|
Kaliman I Asen
Kaliman Asen I, also known as Coloman Asen I or Koloman ( bg, Калиман Асен I; 1234-August/September 1246) was Emperor (Tsar) of Bulgaria from 1241 to 1246. He was the son of Ivan Asen II of Bulgaria and Anna Maria of Hungary. He was only seven when he succeeded his father in 1241. In the following years, the Mongols invaded Bulgaria and imposed a yearly tax on the country. He may have been poisoned, according to contemporaneous rumors about his death. Early life Kaliman was the son of Ivan Asen II of Bulgaria and Anna Maria of Hungary. He was born in 1234. His mother died before 1237, when his widowed father married Irene Komnene Doukaina. Ivan Asen also died in the first half of 1241. Reign Kaliman was only seven when he succeeded his father. Although no primary sources provide information about the government of the country during the minor monarch's reign, Bulgaria was obviously ruled by one or more regents. Historian Alexandru Madgearu proposes that Ivan Ase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bulgarian Monarchs
The monarchs of Bulgaria ruled the country during three periods of Bulgaria's history as an independent country: from the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 to the Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria in 1018; from the Uprising of Asen and Peter that established the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1185 to the annexation of the rump Bulgarian state into the Ottoman Empire in 1396; and from the re-establishment of an independent Principality of Bulgaria in 1878 to the abolition of monarchy in a referendum held on 15 September 1946. This list does not include the mythical Bulgar rulers and the rulers of Old Great Bulgaria listed in the Nominalia of the Bulgarian rulers, as well as unsuccessful claimants to the throne who are not generally listed among the Bulgarian monarchs, neither rulers of Volga Bulgaria, or other famous Bulgarian rulers as Kuber or Alcek. Early Bulgarian rulers possibly used the title ''Kanasubigi'' (possibly related to Knyaz, Khan) before the 7th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batu Khan
Batu Khan ( – 1255),, ''Bat haan'', tt-Cyrl, Бату хан; ; russian: хан Баты́й was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Golden Horde, a constituent of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi, thus a grandson of Genghis Khan. His '' ulus'' ruled over the Kievan Rus', Volga Bulgaria, Cumania, and the Caucasus for around 250 years. Personality and appearance According to Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, Batu was "kind enough to his own people, but he is greatly feared by them. He is, however, most cruel in fight; he is very shrewd and extremely crafty in warfare, for he has been waging war for a long time." William of Rubruck described him as about the height of his lord John de Beaumont and his entire face was covered with reddish spots. Early years After his son Jochi's death, Genghis Khan assigned Jochi's appanages to his sons. The Great Khan installed Batu as Khan of the Golden Horde (also known as the Ulus of Jochi or Kipchak Khanate). Jochi's eldest son, Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
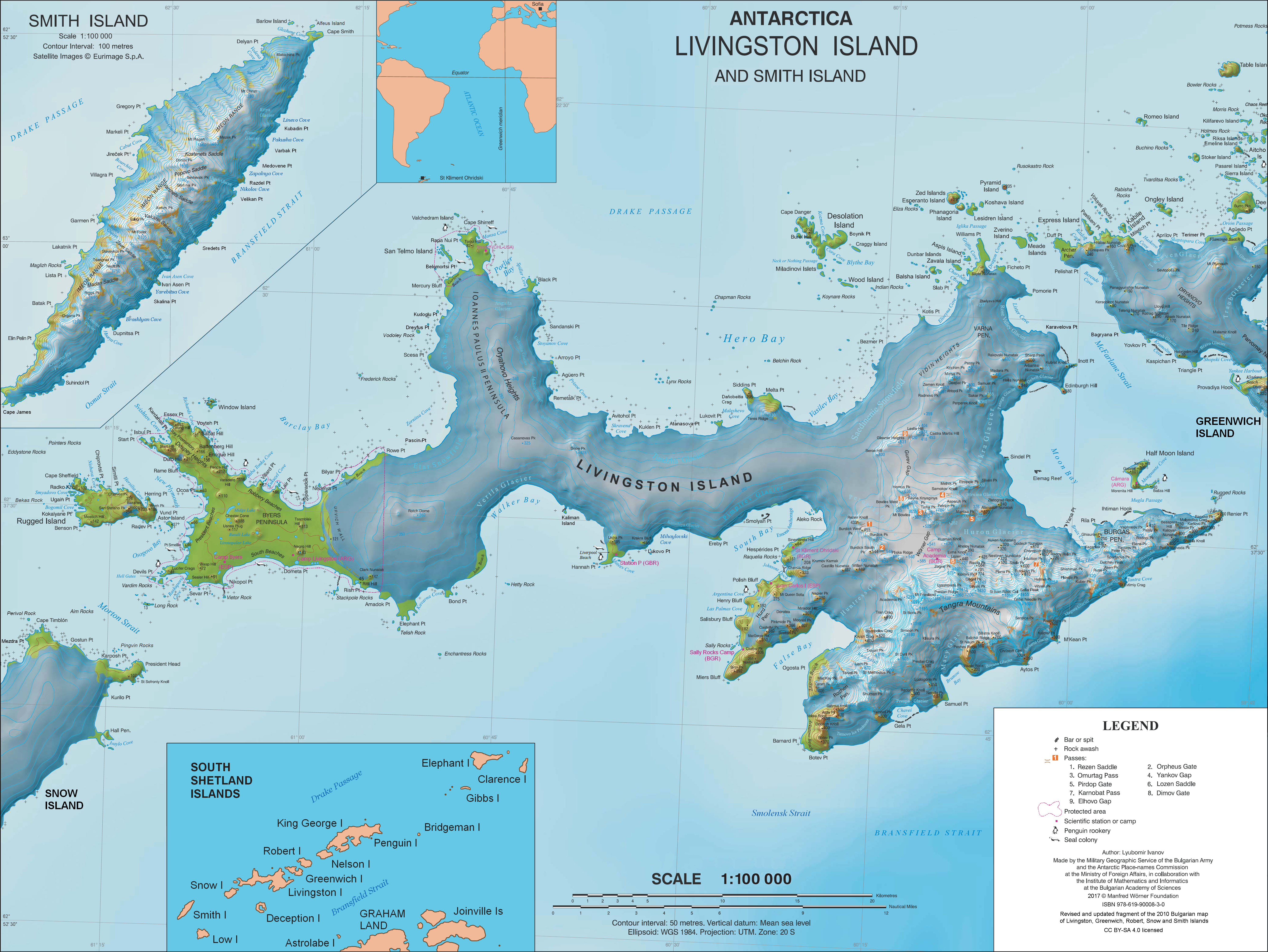
Kaliman Island
Kaliman Island ( bg, остров Калиман, ostrov Kaliman, ) is the triangular, flat rocky island extending 250 m in south-southeast to north-northwest direction and 80 m wide in Walker Bay, Livingston Island in Antarctica. It is named after Czar Kaliman Asen of Bulgaria (1241–1246 AD). Location Kaliman Island is located at , which is 3.9 km northwest of Hannah Point, 9.5 km northeast of Bond Point and 4.62 km south of Snow Peak, and connected to Livingston Island on the north by a 600 m long moraine tombolo. Formed as result of the retreat of Verila Glacier in the first decade of 21st century. Bulgarian mapping in 2009 and 2017. Maps * L.L. IvanovAntarctica: Livingston Island and Greenwich, Robert, Snow and Smith Islands Scale 1:120000 topographic map. Troyan: Manfred Wörner Foundation, 2009. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Central and Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester River. An initially independent and later autonomous state, it existed from the 14th century to 1859, when it united with Wallachia () as the basis of the modern Romanian state; at various times, Moldavia included the regions of Bessarabia (with the Budjak), all of Bukovina and Hertsa. The region of Pokuttya was also part of it for a period of time. The western half of Moldavia is now part of Romania, the eastern side belongs to the Republic of Moldova, and the northern and southeastern parts are territories of Ukraine. Name and etymology The original and short-lived reference to the region was ''Bogdania'', after Bogdan I, the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vissarion Of Bulgaria
