|
Kôdi Husimi
Kōji Husimi (June 29, 1909 – May 8, 2008, ja, 伏見康治) was a Japanese theoretical physicist who served as the president of the Science Council of Japan.. Husimi trees in graph theory, the Husimi Q representation in quantum mechanics, and Husimi's theorem in the mathematics of paper folding are named after him. Education and career Husimi studied at the University of Tokyo, graduating in 1933. He spent a year there as an assistant, and then moved to Osaka University in 1934, where he soon began working with Seishi Kikuchi. At Osaka, he became Dean of the Faculty of Science. He moved to Nagoya University in 1961, and directed the plasma institute there. He retired in 1973, and became a professor emeritus of both Nagoya and Osaka. Contributions Physics A 1940 paper by Husimi introduced the Husimi Q representation in quantum mechanics. Husimi also gave the name to the kagome lattice, frequently used in statistical mechanics. Graph theory In the mathematical area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka University
, abbreviated as , is a public research university located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. It is one of Japan's former Imperial Universities and a Designated National University listed as a "Top Type" university in the Top Global University Project. The university is often ranked among the top three public universities in Japan, along with the University of Tokyo and Kyoto University. It is ranked third overall among Japanese universities and 75th worldwide in the 2022 QS World University Rankings. Osaka University was one of the earliest modern universities in Japan at its founding in 1931. The history of the institution includes much older predecessors in Osaka such as the Kaitokudō founded in 1724 and the Tekijuku founded in 1838. In 2007, it merged with Osaka University of Foreign Studies and became the largest national university in Japan. Osaka University is one of the most productive research institutions in Japan. Numerous prominent scholars and scientists have attend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block Graph
In graph theory, a branch of combinatorial mathematics, a block graph or clique tree. is a type of undirected graph in which every biconnected component (block) is a clique. Block graphs are sometimes erroneously called Husimi trees (after Kôdi Husimi), but that name more properly refers to cactus graphs, graphs in which every nontrivial biconnected component is a cycle. Block graphs may be characterized as the intersection graphs of the blocks of arbitrary undirected graphs.. Characterization Block graphs are exactly the graphs for which, for every four vertices , , , and , the largest two of the three distances , , and are always equal... They also have a forbidden graph characterization as the graphs that do not have the diamond graph or a cycle of four or more vertices as an induced subgraph; that is, they are the diamond-free chordal graphs. They are also the Ptolemaic graphs (chordal distance-hereditary graphs) in which every two nodes at distance two from each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1909 Births
Nineteen or 19 may refer to: * 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20 * one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019 Films * ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film * ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film Music * 19 (band), a Japanese pop music duo Albums * ''19'' (Adele album), 2008 * ''19'', a 2003 album by Alsou * ''19'', a 2006 album by Evan Yo * ''19'', a 2018 album by MHD * ''19'', one half of the double album '' 63/19'' by Kool A.D. * '' Number Nineteen'', a 1971 album by American jazz pianist Mal Waldron * ''XIX'' (EP), a 2019 EP by 1the9 Songs * "19" (song), a 1985 song by British musician Paul Hardcastle. * "Nineteen", a song by Bad4Good from the 1992 album ''Refugee'' * "Nineteen", a song by Karma to Burn from the 2001 album ''Almost Heathen''. * "Nineteen" (song), a 2007 song by American singer Billy Ray Cyrus. * "Nineteen", a song by Tegan and Sara from the 2007 album '' The Con''. * "XIX" (song), a 2014 song by Slip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Base
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhombus
In plane Euclidean geometry, a rhombus (plural rhombi or rhombuses) is a quadrilateral whose four sides all have the same length. Another name is equilateral quadrilateral, since equilateral means that all of its sides are equal in length. The rhombus is often called a "diamond", after the diamonds suit in playing cards which resembles the projection of an octahedral diamond, or a lozenge, though the former sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 60° angle (which some authors call a calisson after the French sweet – also see Polyiamond), and the latter sometimes refers specifically to a rhombus with a 45° angle. Every rhombus is simple (non-self-intersecting), and is a special case of a parallelogram and a kite. A rhombus with right angles is a square. Etymology The word "rhombus" comes from grc, ῥόμβος, rhombos, meaning something that spins, which derives from the verb , romanized: , meaning "to turn round and round." The word was used both by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
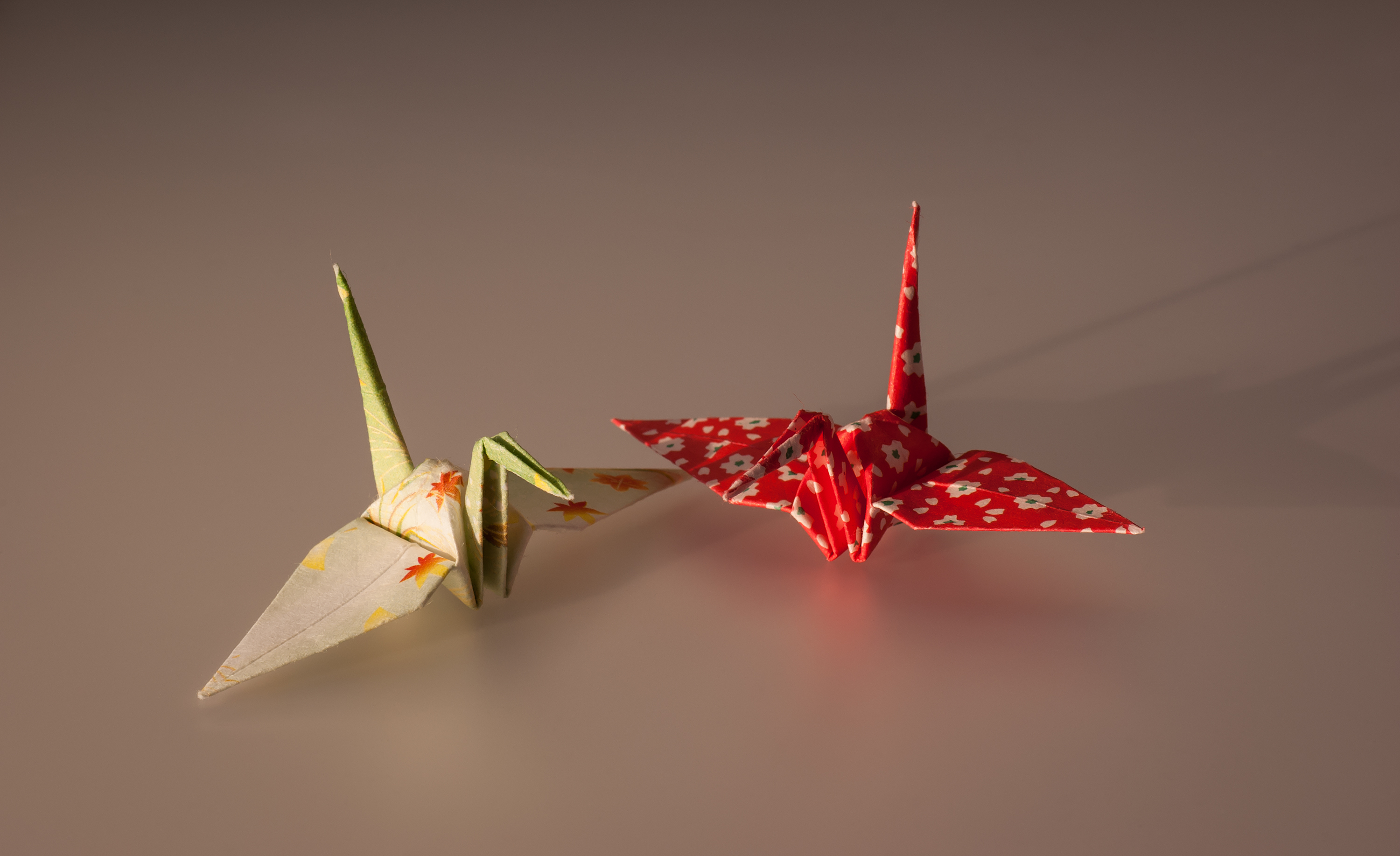
Orizuru
The ''orizuru'' (折鶴 ''ori-'' "folded," ''tsuru'' "crane"), or paper crane, is a design that is considered to be the most classic of all Japanese origami.Jccc Origami Crane Project – Materials For Teachers & Students. MEANING OF THE ORIGAMI CRANE (n.d.): n. pag. Web. 16 Feb. 2017. In Japanese culture, it is believed that its wings carry souls up to paradise, and it is a representation of the Japanese red-crowned crane, referred to as the "Honourable Lord Crane" in Japanese culture. It is often used as a ceremonial wrapper or restaurant table decoration. A thousand orizuru strung together is called ''senbazuru'' (千羽鶴), meaning "thousand cranes", and it is said that if someone folds a thousand cranes, they are granted one wish."Senbazuru." Senbazuru , TraditionsCustoms.com. N.p., n.d. Web. 16 Feb. 2017. The significance of ''senbazuru'' is featured in '' Sadako and the Thousand Paper Cranes'', a classic story based on the life of Sadako Sasaki, a ''hibakusha'' gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origami
) is the Japanese art of paper folding. In modern usage, the word "origami" is often used as an inclusive term for all folding practices, regardless of their culture of origin. The goal is to transform a flat square sheet of paper into a finished sculpture through folding and sculpting techniques. Modern origami practitioners generally discourage the use of cuts, glue, or markings on the paper. Origami folders often use the Japanese word ' to refer to designs which use cuts. On the other hand, in the detailed Japanese classification, origami is divided into stylized ceremonial origami (儀礼折り紙, ''girei origami'') and recreational origami (遊戯折り紙, ''yūgi origami''), and only recreational origami is generally recognized as origami. In Japan, ceremonial origami is generally called "origata" ( :ja:折形) to distinguish it from recreational origami. The term "origata" is one of the old terms for origami. The small number of basic origami folds can be combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pugwash Conferences On Science And World Affairs
