|
Kent, OH
Kent is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the largest city in Portage County. It is located along the Cuyahoga River in Northeast Ohio on the western edge of the county. The population was 28,215 at the 2020 Census. The city is counted as part of the Akron Metropolitan Statistical Area and the larger Cleveland–Akron–Canton Combined Statistical Area. Part of the Connecticut Western Reserve, Kent was settled in 1805 and was known for many years as Franklin Mills. Settlers were attracted to the area due to its location along the Cuyahoga River as a place for water-powered mills. Later development came in the 1830s and 1840s as a result of the settlement's position along the route of the Pennsylvania and Ohio Canal. Leading up to the American Civil War, Franklin Mills was noted for its activity in the Underground Railroad. With the decline of the canal and the emergence of the railroad, the town became the home of the Atlantic and Great Western Railroad maintenance shops t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Standard Time Zone
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico, Panama, Colombia, mainland Ecuador, Peru, and a small portion of westernmost Brazil in South America, along with certain Caribbean and Atlantic islands. Places that use: * Eastern Standard Time (EST), when observing standard time (autumn/winter), are five hours behind Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−05:00). * Eastern Daylight Time (EDT), when observing daylight saving time (spring/summer), are four hours behind Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−04:00). On the second Sunday in March, at 2:00 a.m. EST, clocks are advanced to 3:00 a.m. EDT leaving a one-hour "gap". On the first Sunday in November, at 2:00 a.m. EDT, clocks are moved back to 1:00 a.m. EST, thus "duplicating" one hour. Southern parts of the zone (Panama and the Caribbean) do not observe daylight saving time. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic And Great Western Railroad
The Atlantic and Great Western Railroad began as three separate railroads: the Erie and New York City Railroad based in Jamestown, New York; the Meadville Railroad based in Meadville, Pennsylvania (renamed A&GW in April 1858); and the Franklin and Warren Railroad based in Franklin Mills, Ohio (renamed A&GW in January 1853). The owners of the three railroads had been working closely together since an October 8, 1852, meeting in Cleveland to plan an expansion of the "Great Broad Route", the Erie Railroad, through their respective areas. On March 12, 1862, general control of all three companies was placed under a central board made of two directors from each of the companies. The Ohio Board was represented by Marvin Kent and Worthy S. Streator; the Pennsylvania Board by William Reynolds and John Dick; and the New York Board by A. F. Allen and Thomas W. Kennard. William Reynolds was elected President of the Board. The line reached Cleveland on November 18, 1863, and was connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. The network was assisted by abolitionists and others sympathetic to the cause of the escapees. The enslaved persons who risked escape and those who aided them are also collectively referred to as the "Underground Railroad". Various other routes led to Mexico, where slavery had been abolished, and to islands in the Caribbean that were not part of the slave trade. An earlier escape route running south toward Florida, then a Spanish possession (except 1763–1783), existed from the late 17th century until approximately 1790. However, the network now generally known as the Underground Railroad began in the late 18th century. It ran north and grew steadily until the Emancipation Proclamation was signed by President Abraham Lincoln.Vox, Lisa"How D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania And Ohio Canal
The Pennsylvania and Ohio Canal, also known as the P & O Canal, the Cross Cut Canal and the Mahoning Canal was a shipping canal which operated from 1840 until 1877 (though the canal was completely abandoned by 1872). It was unique in that it served to connect canals in two states (the Ohio and Erie Canal in Ohio and the Beaver and Erie Canal in Pennsylvania) and was funded by private interests. History In Warren, Ohio, Warren, Ohio, at a convention held on November 13, 1833, 109 delegates decided to privately fund the Pennsylvania and Ohio Canal as neither state felt it should spend money on a canal that led to another state. Construction began on September 17, 1835, when the two engineers of the canal struck iron stakes in the ground at the center of what was known as the "Portage Summit" between what is now Kent, Ohio, and Ravenna. Workers manually dug the of the P & O using picks, shovels, and wheelbarrows. It ran from New Castle, Pennsylvania, New Castle, Pennsylvania, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connecticut Western Reserve
The Connecticut Western Reserve was a portion of land claimed by the Colony of Connecticut and later by the state of Connecticut in what is now mostly the northeastern region of Ohio. The Reserve had been granted to the Colony under the terms of its charter by King Charles II. Connecticut relinquished its claim to some of its western lands to the United States in 1786 following the American Revolutionary War and preceding the 1787 establishment of the Northwest Territory. Despite ceding sovereignty to the United States, Connecticut retained ownership of the eastern portion of its cession, south of Lake Erie. It sold much of this "Western Reserve" to a group of speculators who operated as the Connecticut Land Company; they sold it in portions for development by new settlers. The phrase Western Reserve is preserved in numerous institutional names in Ohio, such as Western Reserve Academy, Case Western Reserve University, and Western Reserve Hospital. In the 19th century, the West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
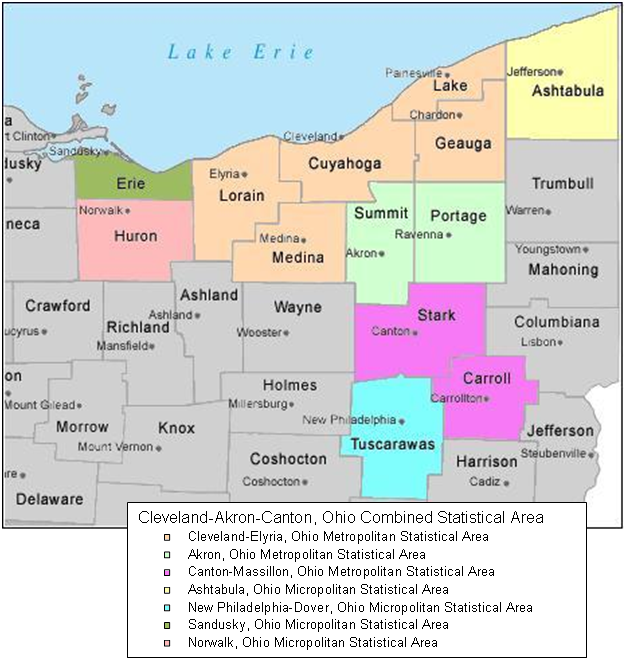
Cleveland–Akron–Canton Combined Statistical Area
The region Northeast Ohio, in the US state of Ohio, in its most expansive usage contains six metropolitan areas ( Cleveland–Elyria, Akron, Canton–Massillon, Youngstown–Warren, Mansfield, and Weirton–Steubenville) along with eight micropolitan statistical areas. Most of the region is considered either part of the Cleveland–Akron–Canton, OH Combined Statistical Area and media market or the Youngstown–Warren, OH-PA Combined Statistical Area and media market. In total the region is home to 4,502,460 residents. It is also a part of the Great Lakes megalopolis, containing over 54 million people. Northeast Ohio also includes most of the area known historically as the Connecticut Western Reserve. In 2011, the Intelligent Community Forum ranked Northeast Ohio as a global Smart 21 Communities list. It has the highest concentration of Hungarian Americans in the United States. Composition Different sources define the region as having various boundaries. At its largest, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akron Metropolitan Area
The Akron, OH Metropolitan Statistical Area, sometimes referred to as Greater Akron, is defined by the United States Office of Management and Budget as an area consisting of two counties, Summit and Portage, in Northeast Ohio and anchored by the city of Akron. As of the 2020 census, the MSA had a population of 702,219. The Akron MSA is also part of the larger Cleveland–Akron–Canton, OH Combined Statistical Area, which has a population of 3,633,962 people as of the 2020 census, the largest metropolitan area in Ohio. Historically, Greater Akron was known as the center of the United States' tire and rubber industry throughout the 20th century, and today one major tire company (Goodyear Tire and Rubber) still is based there. More recently, the area has become a center of polymer science research and manufacturing for the country, and is home to five Fortune 1000 corporations. Communities Places with more than 100,000 inhabitants *Akron (principal city) – 190,469 Pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Ohio
The region Northeast Ohio, in the US state of Ohio, in its most expansive usage contains six metropolitan areas ( Cleveland–Elyria, Akron, Canton–Massillon, Youngstown–Warren, Mansfield, and Weirton–Steubenville) along with eight micropolitan statistical areas. Most of the region is considered either part of the Cleveland–Akron–Canton, OH Combined Statistical Area and media market or the Youngstown–Warren, OH-PA Combined Statistical Area and media market. In total the region is home to 4,502,460 residents. It is also a part of the Great Lakes megalopolis, containing over 54 million people. Northeast Ohio also includes most of the area known historically as the Connecticut Western Reserve. In 2011, the Intelligent Community Forum ranked Northeast Ohio as a global Smart 21 Communities list. It has the highest concentration of Hungarian Americans in the United States. Composition Different sources define the region as having various boundaries. At its largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Names Information System
The Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) is a database of name and locative information about more than two million physical and cultural features throughout the United States and its territories, Antarctica, and the associated states of the Marshall Islands, Federated States of Micronesia, and Palau. It is a type of gazetteer. It was developed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) in cooperation with the United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) to promote the standardization of feature names. Data were collected in two phases. Although a third phase was considered, which would have handled name changes where local usages differed from maps, it was never begun. The database is part of a system that includes topographic map names and bibliographic references. The names of books and historic maps that confirm the feature or place name are cited. Variant names, alternatives to official federal names for a feature, are also recorded. Each feature receives a per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Information Processing Standard
The Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) of the United States are a set of publicly announced standards that the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed for use in computer systems of non-military, American government agencies and contractors. FIPS standards establish requirements for ensuring computer security and interoperability, and are intended for cases in which suitable industry standards do not already exist. Many FIPS specifications are modified versions of standards the technical communities use, such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Specific areas of FIPS standardization The U.S. government has developed various FIPS specifications to standardize a number of topics including: * Codes, e.g., FIPS county codes or codes to indicate weather conditions or emergency indications. In 1994, Nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)