|
Kampfgeschwader 30
''Kampfgeschwader'' 30 (KG 30) was a Luftwaffe bomber wing during World War II. Service history Formed on 15 November 1939 in Greifswald. I Gruppe formed 1 September, II Gruppe on 23 September and III Gruppe on 1 January 1940, based in Greifswald then Barth. IV Gruppe was formed 27 Oct 1940 as Erg.Sta./KG 30, and in April 1941 was increased to Gruppe strength. KG 30 was equipped with the Junkers Ju 88 and was initially trained as an anti-shipping and maritime attack unit: at the start of October 1939 it was attached to X. Fliegerkorps. On 16 October 1939 it attacked naval ships anchored off Rosyth Dockyard in the Firth of Forth. II./KG 30 operated under ''X. Fliegerkorps'' for Operation Weserübung, the invasion of Norway. The unit Ju 88s engaged Allied shipping as its main target. On 9 April 1940, in cooperation with high-level bombing Heinkel He 111s of KG 26, Ju 88s of II./KG 30 dive-bombed and damaged the battleship and sank the destroyer . The unit lost four Ju 88s in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an aircraft occurred in the Italo-Turkish War, with the first major deployments coming in the World War I, First World War and World War II, Second World War by all major airforces causing devastating damage to cities, towns, and rural areas. The first purpose built bombers were the Italy, Italian Caproni Ca 30 and United Kingdom, British Bristol T.B.8, both of 1913. Some bombers were decorated with nose art or victory markings. There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strategic bombing is done by heavy bombers primarily designed for long-range bombing missions against strategic targets to diminish the enemy's ability to wage war by limiting access to resources through crippling infrastructure or reduci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the City Region of Amsterdam, urban area and 2,480,394 in the Amsterdam metropolitan area, metropolitan area. Located in the Provinces of the Netherlands, Dutch province of North Holland, Amsterdam is colloquially referred to as the "Venice of the North", for its large number of canals, now designated a World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site. Amsterdam was founded at the mouth of the Amstel River that was dammed to control flooding; the city's name derives from the Amstel dam. Originally a small fishing village in the late 12th century, Amsterdam became a major world port during the Dutch Golden Age of the 17th century, when the Netherlands was an economic powerhouse. Amsterdam is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber Wings Of The Luftwaffe 1933-1945
A bomber is a military combat aircraft designed to attack ground and naval targets by dropping air-to-ground weaponry (such as bombs), launching torpedoes, or deploying air-launched cruise missiles. The first use of bombs dropped from an aircraft occurred in the Italo-Turkish War, with the first major deployments coming in the First World War and Second World War by all major airforces causing devastating damage to cities, towns, and rural areas. The first purpose built bombers were the Italian Caproni Ca 30 and British Bristol T.B.8, both of 1913. Some bombers were decorated with nose art or victory markings. There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strategic bombing is done by heavy bombers primarily designed for long-range bombing missions against strategic targets to diminish the enemy's ability to wage war by limiting access to resources through crippling infrastructure or reducing industrial output. Tactical bombing is aimed at countering en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanns Heise
Hanns Horst Heise (1 February 1913 – 18 May 1992) was a highly decorated Oberstleutnant in the Luftwaffe during World War II, and a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross. The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross was awarded to recognise extreme battlefield bravery or successful military leadership. Awards and decorations * Aviator badge * Front Flying Clasp of the Luftwaffe * Ehrenpokal der Luftwaffe (15 September 1941) * Iron Cross (1939) ** 2nd Class ** 1st Class * German Cross in Gold (13 January 1942) * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 3 September 1942 as ''Hauptmann is a German word usually translated as captain when it is used as an officer's rank in the German, Austrian, and Swiss armies. While in contemporary German means 'main', it also has and originally had the meaning of 'head', i.e. ' literally ...'' and '' Gruppenkommandeur'' of the IV./Kampfgeschwader 76Fellgiebel 2000, p. 179. * Legion of Merit 1971 References Citations Bibliography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernhard Jope
Bernhard Jope (10 May 1914 – 31 July 1995) was a German bomber pilot during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves of Nazi Germany. As part of Kampfgeschwader 40 (bomber wing), Jope flew missions across the North Sea and Atlantic Ocean in support of the German navy, damaging in October 1940 the . In 1943, he led Kampfgeschwader 100 in the attacks on the , the British battleship and cruiser , and the US cruiser . Biography Bernhard Jope joined the military service of the Luftwaffe on 1 April 1935 after graduating from the ''Königliche Technische Hochschule zu Danzig'' (technical university in Gdańsk-Wrzeszcz) in aircraft construction. Prior to joining the military service he had already almost completed his flight training at the ''Deutsche Verkehrsfliegerschule'' (German Air Transport School). In support of the ''Kriegsmarine'', Jope flew the Focke-Wulf Fw 200 Condor on experimental missions across the North Sea and Atla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmund-Ulrich Freiherr Von Gravenreuth
The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross (german: Ritterkreuz des Eisernen Kreuzes) and its variants were the highest awards in the military and paramilitary forces of Nazi Germany during World War II. The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross was awarded for a wide range of reasons and across all ranks, from a senior commander for skilled leadership of his troops in battle to a low-ranking soldier for a single act of extreme gallantry. A total of 7,321 awards were made between its first presentation on 30 September 1939 and its last bestowal on 17 June 1945. This number is based on the acceptance by the Association of Knight's Cross Recipients (AKCR). Presentations were made to members of the three military branches of the Wehrmacht—the Heer (Army), Kriegsmarine (Navy) and Luftwaffe (Air Force)—as well as the Waffen-SS, the Reich Labour Service and the Volkssturm (German national militia). There were also 43 foreign recipients of the award. These recipients are listed in the 1986 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Bloedorn
Erich Bloedorn (6 July 1902 – 30 November 1975) was a German Luftwaffe bomber pilot and recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross during World War II. The Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross was awarded to recognise extreme battlefield bravery or successful military leadership. Life Bloedorn studied at the University of Königsberg and became a member of the Corps Masovia in summer 1921. In 1924 he gave up studying and joined the Reichswehr in Allenstein, Masuria. When he was lieutenant in the :de:2. (Preußisches) Infanterie-Regiment (Reichswehr) in Lötzen he made a bet: to reach Istanbul via Munich within 10 days, alone by motorcycle. He did and the German embassy gave a function. He retired major from the Reichswehr in 1930 to serve on the General Staff of former ''Generaloberst'' Hans von Seeckt, who served as a military advisor to Chiang Kai-shek in Nanking and Shanghai. In 1936 Bloedorn joined the Luftwaffe and served as Hauptmann in Berlin. In 1940 he b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbert Rieckhoff
__NOTOC__ Herbert Rieckhoff (25 December 1898 – 30 November 1948) was a German general during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. Awards and decorations * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 5 July 1941 as ''Oberst'' and '' Geschwaderkommodore'' of Kampfgeschwader 2 * German Cross The War Order of the German Cross (german: Der Kriegsorden Deutsches Kreuz), normally abbreviated to the German Cross or ''Deutsches Kreuz'', was instituted by Adolf Hitler on 28 September 1941. It was awarded in two divisions: in gold for repe ... in Gold on 27 July 1943 as ''Oberst im Generalstab'' (in the General Staff) of Luftflotte 1Patzwall & Scherzer 2001, p. 378. References Citations Bibliography * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Rieckhoff, Herbert 1898 births 1948 deaths Military personnel from Berlin People from the Province of Brandenburg German Army personnel of World War I Luftwaffe World War II generals Recipients of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
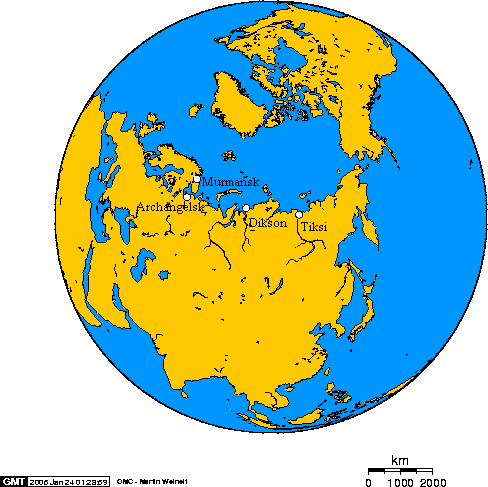
Golden Comb (tactic)
The Golden Comb (german: die Goldene Zange) was an anti-ship tactic developed by the during the Second World War for use against Allied convoys taking supplies to the Soviet Union by the Arctic route. It was first employed against Convoy PQ 18 in September 1942. Background Before 1942 the lacked a means to attack ships at sea due to the inter-service rivalry between the , which regarded all air operations as its domain and the German navy (), which saw the development, production and use of torpedoes as naval matter. Germany had no torpedo bomber force, in contrast to the forces of other world powers, even the other Axis nations like Italy with the land-based or the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service which used the Type 91 torpedo in the Attack on Pearl Harbor, having revealed its manufacturing details to Germany in early August 1942. In early 1942, when the Allied Arctic convoy cycle was becoming well established, the was ordered to form a torpedo bomber force. Two , III/ ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convoy PQ 18
Convoy PQ 18 was an Arctic convoy of forty Allied freighters from Scotland and Iceland to Arkhangelsk in the Soviet Union in the war against Nazi Germany. The convoy departed Loch Ewe, Scotland on 2 September 1942, rendezvoused with more ships and escorts at Iceland and arrived at Arkhangelsk on 21 September. An exceptionally large number of escorts was provided by the Royal Navy in Operation EV, including the first escort carrier to accompany an Arctic convoy. Detailed information on German intentions was provided by the code breakers at Bletchley Park and elsewhere, through Ultra signals decrypts and eavesdropping on ''Luftwaffe'' wireless communications. The German ''B-Dienst'' read some British signals and ''Luftwaffe'' used the lull in convoys after Convoy PQ 17 (27 June – 10 July) to prepare a maximum effort with the ''Kriegsmarine''. From 12 to 21 September PQ 18 was attacked by bombers, torpedo-bombers, U-boats and mines, which sank thirteen ships at a cost of forty-fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KG 4
''Kampfgeschwader'' 4 "General Wever" (KG 4) (Battle Wing 4) was a Luftwaffe bomber wing during World War II. The unit was formed in May 1939. The unit operated the Dornier Do 17, Junkers Ju 88 and Heinkel He 111 medium bombers, with later service on the Heinkel He 177 heavy bomber. The wing was named after General Walther Wever, the prime pre-war proponent for a strategic bombing capability for the Luftwaffe, who was killed in an aircraft accident in 1936. History ''Stab''/KG 4 and I./KG 4 were formed on 1 May 1939 at Erfurt and was initially equipped with the He 111 Ps, borrowed from KG 253. The unit spent most of the summer training and recruiting personnel from the flight schools. Operational history Invasion of Poland On 25 August the unit was transferred to Langenau under the Command of ''Luftflotte 4''. It began the Polish Campaign attacking airfields and railway yards. ''Stab''/KG 4 was withdrawn on 20 September. I./KG 4 attacked airfields at Dęblin and Krakow on 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schiphol
Amsterdam Airport Schiphol , known informally as Schiphol Airport ( nl, Luchthaven Schiphol, ), is the main international airport of the Netherlands. It is located southwest of Amsterdam, in the municipality of Haarlemmermeer in the province of North Holland. It is the world's third busiest airport by international passenger traffic in 2021. With almost 72 million passengers in 2019, it is the third-busiest airport in Europe in terms of passenger volume and the busiest in Europe in terms of aircraft movements. With an annual cargo tonnage of 1.74 million, it is the 4th busiest in Europe. AMS covers a total area of of land. The airport is built on the single-terminal concept: one large terminal split into three large departure halls. Schiphol is the hub for KLM and its regional affiliate KLM Cityhopper as well as for Corendon Dutch Airlines, Martinair, Transavia and TUI fly Netherlands. The airport also serves as a base for EasyJet. Schiphol opened on 16 September 1916 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)