The Pugwash Conferences on Science and World Affairs is an international organization that brings together scholars and public figures to work toward reducing the danger of armed conflict and to seek solutions to global security threats. It was founded in 1957 by Joseph Rotblat and Bertrand Russell in Pugwash, Nova Scotia, Canada, following the release of the Russell–Einstein Manifesto in 1955. Rotblat and the Pugwash Conference jointly won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1995 for their efforts on nuclear disarmament.Russell's exclusion is explained because the Nobel Prizes are never awarded posthumously. International Student/Young Pugwash groups have existed since founder Cyrus Eaton's death in 1979. Origin of the Pugwash Conferences The Russell–Einstein Manifesto, released July 9, 1955, called for a conference for scientists to assess the dangers of weapons of mass destruction (then only considered to be nuclear weapons). Cyrus Eaton, an industrialist and philanthropist, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first test of a fission ("atomic") bomb released an amount of energy approximately equal to . The first thermonuclear ("hydrogen") bomb test released energy approximately equal to . Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons TNT (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than . A nuclear device no larger than a conventional bomb can devastate an entire city by blast, fire, and radiation. Since they are weapons of mass destruction, the proliferation of nuclear weapons is a focus of international relations policy. Nuclear weapons have been dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear ''fission'' of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear ''decay'' processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as ''Voyager 2''. Generating electricity from ''fusion'' power remains the focus of international research. Most nuclear power plants use thermal reactors with enriched uranium in a once-through fuel cycle. Fuel is removed when the percentage of neutron absorbing atoms becomes so large that a chain reaction can no longer be sustained, typically three years. It is then cooled for several years in on-site spent fuel pools before being transferred to long term storage. The spent fuel, though low in volume, is high-level radioactiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gary Chartrand
Gary Theodore Chartrand (born 1936) is an American-born mathematician who specializes in graph theory. He is known for his textbooks on introductory graph theory and for the concept of a highly irregular graph. Biography Gary Chartrand was born in 1936. He was raised in Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan and attended J. W. Sexton High School located in Lansing, Michigan. As an undergraduate student, he initially majored in chemical engineering, but switched to mathematics in his junior year, in which he also became a member of the honorary mathematics society Pi Mu Epsilon. He earned his B. S. from Michigan State University, where he majored in mathematics and minored in physical sciences and foreign languages. Michigan State University also awarded him a Master of Science and a PhD for his work in graph theory in 1964. Chartrand became the first doctoral student of Edward Nordhaus, and the first doctoral student at Michigan State University to research graph theory. His dissertation was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehdi Behzad
Mehdi Behzad (Persian:مهدی بهزاد; born April 22, 1936) is an Iranian mathematician specializing in graph theory. He introduced his total coloring theory (also known as "Behzad's conjecture" or "the total chromatic number conjecture") during his Ph.D. studies in 1965. Despite the active work during the last 50 years this conjecture remains as challenging as it is open. In fact, Behzad's conjecture now belongs to mathematics’ classic open problems. Behzad has been instrumental in institutionalizing mathematics education and popularization of mathematics in Iran, and has received numerous awards and recognition for his lifetime service to the Iranian scientific community. Graph theory Behzad is the coauthor of two text books on graph theory published in 1972 and 1979 in the U.S., which were among the key references on this new field of mathematics. He has been one of the direct collaborators of Paul Erdős. Professorship Behzad was the first faculty member of Sharif U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)