|
KHOPCA Clustering Algorithm
KHOPCA is an adaptive clustering algorithm originally developed for dynamic networks. KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) provides a fully Distributed computing, distributed and localized approach to group elements such as nodes in a network according to their distance from each other. KHOPCA operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines clusters, which are optimal with respect to the applied distance function. KHOPCA's clustering process explicitly supports joining and leaving of nodes, which makes KHOPCA suitable for highly dynamic networks. However, it has been demonstrated that KHOPCA also performs in static networks. Besides applications in ad hoc and wireless sensor networks, KHOPCA can be used in localization and navigation problems, networked Swarm intelligence, swarming, and real-time Cluster analysis, data clustering and analysis. Algorithm description KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
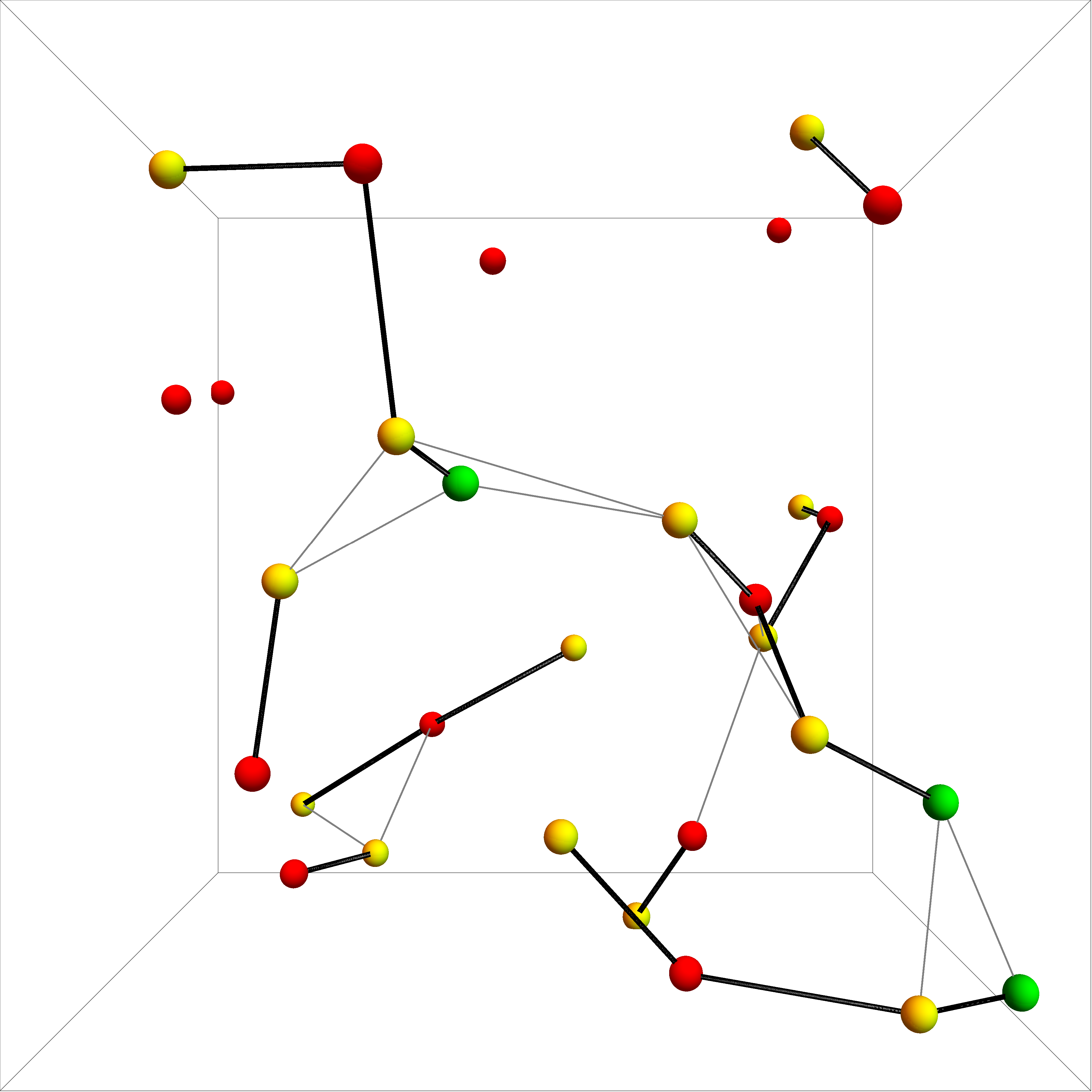
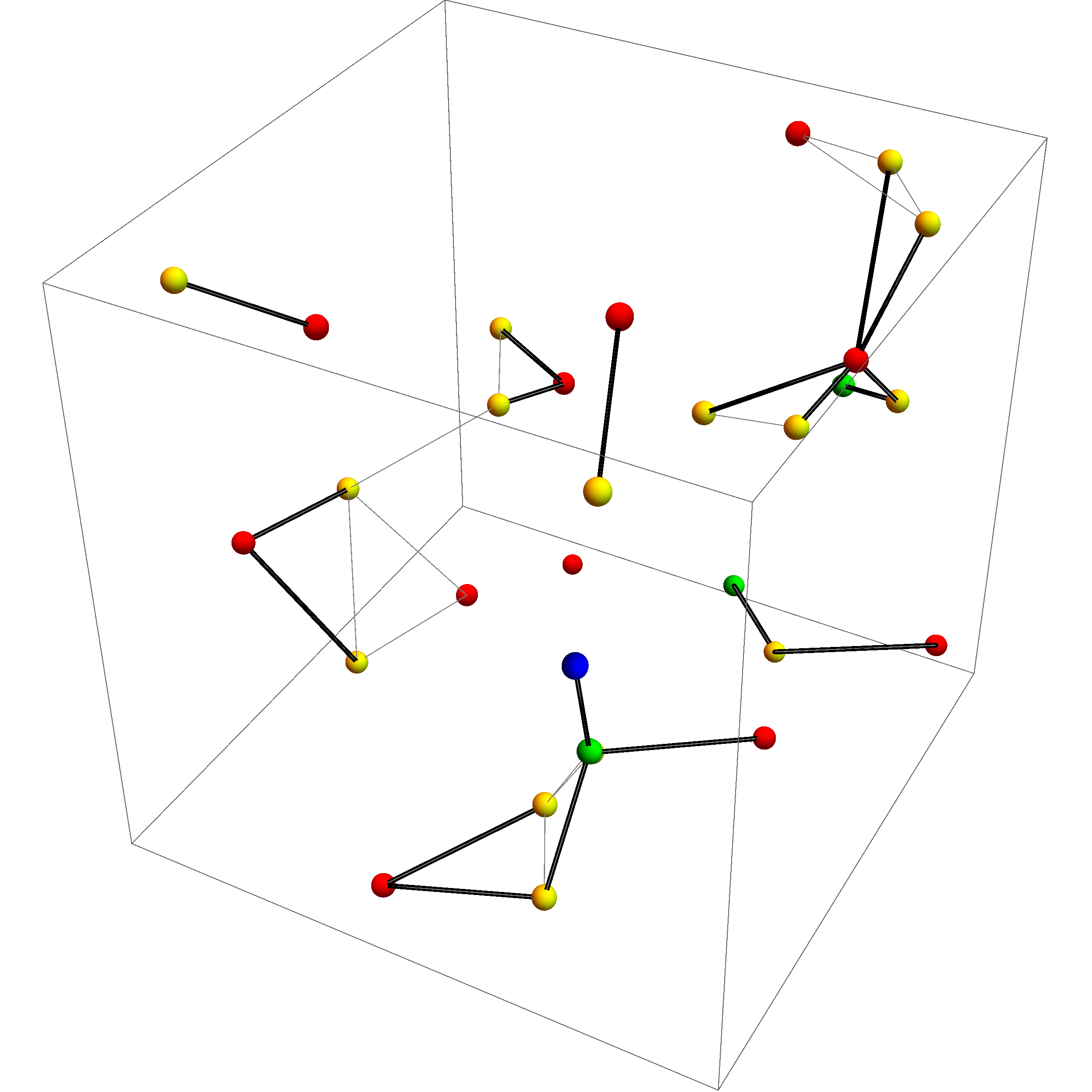
KHOPCA 3D Example 1
KHOPCA is an adaptive clustering algorithm originally developed for dynamic networks. KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) provides a fully Distributed computing, distributed and localized approach to group elements such as nodes in a network according to their distance from each other. KHOPCA operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines clusters, which are optimal with respect to the applied distance function. KHOPCA's clustering process explicitly supports joining and leaving of nodes, which makes KHOPCA suitable for highly dynamic networks. However, it has been demonstrated that KHOPCA also performs in static networks. Besides applications in ad hoc and wireless sensor networks, KHOPCA can be used in localization and navigation problems, networked Swarm intelligence, swarming, and real-time Cluster analysis, data clustering and analysis. Algorithm description KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clustering Algorithm
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis itself is not one specific algorithm, but the general task to be solved. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or particular statistical distributions. Clustering can therefore be formulated as a multi-objective optimization problem. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different computer network, networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by message passing, passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. The components of a distributed system interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the clock synchronization, lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from service-oriented architecture, SOA-based systems to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer, peer-to-peer applications. A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program, and ''distributed programming' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireless Sensor Network
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) refer to networks of spatially dispersed and dedicated sensors that monitor and record the physical conditions of the environment and forward the collected data to a central location. WSNs can measure environmental conditions such as temperature, sound, pollution levels, humidity and wind. These are similar to wireless ad hoc networks in the sense that they rely on wireless connectivity and spontaneous formation of networks so that sensor data can be transported wirelessly. WSNs monitor physical conditions, such as temperature, sound, and pressure. Modern networks are bi-directional, both collecting data and enabling control of sensor activity. The development of these networks was motivated by military applications such as battlefield surveillance. Such networks are used in industrial and consumer applications, such as industrial process monitoring and control and machine health monitoring. A WSN is built of "nodes" – from a few to hundreds or th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swarm Intelligence
Swarm intelligence (SI) is the collective behavior of decentralized, self-organized systems, natural or artificial. The concept is employed in work on artificial intelligence. The expression was introduced by Gerardo Beni and Jing Wang in 1989, in the context of cellular robotic systems. SI systems consist typically of a population of simple agents or boids interacting locally with one another and with their environment.Hu, J.; Turgut, A.; Krajnik, T.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Occlusion-Based Coordination Protocol Design for Autonomous Robotic Shepherding Tasks IEEE Transactions on Cognitive and Developmental Systems, 2020. The inspiration often comes from nature, especially biological systems. The agents follow very simple rules, and although there is no centralized control structure dictating how individual agents should behave, local, and to a certain degree random, interactions between such agents lead to the emergence of "intelligent" global behavior, unknown to the individual a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistics, statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis itself is not one specific algorithm, but the general task to be solved. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small Distance function, distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or particular statistical distributions. Clustering can therefore be formulated as a multi-object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KHOPCA Rule 1
KHOPCA is an adaptive clustering algorithm originally developed for dynamic networks. KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) provides a fully distributed and localized approach to group elements such as nodes in a network according to their distance from each other. KHOPCA operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines clusters, which are optimal with respect to the applied distance function. KHOPCA's clustering process explicitly supports joining and leaving of nodes, which makes KHOPCA suitable for highly dynamic networks. However, it has been demonstrated that KHOPCA also performs in static networks. Besides applications in ad hoc and wireless sensor networks, KHOPCA can be used in localization and navigation problems, networked swarming Swarm behaviour, or swarming, is a collective behaviour exhibited by entities, particularly animals, of similar size which aggregate together, perhaps milling about the same spot or perhaps moving ''en masse'' or migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KHOPCA Rule 2 A
KHOPCA is an adaptive clustering algorithm originally developed for dynamic networks. KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) provides a fully distributed and localized approach to group elements such as nodes in a network according to their distance from each other. KHOPCA operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines clusters, which are optimal with respect to the applied distance function. KHOPCA's clustering process explicitly supports joining and leaving of nodes, which makes KHOPCA suitable for highly dynamic networks. However, it has been demonstrated that KHOPCA also performs in static networks. Besides applications in ad hoc and wireless sensor networks, KHOPCA can be used in localization and navigation problems, networked swarming Swarm behaviour, or swarming, is a collective behaviour exhibited by entities, particularly animals, of similar size which aggregate together, perhaps milling about the same spot or perhaps moving ''en masse'' or migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KHOPCA Rule 3 A
KHOPCA is an adaptive clustering algorithm originally developed for dynamic networks. KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) provides a fully distributed and localized approach to group elements such as nodes in a network according to their distance from each other. KHOPCA operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines clusters, which are optimal with respect to the applied distance function. KHOPCA's clustering process explicitly supports joining and leaving of nodes, which makes KHOPCA suitable for highly dynamic networks. However, it has been demonstrated that KHOPCA also performs in static networks. Besides applications in ad hoc and wireless sensor networks, KHOPCA can be used in localization and navigation problems, networked swarming Swarm behaviour, or swarming, is a collective behaviour exhibited by entities, particularly animals, of similar size which aggregate together, perhaps milling about the same spot or perhaps moving ''en masse'' or migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KHOPCA Rule 4 A
KHOPCA is an adaptive clustering algorithm originally developed for dynamic networks. KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) provides a fully distributed and localized approach to group elements such as nodes in a network according to their distance from each other. KHOPCA operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines clusters, which are optimal with respect to the applied distance function. KHOPCA's clustering process explicitly supports joining and leaving of nodes, which makes KHOPCA suitable for highly dynamic networks. However, it has been demonstrated that KHOPCA also performs in static networks. Besides applications in ad hoc and wireless sensor networks, KHOPCA can be used in localization and navigation problems, networked swarming Swarm behaviour, or swarming, is a collective behaviour exhibited by entities, particularly animals, of similar size which aggregate together, perhaps milling about the same spot or perhaps moving ''en masse'' or migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KHOPCA 1D Example 1
KHOPCA is an adaptive clustering algorithm originally developed for dynamic networks. KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) provides a fully distributed and localized approach to group elements such as nodes in a network according to their distance from each other. KHOPCA operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines clusters, which are optimal with respect to the applied distance function. KHOPCA's clustering process explicitly supports joining and leaving of nodes, which makes KHOPCA suitable for highly dynamic networks. However, it has been demonstrated that KHOPCA also performs in static networks. Besides applications in ad hoc and wireless sensor networks, KHOPCA can be used in localization and navigation problems, networked swarming Swarm behaviour, or swarming, is a collective behaviour exhibited by entities, particularly animals, of similar size which aggregate together, perhaps milling about the same spot or perhaps moving ''en masse'' or migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KHOPCA 2D K3a
KHOPCA is an adaptive clustering algorithm originally developed for dynamic networks. KHOPCA (k-hop clustering algorithm) provides a fully distributed and localized approach to group elements such as nodes in a network according to their distance from each other. KHOPCA operates proactively through a simple set of rules that defines clusters, which are optimal with respect to the applied distance function. KHOPCA's clustering process explicitly supports joining and leaving of nodes, which makes KHOPCA suitable for highly dynamic networks. However, it has been demonstrated that KHOPCA also performs in static networks. Besides applications in ad hoc and wireless sensor networks, KHOPCA can be used in localization and navigation problems, networked swarming Swarm behaviour, or swarming, is a collective behaviour exhibited by entities, particularly animals, of similar size which aggregate together, perhaps milling about the same spot or perhaps moving ''en masse'' or migrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |