|
Kashubs
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in north-central Poland. Their settlement area is referred to as Kashubia. They speak the Kashubian language, which is classified as a separate language closely related to Polish. The Kashubs are closely related to the Poles and sometimes classified as their subgroup. The Kashubs are grouped with the Slovincians as Pomeranians. Similarly, the Slovincian (now extinct) and Kashubian languages are grouped as Pomeranian languages, with Slovincian (also known as Łeba Kashubian) either a distinct language closely related to Kashubian,Dicky Gilbers, John A. Nerbonne, J. Schaeken, ''Languages in Contact'', Rodopi, 2000, p. 329, or a Kashubian dialect.Christina Yurkiw Bethin, ''Slavic Prosody: Language Change and Phonological Theory'', pp. 160ff, Camb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaszëbsczi Herb
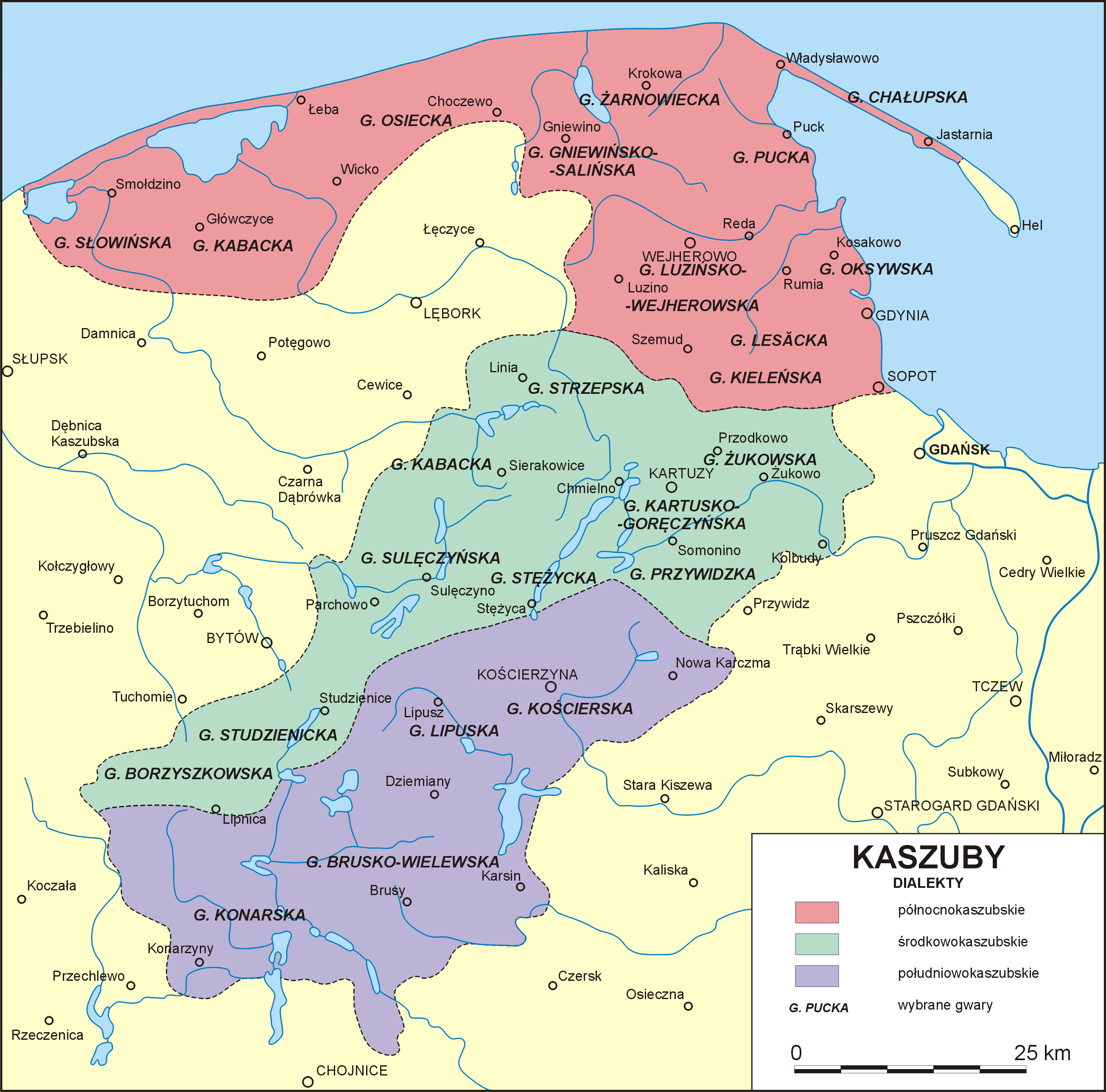
Kashubian or Cassubian (Kashubian: ', pl, język kaszubski) is a West Slavic language belonging to the Lechitic subgroup along with Polish and Silesian.Stephen Barbour, Cathie Carmichael, ''Language and Nationalism in Europe'', Oxford University Press, 2000, p.199, Although often classified as a language in its own right, it is sometimes viewed as a dialect of Pomeranian or as a dialect of Polish. In Poland, it has been an officially recognized ethnic-minority language since 2005. Approximately 108,000 people use mainly Kashubian at home. It is the only remnant of the Pomeranian language. It is close to standard Polish with influence from Low German and the extinct Polabian (West Slavic) and Old Prussian (West Baltic) languages. The Kashubian language exists in two different forms: vernacular dialects used in rural areas, and literary variants used in education. Origin Kashubian is assumed to have evolved from the language spoken by some tribes of Pomeranians called Kash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashubian Language
Kashubian or Cassubian (Kashubian: ', pl, język kaszubski) is a West Slavic language belonging to the Lechitic subgroup along with Polish and Silesian.Stephen Barbour, Cathie Carmichael, ''Language and Nationalism in Europe'', Oxford University Press, 2000, p.199, Although often classified as a language in its own right, it is sometimes viewed as a dialect of Pomeranian or as a dialect of Polish. In Poland, it has been an officially recognized ethnic-minority language since 2005. Approximately 108,000 people use mainly Kashubian at home. It is the only remnant of the Pomeranian language. It is close to standard Polish with influence from Low German and the extinct Polabian (West Slavic) and Old Prussian (West Baltic) languages. The Kashubian language exists in two different forms: vernacular dialects used in rural areas, and literary variants used in education. Origin Kashubian is assumed to have evolved from the language spoken by some tribes of Pomeranians called Kas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierakowice, Pomeranian Voivodeship
Sierakowice ( csb, Serakòjce; german: Sierakowitz) is a village in Kartuzy County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, Kashubia in northern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Sierakowice. It lies approximately west of Kartuzy and west of the regional capital Gdańsk. Kashubian language, Kashubian is here in official use, as a regional language or an auxiliary language.Gerald Stone, Slav outposts in Central European history : the Wends, Sorbs and Kashubs, London, UK : Bloomsbury Academic, an imprint of Bloomsbury Publishing Plc, 2016, pp. 348 - 9 This means that in principle, it is possible to address gmina's administration in Kashubian and receive an answer in the same language. In Sierakowice, roads direction signage is bilingual Polish/Kashubian. Kashubian vetch (''Vicia cassubica'') is native to the village. Kashubian vetch means vetch of Kashubia, the home of Kashubs. For details of the history of the region, see ''History of Pomerania''. Some o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg. Sorbs traditionally speak the Sorbian languages (also known as "Wendish" and "Lusatian"), which are closely related to Czech, Polish, Kashubian, Silesian, and Slovak. Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian are officially recognized minority languages in Germany. Due to a gradual and increasing assimilation between the 17th and 20th centuries, virtually all Sorbs also spoke German by the early 20th century. In the newly created German nation state of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, policies were implemented in an effort to Germanize the Sorbs. These policies reached their climax under the Nazi regime, who denied the existence of the Sorbs as a distinct Slavic people by referring to them as "Sorbian-speaking Germans". The communit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linia, Pomeranian Voivodeship
Linia ( csb, Lëniô; formerly german: Linde) is a village in Wejherowo County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Linia. It lies approximately south-west of Wejherowo and west of the regional capital Gdańsk. Kashubian is spoken in the village as a secondary language.Gerald Stone, Slav outposts in Central European history : the Wends, Sorbs and Kashubs, London, UK : Bloomsbury Academic, an imprint of Bloomsbury Publishing Plc, 2016, pp. 348 - 9 For details of the history of the region, see ''History of Pomerania The history of Pomerania starts shortly before 1000 AD with ongoing conquests by newly arrived Polans rulers. Before that, the area was recorded nearly 2000 years ago as Germania, and in modern-day times Pomerania is split between Germany and Pol ...''. Every year, the local Communal Cultural Centre organise the Kashubian Embroidery Competition in the village. The village has a population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kartuzy
Kartuzy () ( Kashubian ''Kartuzë'', ''Kartëzë'', or ''Kartuzé''; formerly german: Karthaus) is a town in northern Poland, located in the historic Eastern Pomerania (Pomerelia) region. It is the capital of Kartuzy County in Pomeranian Voivodeship. Geographical location Kartuzy is located about west of Gdańsk and south-east of the town of Lębork on a plateau at an altitude of approximately above sea level in the average. The plateau, which is divided by the Radaune lake, comprises the highest parts of the Baltic Sea Plate. In the west of this lake are the highest points of the headwaters of rivers Łeba, Słupia and Bukowina at an altitude of up to . A hill in the south of the lake is high. History Kartuzy was established about 1380 as a monastery for Carthusian monks descending from Prague in the Kingdom of Bohemia, after whom it received its name. The charterhouse was vested with large estates by the State of the Teutonic Order. According to the Second Peace of Tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szemud
{{Wejherowo-geo-stub ...
Szemud ( csb, Szëmôłd; formerly german: Schönwalde) is a village in Wejherowo County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Szemud. It lies approximately south of Wejherowo and north-west of the regional capital Gdańsk. The village has a population of 1,639. References Szemud Szemud ( csb, Szëmôłd; formerly german: Schönwalde) is a village in Wejherowo County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Szemud. It lies approximately south of Wej ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chmielno, Pomeranian Voivodeship
] Chmielno ( Kashubian language, Kashubian ''Chmielno'') is a village in Kartuzy County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, Kashubia in northern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Chmielno. It lies approximately west of Kartuzy and west of the regional capital Gdańsk. Kashubian ceramics from Chmielno is characterized by the motifs of the Kashubian star, fish-scales, tulips, lilies, wreaths, lilac branches, all complemented by wavy lines and dots. For details of the history of the region, see ''History of Pomerania The history of Pomerania starts shortly before 1000 AD with ongoing conquests by newly arrived Polans rulers. Before that, the area was recorded nearly 2000 years ago as Germania, and in modern-day times Pomerania is split between Germany and Pol ...''. The village has a population of 1,580. References Chmielno {{Kartuzy-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomeranian Language
), East Low German, East Pomeranian dialect The Pomeranian language (Polish: ''pomorszczyzna'' or ''język pomorski'', German: ''Pomoranisch'' or ''die pomoranische Sprache'') is in the Pomeranian group of Lechitic languages (Polish: ''grupa pomorska języków lechickich'', German: ''die pomoranische Gruppe der lechischen Sprachen'') within the West Slavic languages. In medieval contexts, it refers to the dialects spoken by the Slavic Pomeranians. In modern contexts, the term is sometimes used synonymously with " Kashubian" and may also include extinct Slovincian. The name ''Pomerania'' comes from Slavic , which means "andby the sea". Ancient Pomeranian During the early medieval Slavic migrations, the area between the Oder and Vistula rivers was settled by tribes grouped as Pomeranians. Their dialects, sometimes referred to as Ancient Pomeranian, had a transitory character between the Polabian dialects spoken west of Pomerania and the Old Polish dialects spoken to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship, Pomorskie Region, or Pomerania Province (Polish: ''Województwo pomorskie'' ; ( Kashubian: ''Pòmòrsczé wòjewództwò'' ), is a voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk. The voivodeship was established on January 1, 1999, out of the former voivodeships of Gdańsk, Elbląg and Słupsk, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1997. It is bordered by West Pomeranian Voivodeship to the west, Greater Poland and Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeships to the south, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship to the east, and the Baltic Sea to the north. It also shares a short land border with Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast), on the Vistula Spit. The voivodeship comprises most of Pomerelia (the easternmost part of historical Pomerania), as well as an area east of the Vistula River. The western part of the province, around Słupsk, belonged historically to Farther Pomerania. The central parts of the province belong to Pomer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benennungen der bekanntesten Städte etc., Meere, Seen, Berge und Flüsse in allen Theilen der Erde nebst einem deutsch-lateinischen Register derselben''. T. Ein Supplement zu jedem lateinischen und geographischen Wörterbuche. Dresden: G. Schönfeld’s Buchhandlung (C. A. Werner), 1861, p. 71, 237.); Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. * , )Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benennungen der bekanntesten Städte etc., Meere, Seen, Berge und Flüsse in allen Theilen der Erde nebst einem deutsch-lateinischen Register derselben''. T. Ein Supplement zu jedem lateinischen und geographischen Wörterbuche. Dresden: G. Schönf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpeg/1200px-Brama_Zuraw_W_Gdansku_(153003103).jpeg)