|
Kalavaara Betta
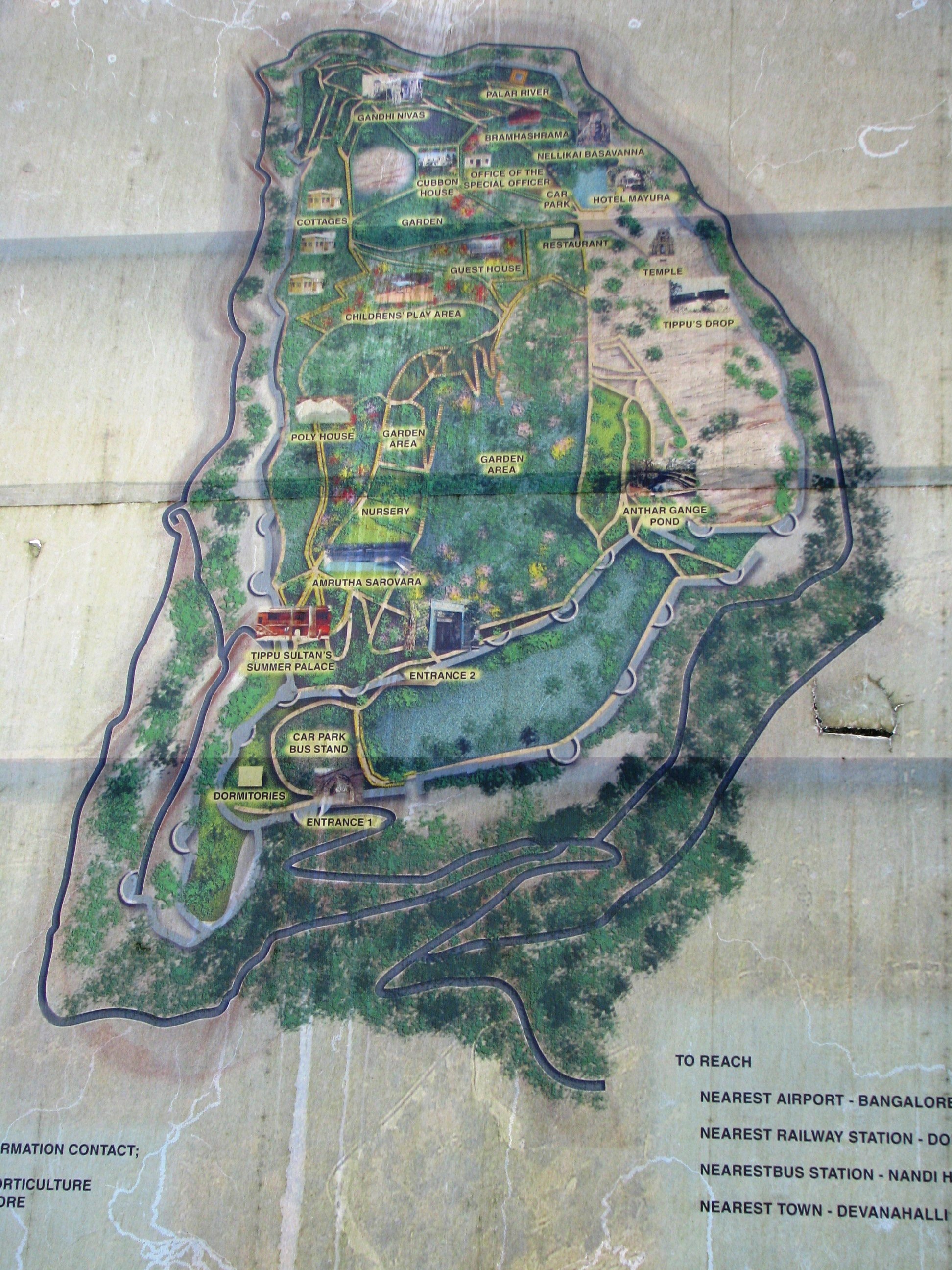
Nandi Hills (Anglicised forms include ''Nandidurg'' and ''Nandydoorg'') is an ancient hill station built by Ganga Dynasty in the Chikkaballapur district of Karnataka state. It is 10 km from Chickballapur town and approximately 60 km from Bengaluru. The hills are near the town Nandi. In traditional belief, the hills are the origin of the Arkavathy river, Ponnaiyar River, Palar River, Papagni River and Penna River. Watching the sunrise at Nandi Hills is popular with tourists. The first ever SAARC summit hosted by India was held at Nandi Hills in 1986. Etymology There are many stories about the origin of the name Nandi Hills. During the Chola period, Nandi Hills was called Anandagiri meaning The Hill of Happiness. It is also perhaps called Nandi Hills because the hills resemble a sleeping bull. Another theory holds that the hill gets its name from an ancient, 1300-year-old, Dravidian-style temple, and for the Nandi (bull), statue situated on this hill. History Nandi Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de facto'' sovereignty ( suzerainty) over the princely states. 1947–1950 Between 1947 and 1950 the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nandi (bull)
Nandi ( sa, नन्दि), also known as Nandikeshwara or Nandideva, is the bull vahana of the Hindu god Shiva. He is also the guardian deity of Kailash, the abode of Shiva. Almost all Shiva temples display stone-images of a seated Nandi, generally facing the main shrine. According to Saivite siddhantic tradition, he is considered as the chief guru of eight disciples of Nandinatha Sampradaya, namely, Sanaka, Sanatana, Sanandana, Sanatkumara, Tirumular, Vyagrapada, Patanjali, and Sivayoga Muni, who were sent in eight different directions, to spread the wisdom. The Cham Hindus of Vietnam believes that when they die, the Nandi will come and take their soul to the holy land of India from Vietnam. The Sanskrit word nandi ( sa, नन्दि) has the meaning of happy, joy, and satisfaction, the properties of divine guardian of Shiva- Nandi. It is recently documented, that the application of the name Nandi to the bull (Sanskrit: ''Vṛṣabha''), is in fact a development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Cleghorn (forester)
Hugh Francis Clarke Cleghorn of Stravithie (9 August 1820 – 16 May 1895) was a Madras-born Scottish physician, botanist, forester and land owner. Sometimes known as the father of scientific forestry in India, he was the first Conservator of Forests for the Madras Presidency, and twice acted as Inspector General of Forests for India. After a career spent in India Cleghorn returned to Scotland in 1868, where he was involved in the first ever International Forestry Exhibition, advised the India Office on the training of forest officers, and contributed to the establishment of lectureships in botany at the University of St Andrews and in forestry at the University of Edinburgh. The plant genus '' Cleghornia'' was named after him by Robert Wight. Early life Cleghorn was born in Madras on 9 August 1820, where his father, Peter (also known as Patrick) (1783 – 1863) was Registrar and Prothonotary in the Madras Supreme Court. His mother Isabella (''née'' Allan) died in Madras (1 Jun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Heyne
Benjamin Heyne FLS (1770, Pirna, Döbra – 6 February 1819, Madras) was a German botanist, naturalist, and surgeon who worked in British India as a Botanist to Samalkot in the Madras Presidency under the British East India Company. He collected and described plants from southern India, many of which were named after him by European botanists. Life and work in India The son of German classical scholar and archaeologist Christian Gottlob Heyne and Therese Weiss, daughter of German composer and lutenist Sylvius Leopold Weiss, Benjamin Heyne was born in Döbra, Germany. In later life, Heyne joined the Tranquebar Mission run by Moravians where he took an interest in the botanical gardens. Through William Roxburgh he obtained a position in the Madras Presidency as a botanist at Samalkot around 1794. He was involved in introducing new food plants to overcome famines and these included potatoes and breadfruit. After the fall of Tipu Sultan, he was appointed to look for a new site for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypericum Mysorense
''Hypericum mysorense'' is a species of flowering plant in the Hypericaceae family. It is primarily found at high elevations in the Western Ghats of India and the mountains of Sri Lanka, but was also reported from Socoro by Isaac Bayley Balfour in the 19th century. It was studied to improve understanding of endosperm formation in ''Hypericum'', and the identification of a number of xanthone derivatives from this species contributed to the chemotaxonomic description of subfamily Hypericoideae. ''Hypericum mysorense'' has been used to treat wounds as part of the Ayurvedic system of traditional medicine Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the .... Some research into the possibility of antiherpetic properties in ''H. mysorense'' extracts has been performed. References E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horticulture
Horticulture is the branch of agriculture that deals with the art, science, technology, and business of plant cultivation. It includes the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, herbs, sprouts, mushrooms, algae, flowers, seaweeds and non-food crops such as grass and ornamental trees and plants. It also includes plant conservation, landscape restoration, landscape and garden design, construction, and maintenance, and arboriculture, ornamental trees and lawns. The study and practice of horticulture have been traced back thousands of years. Horticulture contributed to the transition from nomadic human communities to sedentary, or semi-sedentary, horticultural communities.von Hagen, V.W. (1957) The Ancient Sun Kingdoms Of The Americas. Ohio: The World Publishing Company Horticulture is divided into several categories which focus on the cultivation and processing of different types of plants and food items for specific purposes. In order to conserve the science of horticultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Cubbon (army Officer)
Lieutenant-General Sir Mark Cubbon KCB (23 August 1775 – 23 April 1861) was a British army officer with the East India Company who was the Chief Commissioner of Mysore 1834 to 1861. During his tenure, he established a law and order system, introduced judicial and economic reforms and through action in all spheres of governance helped develop the economy of Mysore. He resigned from his office in 1860 due to ill-health and left for England for the first time since his arrival in India as a cadet in 1800. The administration of the Kingdom of Mysore under his leadership ensured that the 1857 rebellion had almost no impact in the region. He died in 1861 on board ship at Suez. Cubbon Road and Cubbon Park in Bangalore are named after him. Early life Cubbon was born at the vicarage of Maughold, Isle of Man on 23 August 1775. His father was Vicar Thomas Cubbon and his mother Margaret Wilks was the sister of Colonel Mark Wilks. The seventh of ten children, he grew up enjoying scrambling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Cunningham (Indian Army Officer)
Francis Cunningham (1820 – 3 December 1875) was an officer in the Madras Army, member of the Mysore Commission as secretary to Mark Cubbon (army officer), Mark Cubbon, and a literary editor. He published a three volume revised edition of Gifford's ''Works of Ben Jonson'' in 1871. Cunningham road in Bangalore is named after him. Life Francis Cunningham was the son of the poet Allan Cunningham (author), Allan Cunningham and the younger brother of historian Joseph Davey Cunningham, Joseph Davey (1812–1851, who wrote on the ''History of the Sikhs''), (1816–1869), author and literary editor and archaeologist Sir Alexander Cunningham (1814–1893, who founded the Archaeological Survey of India), who also spent most of their working lives in India. His younger brother Peter Cunningham (writer, born 1816), Peter Cunningham (1816–1869) also became a literary editor, best known for his ''Handbook of London''. The brothers' cadetships were obtained through a friend of their father's, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a realm in South India, southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. From 1799 until 1950, it was a princely state, until 1947 in a subsidiary alliance with Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India. The British took Direct Control over the Princely state, Princely State in 1831.Rajakaryaprasakta Rao Bahadur (1936), p383 It then became Mysore State (later enlarged and renamed to Karnataka) with its ruler remaining as Rajapramukh until 1956, when he became the first Governor of the reformed state. The kingdom, which was founded and ruled for most part by the Hindu Wodeyar family, initially served as feudatories under the Vijayanagara Empire. The 17th century saw a steady expansion of its territory and during the rule of Kanthirava Narasaraja I, Narasaraja Wodeyar I and Chikka Devaraja, Chikka Devaraja Wodeyar, the kingdom annexed large expanses of what is now southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Anglo-Mysore War
The Third Anglo-Mysore War (1790–1792) was a conflict in South India between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company, the Kingdom of Travancore, the Maratha Empire, and the Nizam of Hyderabad. It was the third of four Anglo-Mysore Wars. Background Tipu Sultan, the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore, and his father Hyder Ali before him, had previously fought twice with the forces of the British East India Company. The First Anglo-Mysore War, fought in the 1760s, had ended inconclusively on both sides, with treaty provisions including promises of mutual assistance in future conflicts. British failure to support Mysore in conflicts with the Maratha Empire and other actions supportive of Mysore's enemies led Hyder to develop a dislike for the British. After the British took the French-controlled port of Mahé in 1779, Hyder, who had been receiving military supplies through that port and had placed it under his protection, opened the Second Anglo-Mysore War. This w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis
Charles Cornwallis, 1st Marquess Cornwallis, (31 December 1738 – 5 October 1805), styled Viscount Brome between 1753 and 1762 and known as the Earl Cornwallis between 1762 and 1792, was a British Army general and official. In the United States and the United Kingdom, he is best remembered as one of the leading British generals in the American War of Independence. His surrender in 1781 to a combined American and French force at the siege of Yorktown ended significant hostilities in North America. He later served as a civil and military governor in Ireland, where he helped bring about the Act of Union; and in India, where he helped enact the Cornwallis Code and the Permanent Settlement. Born into an aristocratic family and educated at Eton and Cambridge, Cornwallis joined the army in 1757, seeing action in the Seven Years' War. Upon his father's death in 1762 he became Earl Cornwallis and entered the House of Lords. From 1766 until 1805 he was Colonel of the 33rd Regimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_Bangalore_(1890)._Curzon_Collection's_'Souvenir_of_Mysore_Album'.jpg)