Vissarion ( bg, Висарион) was a Patriarch of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church in the 13th century. He is the only Bulgarian Patriarch who was not included in the list of Patriarchs in the medieval ''Book of Boril''. The only testimony of his existence is an undated seal reading "Vissarion, by the grace of God Patriarch of the Bulgarians". It is suggested that he presided over the Bulgarian Church during the rule of emperor Ivan Asen II (r. 1218–1241) and was omitted in the lists because he supported the union with the Catholic Church concluded by emperor Kaloyan (r. 1197–1207) and abolished by Ivan Asen II. Bulgarian historians believe he can be identified with "Patriarch Spiridon", known from a recently discovered hagiography, whose name is not mentioned in any historical sources. In 1238 that Patriarch opposed the third marriage of Ivan Asen II to Irene Komnene Doukaina because it was non-canonical. The emperor, who loved Irene "no less than Marcus Antonius loved Cleopatr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Akropolites
George Akropolites ( Latinized as Acropolites or Acropolita; el, , ''Georgios Akropolites''; 1217 or 1220 – 1282) was a Byzantine Greek historian and statesman born at Constantinople. Life In his sixteenth year he was sent by his father, the logothete Constantine Akropolites the elder, to the court of John III Doukas Vatatzes, emperor of Nicaea, where Akropolites continued his studies under Theodore Hexapterygos and Nicephorus Blemmydes. The emperor afterwards entrusted George with important state missions, as did his successors (Theodore II Laskaris and Michael VIII Palaiologos). The office of Grand Logothete, or chancellor, was bestowed upon him in 1244. As commander in the field in 1257 against Michael II, despot of Epirus, he showed little military ability. George was captured and kept for two years in prison, from which he was released by Michael Palaiologos. Meanwhile, Michael Palaiologos was proclaimed emperor of Nicaea, afterwards expelling the Latins from Constan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of Rome, which has ecclesiastical jurisdiction over the Catholic Church and the sovereign city-state known as the Vatican City. According to Catholic tradition it was founded in the first century by Saints Peter and Paul and, by virtue of Petrine and papal primacy, is the focal point of full communion for Catholic Christians around the world. As a sovereign entity, the Holy See is headquartered in, operates from, and exercises "exclusive dominion" over the independent Vatican City State enclave in Rome, of which the pope is sovereign. The Holy See is administered by the Roman Curia (Latin for "Roman Court"), which is the central government of the Catholic Church. The Roman Curia includes various dicasteries, comparable to ministries and ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Communion
Full communion is a communion or relationship of full agreement among different Christian denominations that share certain essential principles of Christian theology. Views vary among denominations on exactly what constitutes full communion, but typically when two or more denominations are in full communion it enables services and celebrations, such as the Eucharist, to be shared among congregants or clergy of any of them with the full approval of each. Definition and terminology Full communion is an ecclesiological term for an established relationship between Christian denominations that may be constituted by shared eucharist, doctrine, and ecclesiology. Different denominations emphasize different aspects or define the term differently. Several Protestant denominations base their idea of full communion on the Augsburg Confession which says that "the true unity of the church" is present where "the gospel is rightly preached and sacraments rightly administered." They believe tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Orthodox Church
The Bulgarian Orthodox Church ( bg, Българска православна църква, translit=Balgarska pravoslavna tsarkva), legally the Patriarchate of Bulgaria ( bg, Българска патриаршия, links=no, translit=Balgarska patriarshiya), is an autocephalous Orthodox jurisdiction. It is the oldest Slavic Orthodox church, with some 6 million members in Bulgaria and between 1.5 and 2 million members in a number of European countries, the Americas, Australia, New Zealand and Asia. It was recognized as autocephalous in 1945 by the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople. History Early Christianity The Bulgarian Orthodox Church has its origin in the flourishing Christian communities and churches set up in the Balkans as early as the first centuries of the Christian era. Christianity was brought to the Balkans by the apostles Paul and Andrew in the 1st century AD, when the first organised Christian communities were formed. By the beginning of the 4th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Council Of Lyon
The First Council of Lyon (Lyon I) was the thirteenth ecumenical council, as numbered by the Catholic Church, taking place in 1245. The First General Council of Lyon was presided over by Pope Innocent IV. Innocent IV, threatened by Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II, arrived at Lyon on 2 December 1244, and early the following year he summoned the Church's bishops to the council later that same year. Some two hundred and fifty prelates responded including the Latin Patriarchs of Constantinople, Antioch, and Aquileia (Venice) and 140 bishops. The Latin emperor Baldwin II of Constantinople, Raymond VII, Count of Toulouse, and Raymond Bérenger IV, Count of Provence were among those who participated. With Rome under siege by Emperor Frederick II, the pope used the council to excommunicate and depose the emperor with '' Ad Apostolicae Dignitatis Apicem'', as well as the Portuguese King Sancho II. The council also directed a new crusade (the Seventh Crusade), under the command of L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Innocent IV
Pope Innocent IV ( la, Innocentius IV; – 7 December 1254), born Sinibaldo Fieschi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 25 June 1243 to his death in 1254. Fieschi was born in Genoa and studied at the universities of Parma and Bologna. He was considered in his own day and by posterity as a fine canonist. On the strength of this reputation, he was called to the Roman Curia by Pope Honorius III. Pope Gregory IX made him a cardinal and appointed him governor of the March of Ancona in 1235. Fieschi was elected pope in 1243 and took the name Innocent IV. As pope, he inherited an ongoing dispute over lands seized by the Holy Roman Emperor, and the following year he traveled to France to escape imperial plots against him in Rome. He returned to Rome after the death in 1250 of the Emperor Frederick II. Early life Born in Genoa (although some sources say Manarola) in an unknown year, Sinibaldo was the son of Beatrice Grillo and Ugo Fieschi, Count of Lavag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaccea
Isaccea (; tr, İshakçı) is a small town in Tulcea County, in Northern Dobruja, Romania, on the right bank of the Danube, 35 km north-west of Tulcea. According to the 2011 census, it has a population of 4,955. The town has been inhabited for thousands of years, as it is one of the few places in all the Lower Danube that can be easily forded and thus an easy link between the Balkans and the steppes of Southern Ukraine and Russia, north of the Black Sea. The Danube was for a long time the border between the Romans, later Byzantines and the "barbarian" migrating tribes in the north, making Isaccea a border town, conquered and held by dozens of different peoples. Geography The town has under its administration 103.97 km², of which 3.69 km² are inside the residential areas. The town is divided into three settlements: Isaccea proper (4,789 inhabitants) and two villages, Revărsarea (563 inhabitants) and Tichilești (10 inhabitants). The Tulcea – Brăila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |