Yunnan and Guizhou, in southwestern China. He held the title of Prince of Liang, a hereditary title passed down from one of his forebears, a son of Kublai Khan. Following the Ming dynasty's overthrow of the Yuan, Basalawarmi, from his capital city of Kunming, led one of the last pockets of Yuan resistance to Ming rule. He was able to withstand the advance of other forces of his time due to the relatively remote location of his domain. Meanwhile, Hongwu of Ming, the first emperor of the Ming dynasty, decided to approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-China
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west and the Pacific Ocean to the east. It includes the countries of Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand and Vietnam, with peninsular Malaysia sometimes also being included. The term Indochina (originally Indo-China) was coined in the early nineteenth century, emphasizing the historical cultural influence of Indian and Chinese civilizations on the area. The term was later adopted as the name of the colony of French Indochina (today's Cambodia, Laos, and Vietnam). Today, the term, Mainland Southeast Asia, in contrast to Maritime Southeast Asia, is more commonly referenced. Terminology The origins of the name Indo-China are usually attributed jointly to the Danish-French geographer Conrad Malte-Brun, who referred to the area as in 1804, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwestern Mandarin
Southwestern Mandarin (), also known as Upper Yangtze Mandarin (), is a Mandarin Chinese language spoken in much of Southwest China, including in Sichuan, Yunnan, Chongqing, Guizhou, most parts of Hubei, the northwestern part of Hunan, the northern part of Guangxi and some southern parts of Shaanxi and Gansu. Southwestern Mandarin is spoken by roughly 260 million people. If considered a language distinct from central Mandarin, it would be the eighth-most spoken language by native speakers in the world, behind Mandarin itself, Spanish, English, Hindi, Portuguese, Arabic and Bengali. Overview Modern Southwestern Mandarin was formed by the waves of immigrants brought to the regions during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. Because of the comparatively recent move, such dialects show more similarity to modern Standard Mandarin than to other varieties of Chinese like Cantonese or Hokkien. For example, like most Southern Chinese dialects, Southwestern Mandarin does not possess the retroflex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loloish Language
The Loloish languages, also known as Yi in China and occasionally Ngwi or Nisoic, are a family of fifty to a hundred Sino-Tibetan languages spoken primarily in the Yunnan province of China. They are most closely related to Burmese and its relatives. Both the Loloish and Burmish branches are well defined, as is their superior node, Lolo-Burmese. However, subclassification is more contentious. SIL Ethnologue (2013 edition) estimated a total number of 9 million native speakers of Ngwi languages, the largest group being the speakers of Nuosu (Northern Yi) at 2 million speakers (2000 PRC census). Names ''Loloish'' is the traditional name for the family. Some publications avoid the term under the misapprehension that ''Lolo'' is pejorative, but it is the Chinese rendition of the autonym of the Yi people and is pejorative only when it is written with a particular Chinese character (one that uses a beast, rather than a human, radical), a practice that was prohibited by the Chinese g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yi People
The Yi or Nuosu people,; zh, c=彝族, p=Yízú, l=Yi ethnicity historically known as the Lolo,; vi, Lô Lô; th, โล-โล, Lo-Lo are an ethnic group An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ... in China, Vietnam, and Thailand. Numbering nine million people, they are the seventh largest of the 55 Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic minority groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. They live primarily in rural areas of Sichuan, Yunnan, Guizhou, and Guangxi, usually in mountainous regions. The Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture is home to the largest population of Yi people within mainland China, with two million Yi people in the region. For other countries, as of 1999, there were 3,300 Mantsi language, Mantsi-speaking Lô Lô people living in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolian Culture
The culture of Mongolia has been shaped by the country's nomadic tradition and its position at the crossroads of various empires and civilizations. Mongolian culture is influenced by the cultures of the Mongolic, Turkic, and East Asian peoples, as well as by the country's geography and its history of political and economic interactions with other nations. One of the most distinctive aspects of Mongolian culture is its nomadic pastoral economy, which has shaped the traditional way of life for the Mongols for centuries. The nomadic lifestyle is centered around the family and the community, and involves the herding of animals such as sheep, goats, and yaks. This way of life has had a significant impact on Mongolian culture, influencing everything from the country's social relationships and family structures, to its art, music, and literature. Mongolian culture is also well known for its traditional arts, which include music, dance, and literature. The country's music and dance t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)