|
Kamares (dance)
{{disambig ...
Kamares (Greek: Καμάρες, "arches") may refer to the following places: in Cyprus: *the Kamares aqueduct in Larnaca in Greece: *Kamares, Achaea, a town in the northern part of Achaea *Kamares, Crete, a village in the southern part of the Heraklion regional unit, Crete *Kamares, Sifnos, a village on the island of Sifnos * Kamares, Laconia, a village in the municipal unit Gytheio, Laconia *the Kavala aqueduct, popularly known as ''Kamares'' in Turkey: *the Greek name for the village at the site of the ancient city of Parium Parium (or Parion; el, Πάριον) was a Greek city of Adrasteia in Mysia on the Hellespont. Its bishopric was a suffragan of Cyzicus, the metropolitan see of the Roman province of Hellespontus. History Founded in 709 B.C., the ancient city ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyprus
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an island country located south of the Anatolian Peninsula in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geographically in Western Asia, its cultural ties and geopolitics are overwhelmingly Southern European. Cyprus is the third-largest and third-most populous island in the Mediterranean. It is located north of Egypt, east of Greece, south of Turkey, and west of Lebanon and Syria. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. The northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which was established after the 1974 invasion and which is recognised as a country only by Turkey. The earliest known human activity on the island dates to around the 10th millennium BC. Archaeological remains include the well-preserved ruins from the Hellenistic period such as Salamis and Kourion, and Cypr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bekir Pasha Aqueduct
Kamares Aqueduct, also known as the Bekir Pasha Aqueduct, is an aqueduct near Larnaca, Cyprus. Located outside the city, near the old road to Limassol, it was built starting in 1747. Tassos Mikropoulos has described it as the most prominent water supply built in Cyprus. History The aqueduct was financed by Ebubekir Pasha Ebubekir Pasha ( ota, ابوبکر پاشا; tr, Ebubekir Paşa; 1670 – 1757/1758Tosun, Sevilay"Ebubekir Paşa Ve Kıbrıs'taki İmar Faaliyetleri." Cumhuriyet University Journal of Social Sciences 28.2 (2004): 205-13. Web. 14 Oct. 2013.), also ... (also known as Koca Bekir Pasha or Abu Bakr Pasha) who was the Ottoman Governor of Larnaca.. The structure was in operation until 1939 and consists of 75 arches.. The construction of the aqueduct commenced in 1747 and was completed in 1750, costing a total of 50,000 qirsh which was paid by Ebubekir Pasha. Foreign travellers have often counted it as one of the most important monument constructed during the Otto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larnaca
Larnaca ( el, Λάρνακα ; tr, Larnaka) is a city on the south east coast of Cyprus and the capital of the district of the same name. It is the third-largest city in the country, after Nicosia and Limassol, with a metro population of 144,200 in 2015. Larnaca is known for its palm-tree seafront also called Finikoudes (Greek: Φινικούδες) as well as the Church of Saint Lazarus, Hala Sultan Tekke, Kamares Aqueduct, and Larnaca Castle. It is built on the ruins of ancient Citium, which was the birthplace of Stoic philosopher Zeno. Larnaca is home to the country's primary airport, Larnaca International Airport. It also has a seaport and a marina. Names The name ''Larnaca'' originates from the Ancient Greek noun 'coffer, box; chest, e.g. for household stores; cinerary urn, sarcophagus, coffin; drinking trough, chalice'. An informal etymology attributes the origin of the name to the many ''larnakes'' (sarcophagi) that have been found in the area. Sophocles Hadjisavv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the northeast. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the Geography of Greece, mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring List of islands of Greece, thousands of islands. The country consists of nine Geographic regions of Greece, traditional geographic regions, and has a population of approximately 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras. Greece is considered the cradle of Western culture, Western civilization, being the birthplace of Athenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamares, Achaea
Kamares (Greek: Καμάρες) is a village and a community in the east-northeastern part of Achaea, Greece. Kamares was an independent commune until 1994 when it became part of the municipality of Erineos, of which it was the seat. Erineos became part of the municipality Aigialeia in 2011. The community Kamares consists of the villages Kamares, Bouka and Pefka. Kamares is situated near the Gulf of Corinth, 9 km northwest of Aigio. The Greek National Road 8A Greek National Road 8a ( el, Εθνική Οδός 8a, abbreviated as EO8a) was a toll road in the Attica, Peloponnese and West Greece regions. It connected Athens with the cities of Corinth and Patras. It was built in the 1960s as a replacemen ... (Patras - Corinth) and the railway from Patras to Corinth ( not in operation anymore since OSE announced the suspension of all the rail service in the Peloponnese in January 2011) run through the village. Historical population External linksOfficial website of the munici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamares, Crete
Kamares ( el, Καμάρες) is a village in south-central Crete, Greece. It is the location of an archaeological site of a Minoan sacred cave. The sacred cave at Kamares is slightly offset from a saddle in the Psiloriti Range virtually aligned with the location of nearby Phaistos. Some of the best examples of Middle Minoan pottery have been recovered from the Kamares cave.Gerald Cadogan (1991) '' Palaces of Minoan Crete'', Routledge, 164 pages Kamares has provided the type name for Kamares ware, a ceramic type dating from MM IA, or the First Palace Period. This pottery is a light-on-dark polychrome ware, with forms including jugs and cups. See also *Hagia Triada Hagia Triada (also Ayia Triada, Agia Triada, Agia Trias, , " Holy Trinity") is the archaeological site of an ancient Minoan settlement. Hagia Triada is situated on the western end of a prominent coastal ridge, with Phaistos at the eastern end and ... References Minoan sites in Crete Ancient caves of Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
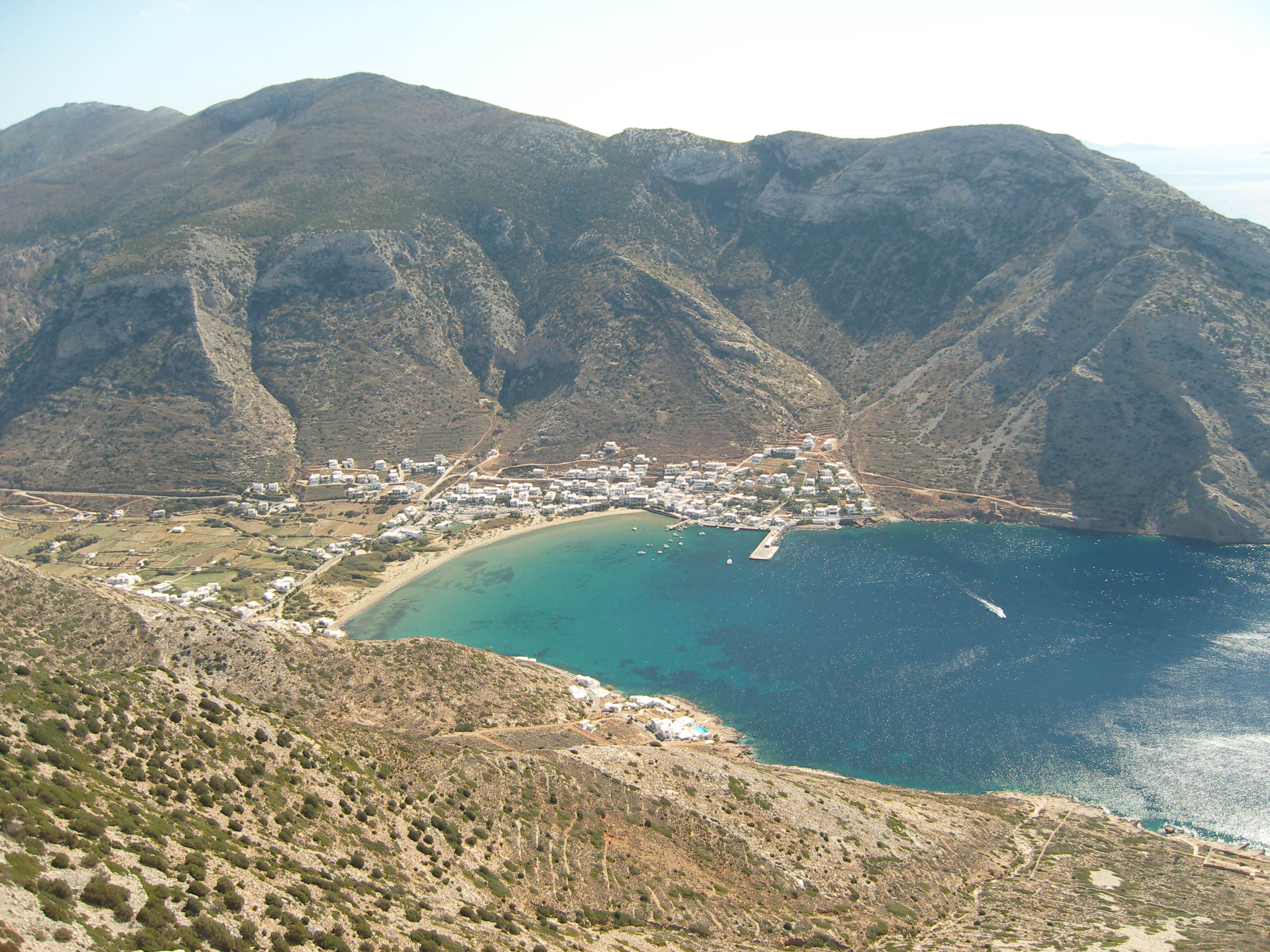
Kamares, Sifnos
Kamares (Greek: Καμάρες) is a village and the main port for the island of Sifnos, Greece Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders .... Kamares is situated in the western side of the island on a natural harbor. The village has a large beach with many restaurants and hotels. The buildings in Kamares form a U-shape around the bay, with most restaurants and shops being directly on the water, and typically the hotels and houses on the hill above them. Visitors to the island arrive via the ferry terminal in the harbor; nearby bus service connects Kamares to the other villages of Sifnos. Gallery File:Bay of Kamares.jpg, Bay of Kamares File:Kamares from Ag. Marina, Sifnos, 15M6920.jpg, View from Agia Marina Church File:Beach of Kamares, Sifnos at Noon.jpg, Beach at Noon File:Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sifnos
Sifnos ( el, Σίφνος) is an island municipality in the Cyclades island group in Greece. The main town, near the center, known as Apollonia (pop. 869), is home of the island's folklore museum and library. The town's name is thought to come from an ancient temple of Apollo on the site of the church of Panayia Yeraniofora. The second-largest town is Artemonas (pop. 800), thought to be named after an ancient temple of Apollo's sister-goddess Artemis, located at the site of the church of Panayia Kokhi. The village of Kastro (pop. 118), was the capital of the island during ancient times until 1836. It is built on top of a high cliff on the island's east shore and today has extensive medieval remains and is the location of the island's archeological museum. The port settlement, on the west coast of the island is known as Kamares (245). Geography Sifnos lies in the Cyclades between Serifos and Milos, west of Delos and Paros, about (80 nautical miles) from Piraeus (Athens' p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
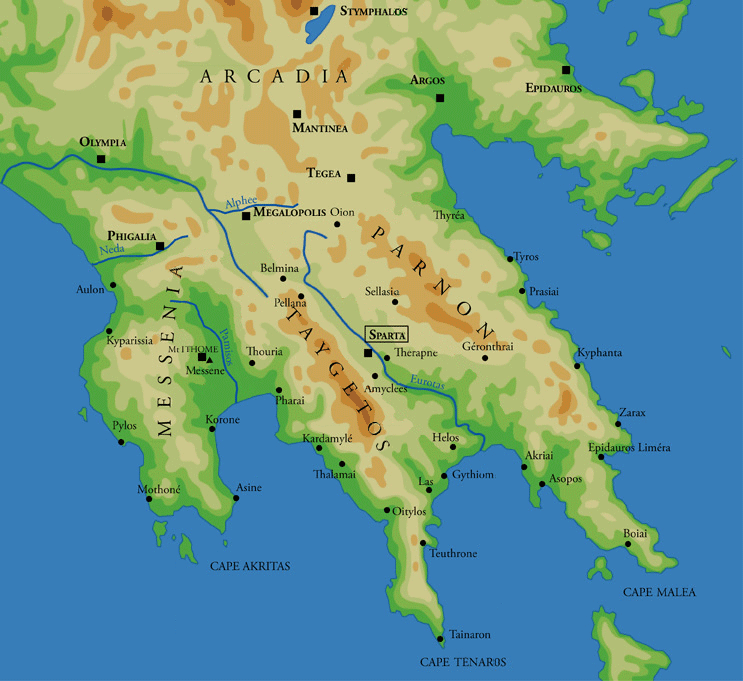
Gytheio
Gytheio ( el, Γύθειο, ) or Gythio, also the ancient Gythium or Gytheion ( grc, Γύθειον), is a town on the eastern shore of the Mani Peninsula, and a former municipality in Laconia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality East Mani, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 197.313 km2. It was the seaport of Sparta, some north. Gytheio is the site of ancient Cranae, a tiny island where according to legend Paris of Troy and Helen from Sparta spent their first night together before departing for Troy, thus igniting the Trojan War. Gytheio used to be an important port until it was destroyed in 4th century AD, possibly by an earthquake. Even thereafter its strategic location gave Gytheio a significant role in Maniot history. Today it is the largest and most important town in Mani. It is also the seat of the municipality of East Mani. Historical population Geography Gytheio is located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavala Aqueduct
The Aqueduct of Kavala, popularly known as the Kamares ( el, Καμάρες, "arches"), is a well-preserved aqueduct in the city of Kavala, Greece, and is one of the city's landmarks. While the aqueduct is of Roman origin, the present structure built by the Ottomans in the 16th century. A Byzantine barrier wall of the early 14th century, built as part of the fortifications on the Acropolis of Kavala, probably also functioned as an aqueduct. If so, it would have been a rare example of a Byzantine aqueduct, since Byzantine cities more typically used wells and cisterns rather than either maintaining existing Roman aqueducts or building new ones. The barrier wall was replaced with the present arched aqueduct during Suleiman the Magnificent's repair and improvement of the Byzantine fortifications. Some authors date that construction to the time of the 1522 Siege of Rhodes, but a more likely date is between 1530 and 1536. As late as 1911, it supplied the city with drinking water from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |