|
Kalbeliya
The Kalbelia are a snake charming tribe from the Thar Desert in Rajasthan, India. The dance is an integral part of their culture and performed by men and women. Kalbelia tribe Kalbelias are followers of Sage Kanifnath, who drank a bowl of poison and was blessed with control over venomous snakes and animals. Kalbelias are divided in two main groups, the Daliwal and Mewara. The Kalbelias moved frequently from one place to another in ancient times. Their traditional occupation is catching snakes and trading snake venom. They rear snakes, dogs, hens, horses, donkeys, pigs and goats. Hence, the dance movements and the costumes of their community bear a resemblance to those of the serpents. They are also called Sapera and Jogira, Gattiwala and Poogiwara. The largest cluster of the Kalbelias is in Pali district, followed by significant other groups in Ajmer, Chittorgarh and Udaipur district. They live a nomadic life and belong to the scheduled tribes. Traditionally, Kalbelia men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulabo Sapera
Gulabo Sapera (aka Gulabo or Dhanvantri; born 1973) is an Indian dancer from Rajasthan, India. Personal life Gulabo was born in 1973 in the nomadic Kalbaliya community. She was the seventh child of her parents. Gulabo Sapera became a celebrity dancer later in life. In 2011, Gulabo featured in the reality television show Bigg Boss as contestant no. 12. On the show, she told the audience that she had been buried alive right after her birth, to be rescued by her mother and aunt. Awards *The Government of India awarded her the Padma Shri Padma Shri ( IAST: ''padma śrī''), also spelled Padma Shree, is the fourth-highest civilian award of the Republic of India, after the Bharat Ratna, the Padma Vibhushan and the Padma Bhushan. Instituted on 2 January 1954, the award is conf ... in 2016. *Bharat Gaurav Award 2021 Television References Indian female dancers Living people Recipients of the Padma Shri in arts 1960 births Dancers from Rajasthan 21st-century I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake Charming
Snake charming is the practice of appearing to hypnotize a snake (often a cobra) by playing and waving around an instrument called a pungi. A typical performance may also include handling the snakes or performing other seemingly dangerous acts, as well as other street performance staples, like juggling and sleight of hand. The practice was historically the profession of some tribesmen in India well into the 20th century but snake charming declined rapidly after the government banned the practice in 1972. Snake-charmer performances still happen in other Asian nations such as Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Malaysia. The tradition is also practiced in North African countries of Egypt, Morocco, and Tunisia. Ancient Egypt was home to one form of snake charming, though the practice as it exists today likely arose in India. It eventually spread throughout Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and North Africa. Despite a sort of golden age in the 20th century, snake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nāga
The Nagas (IAST: ''nāga''; Devanāgarī: नाग) are a divine, or semi-divine, race of half-human, half-serpent beings that reside in the netherworld (Patala), and can occasionally take human or part-human form, or are so depicted in art. A female naga is called a Nagi, or a Nagini. According to legend, they are the children of the sage Kashyapa and Kadru. Rituals devoted to these supernatural beings have been taking place throughout South Asia for at least 2,000 years. They are principally depicted in three forms: as entirely human with snakes on the heads and necks, as common serpents, or as half-human, half-snake beings in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism. ''Nagaraja'' is the title given to the king of the nagas. Narratives of these beings hold cultural significance in the mythological traditions of many South Asian and Southeast Asian cultures, and within Hinduism and Buddhism, they are the ancestral origins of the Nagavanshi Kshatriyas. Etymology In Sanskrit, a () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intangible Heritage List
UNESCO established its Lists of Intangible Cultural Heritage with the aim of ensuring better protection of important intangible cultural heritages worldwide and the awareness of their significance.Compare: This list is published by the Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of Intangible Cultural Heritage, the members of which are elected by State Parties meeting in a General Assembly. Through a compendium of the different oral and intangible treasures of humankind worldwide, the programme aims to draw attention to the importance of safeguarding intangible heritage, which UNESCO has identified as an essential component and as a repository of cultural diversity and of creative expression. The list was established in 2008 when the 2003 Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage took effect. the programme compiles two lists. The longer, Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity, comprises cultural "practices and expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holi
Holi (), also known as the Festival of Colours, the Festival of Spring, and the Festival of Love,The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) p. 874 "Holi /'həʊli:/ noun a Hindu spring festival ...". is an ancient Hindu religious festival and one of the most popular festivals in Hinduism. It celebrates the eternal and divine love of Radha Krishna. The day also signifies the triumph of good over evil, as it commemorates the victory of Lord Vishnu as Narasimha Narayana over Hiranyakashipu. It originated and is predominantly celebrated in the Indian subcontinent but has also spread to other regions of Asia and parts of the Western world through the Indian diaspora.Ebeling, Karin (10), Holi, an Indian Festival, and its Reflection in English Media; Die Ordnung des Standard und die Differenzierung der Diskurse: Akten des 41. Linguistischen Kolloquiums in Mannheim 2006, 1, 107, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objective t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dholak
The ''dholak'' is a two-headed hand drum, a folk percussion instrument. The instrument is about 45 cm in length and 27 cm in breadth and is widely used in ''qawwali'', '' kirtan'', '' lavani'' and '' bhangra''. The drum has two different sized drumheads. The smaller drumhead is made of goat skin for sharp notes while the bigger drumhead is made of buffalo skin for low pitch. The two drumheads allow a combination of bass and treble with rhythmic high and low pitches. The body or shell of the Dholak is made of sheesham or mango wood. The larger membrane has a compound (Syahi) applied which helps to lower the pitch and produce the sound. The smaller drumhead is played with the left hand which produces a high pitch. A cotton rope lacing and screw-turnbuckle are used to release tension while playing. Steel rings/pegs are twisted inside the laces to attain fine tuning. Dholak can be played in three ways — on the player’s lap, while standing, or pressed down with one knee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morsing
The morsing (also mukharshanku, mourching, morching or morchang; Sanskrit: दंत वाद्यन्तरात्मसत्रस्य, Telugu: మోర్సింగ్, Kannada: ಮೋರ್ಸಿಂಗ್, Rajasthani: मोरचंग, Tamil: நாமுழவு அல்லது முகச்சங்கு, Malayalam: മുഖർശംഖ്, English: " jaw harp") is an instrument similar to the Jew's harp, mainly used in Rajasthan, in the Carnatic music of South India, and in Sindh, Pakistan. It can be categorized under lamellophones, which is a sub-category of plucked idiophones. The instrument consists of a metal ring in the shape of a horseshoe with two parallel forks which form the frame, and a metal tongue in the middle, between the forks, fixed to the ring at one end and free to vibrate at the other. The metal tongue, also called the trigger, is bent at the free end in a plane perpendicular to the circular ring so that it can be struck and made t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanjari
Khanjari ( fa, خنجري, also Romanized as Khanjarī; also known as Ḩanjarī-ye Pā’īn, Khanjarī Soflá, and Khanjarī-ye Pā’īn) is a village in Sahra Rural District, Anabad District, Bardaskan County, Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni .... At the 2006 census, its population was 104, in 29 families. References Populated places in Bardaskan County {{Bardaskan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pungi
The pungi (Hindi: पुंगी, ur, پُنگیپُنگی, Burmese: ပုန်ဂိ), originates from the Indian subcontinent. The instrument consists of a reservoir into which air is blown and then channelled into two reed pipes. It is played with no pauses, as the player employs circular breathing. In street performances, the pungi is used for snake charming. History The pungi is an Indian folk music instrument that is mostly played by cobra charmers in Sindh, Pakistan, and Rajasthan, India. The instrument is made from a dry hollowed gourd with two bamboo attachments. It is also a double-reed instrument. The pungi is played by Jogi in the Thar desert. It was theorized that it was made not just for snake charming, but to make people enter a half-conscious state as part of a religious practice. It is in particular played by snake charmers, mostly in the Terai and Nepal, to arouse snakes to dance. The instrument has a high, thin tone and continuous low humming. It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajasthani People
Rajasthani people or Rajasthanis are a group of Indo-Aryan peoples native to Rajasthan ("the land of kingdoms"), a state in Northern India. Their language, Rajasthani, is a part of the western group of Indo-Aryan languages. History The first mention of the word ''Rajasthan'' comes from the works of George Thomas (''Military Memories'') and James Tod (''Annals''). Rajasthan literally means the ''Land of Kingdoms''. However, western Rajasthan and eastern Gujarat were part of "Gurjaratra". The local dialects of the time use the expression ''Rājwār'', the place or land of kings, later ''Rajputana''. Although the history of Rajasthan goes back as far as the Indus Valley civilization, the foundation of the Rajasthani community took shape with the rise of ''Western Middle Kingdoms'' such as Western Kshatrapas. ''Western Kshatrapas'' (35-405 BC) were rulers of the western part of India (Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Southern Sindh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan). They were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Kalbeliya In Cold Desert Night
A tradition is a belief or behavior (folk custom) passed down within a group or society with symbolic meaning or special significance with origins in the past. A component of cultural expressions and folklore, common examples include holidays or impractical but socially meaningful clothes (like lawyers' wigs or military officers' spurs), but the idea has also been applied to social norms such as greetings. Traditions can persist and evolve for thousands of years—the word ''tradition'' itself derives from the Latin ''tradere'' literally meaning to transmit, to hand over, to give for safekeeping. While it is commonly assumed that traditions have an ancient history, many traditions have been invented on purpose, whether that be political or cultural, over short periods of time. Various academic disciplines also use the word in a variety of ways. The phrase "according to tradition", or "by tradition", usually means that whatever information follows is known only by oral tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
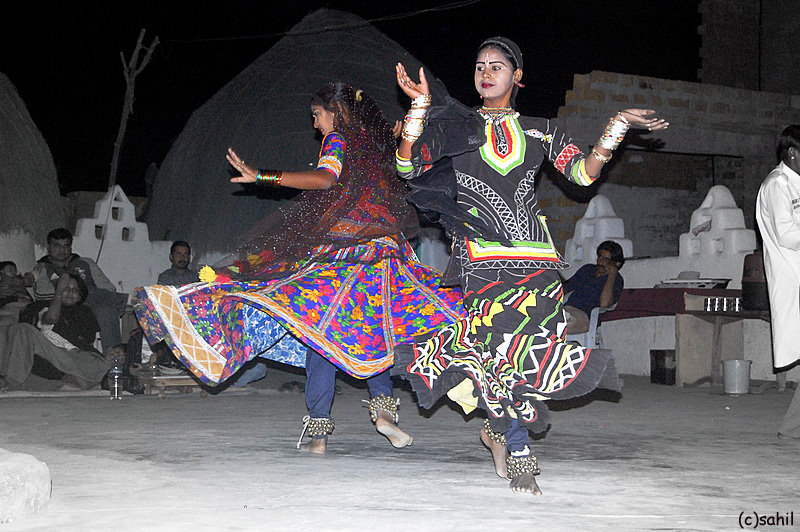

.png)

.jpg)



