|
Kyiv Rus
Kievan Rusʹ, also known as Kyivan Rusʹ ( orv, , Rusĭ, or , , ; Old Norse: ''Garðaríki''), was a state in Eastern and Northern Europe from the late 9th to the mid-13th century.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p.14–16.Kievan Rus Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encompassing a variety of polities and peoples, including East Slavic, Norse, and Finnic, it was ruled by the Rurik dynasty, founded by the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coin Of Vladimir The Great (reverse)
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint (facility), mint in order to facilitate trade. They are most often issued by a government. Coins often have images, numerals, or text on them. Obverse and reverse, ''Obverse'' and its opposite, ''reverse'', refer to the two flat faces of coins and medals. In this usage, ''obverse'' means the wikt:front, front face of the object and ''reverse'' means the wikt:back, back face. The obverse of a coin is commonly called ''heads'', because it often depicts the head of a prominent person, and the reverse ''tails''. Coins are usually made of metal or an alloy, or sometimes of man-made materials. They are usually Disk (mathematics), disc shaped. Coins, made of valuable metal, are stored in large quantities as bullion coins. Other coins are used as money in ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Paganism
Slavic mythology or Slavic religion is the Religion, religious beliefs, myths, and ritual practices of the Slavs before Christianisation of the Slavs, Christianisation, which occurred at various stages between the 8th and the 13th century. The South Slavs, who likely settled in the Balkan Peninsula during the 6th–7th centuries AD, bordering with the Byzantine Empire to the south, came under the sphere of influence of Eastern Christianity, beginning with the creation of writing systems for Slavic languages (first Glagolitic, and then Cyrillic script) in 855 by the brothers Saints Cyril and Methodius and the adoption of Christianity in Bulgaria in 863. The East Slavs followed with the official adoption in 988 by Vladimir the Great of Kievan Rus'. The West Slavs, West Slavs' process of Christianization was more gradual and complicated. The Moravians accepted Christianity as early as 831, the Bohemian dukes followed in 845, Slovaks accepted Christianity somewhere between the years 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Slavs
The East Slavs are the most populous subgroup of the Slavs. They speak the East Slavic languages, and formed the majority of the population of the medieval state Kievan Rus', which they claim as their cultural ancestor.John Channon & Robert Hudson, ''Penguin Historical Atlas of Russia'' (Penguin, 1995), p. 16. Today, the East Slavs consist of Belarusians, Russians, Rusyns, and Ukrainians. History Sources Researchers know relatively little about the Eastern Slavs prior to approximately 859 AD when the first events recorded in the '' Primary Chronicle'' occurred. The Eastern Slavs of these early times apparently lacked a written language. The few known facts come from archaeological digs, foreign travellers' accounts of the Rus' land, and linguistic comparative analyses of Slavic languages. Very few native Rus' documents dating before the 11th century (none before the 10th century) have survived. The earliest major manuscript with information on Rus' history, the '' Prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other geographical factors such as climate and ecology. Climate The climate is mainly Oceanic climate (Cfb), Humid continental climate (Dfb), Subarctic climate (Dfc and Dsc) and Tundra (ET). Geography Northern Europe might be defined roughly to include some or all of the following areas: British Isles, Fennoscandia, the peninsula of Jutland, the Baltic region, Baltic plain that lies to the east and the many islands that lie offshore from mainland Northern Europe and the main European continent. In some cases, Greenland is also included, although it is only politically European, comprising part of the Kingdom of Denmark, and not considered to be geographically in Europe. The area is partly mountainous, including the northern volcanic islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, which spans roughly 40% of the continent's landmass while accounting for approximately 15% of its total population."The Balkans" , ''Global Perspectives: A Remote Sensing and World Issues Site''. Wheeling Jesuit University/Center for Educational Technologies, 1999–2002. It represents a significant part of Culture of Europe, European culture; the main socio-cultural characteristics of Eastern Europe have historically been defined by the traditions of Slavs and Greeks, as well as by the influence of Eastern Christianity as it developed through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
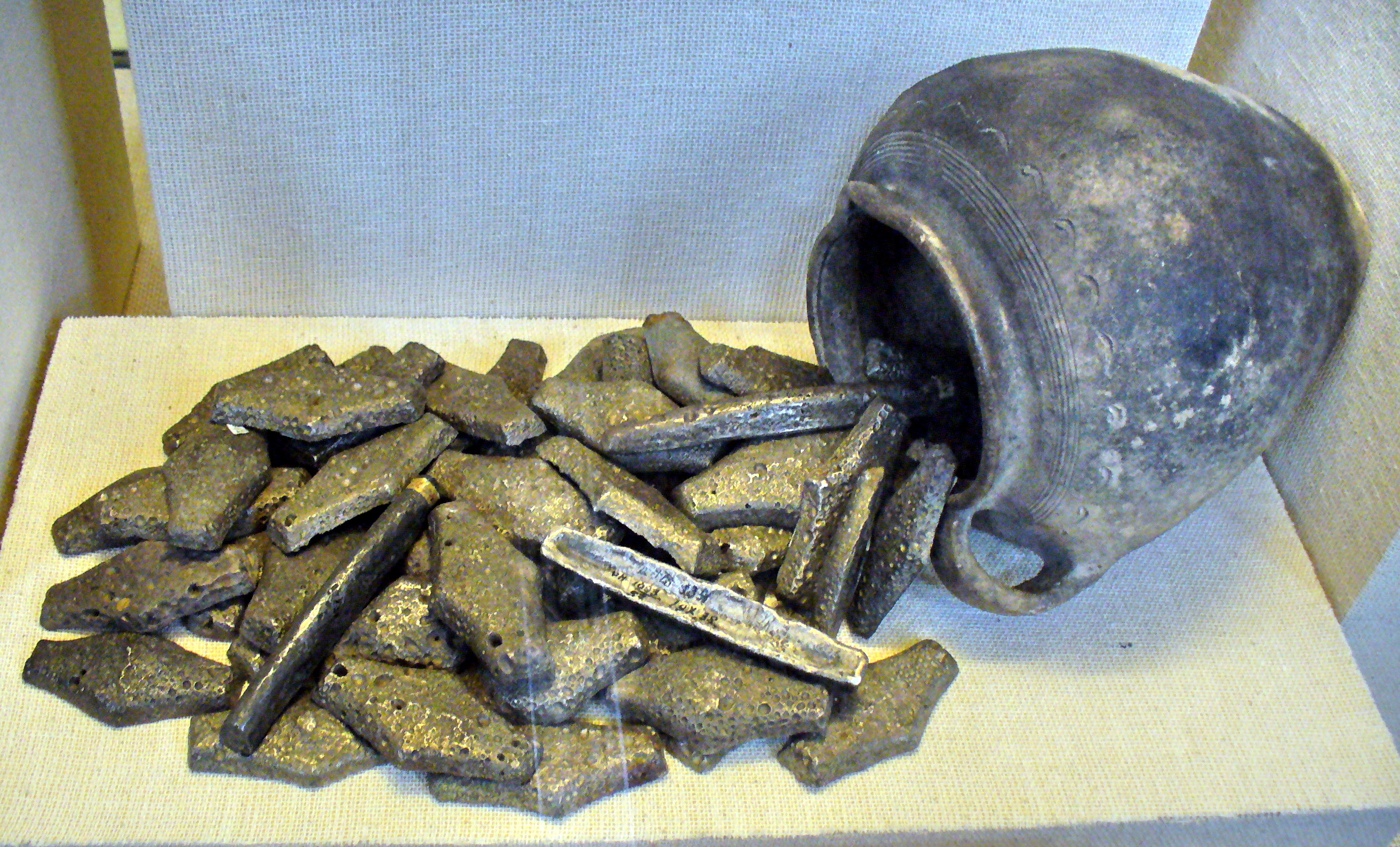
Grivna
Grivna (гривна) was a currency as well as a measure of weight used in Kievan Rus' and other East Slavic countries since the 11th century. Name The word ''grivna'' is derived from from . In Old East Slavic it had the form ''grivĭna''. In modern East Slavic languages it has such forms: russian: гри́вна ''grivna'', uk, гри́вня ''hryvnia'', be, гры́ўня ''hryŭnia''. The name of the contemporary currency of Ukraine, ''hryvnia'', is derived from the ancient grivna. History Early period As its etymology implies the word originally meant a necklace or a torque. The reason why it has taken the meaning of a unit of weight is unclear. The grivnas that have been found at various archaeological sites are not necklaces but bullions of precious metals, usually silver. The weight and the shape of grivnas were not uniform, but varied by region. The grivnas of Novgorod and Pskov were thin long round-edged or three-edged ingots, while Kievan grivnas have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
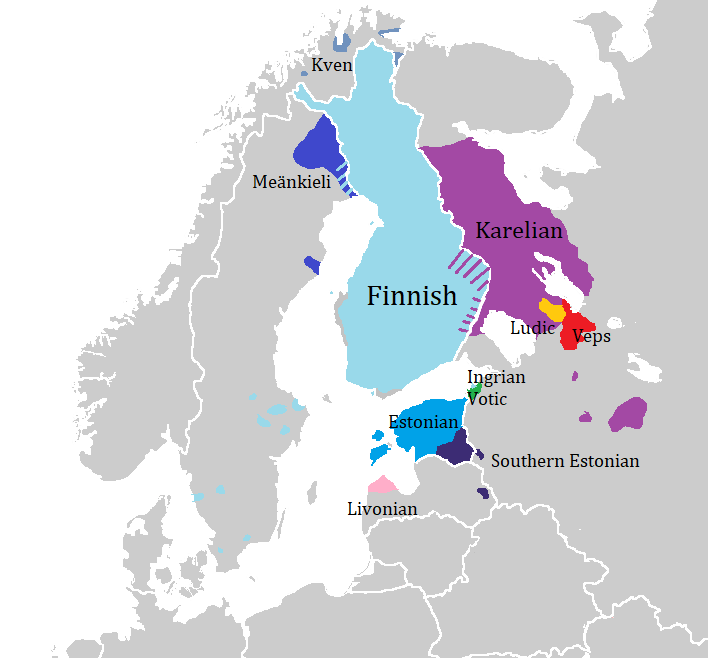
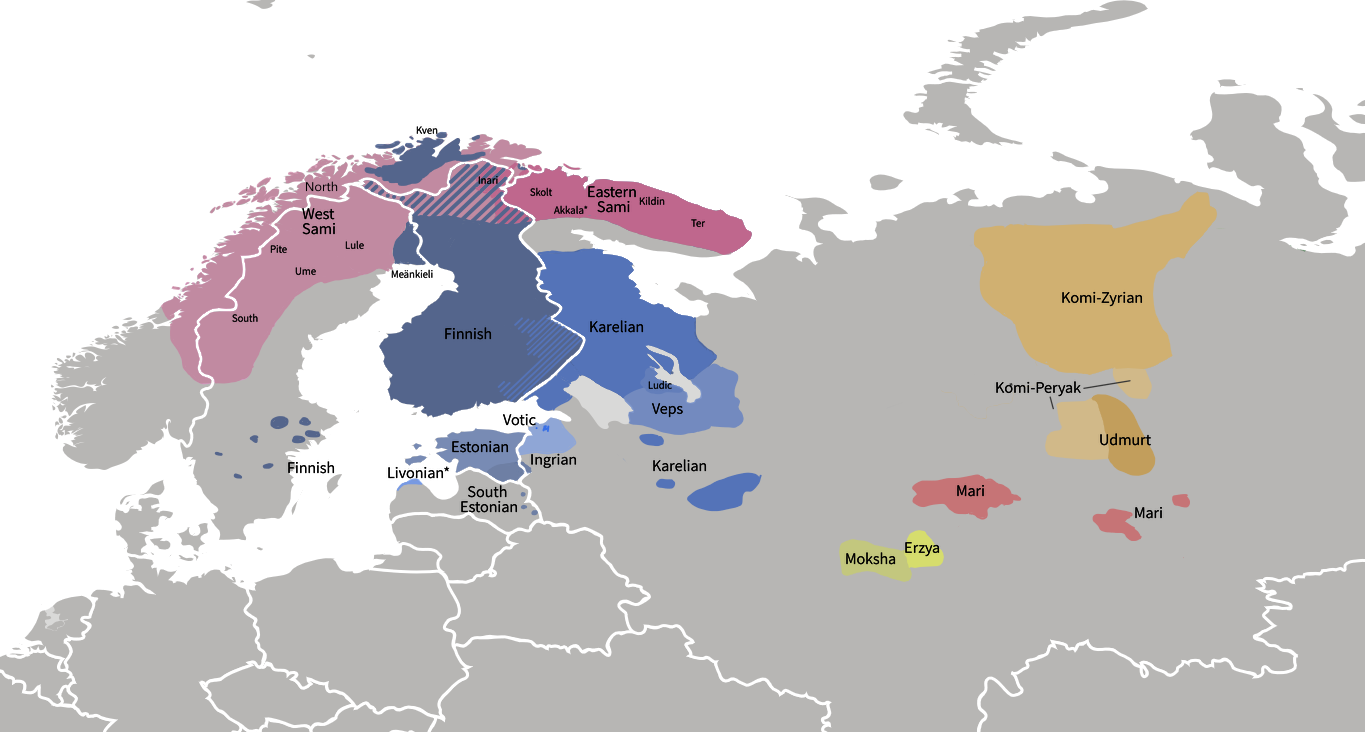
Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Greek
Medieval Greek (also known as Middle Greek, Byzantine Greek, or Romaic) is the stage of the Greek language between the end of classical antiquity in the 5th–6th centuries and the end of the Middle Ages, conventionally dated to the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople in 1453. From the 7th century onwards, Greek was the only language of administration and government in the Byzantine Empire. This stage of language is thus described as Byzantine Greek. The study of the Medieval Greek language and literature is a branch of Byzantine studies, the study of the history and culture of the Byzantine Empire. The beginning of Medieval Greek is occasionally dated back to as early as the 4th century, either to 330 AD, when the political centre of the Roman Empire was moved to Constantinople, or to 395 AD, the division of the empire. However, this approach is rather arbitrary as it is more an assumption of political, as opposed to cultural and linguistic, developments. Indeed, by this time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their Viking expansion, overseas settlements and chronologically coincides with the Viking Age, the Christianization of Scandinavia and the consolidation of Scandinavian kingdoms from about the 7th to the 15th centuries. The Proto-Norse language developed into Old Norse by the 8th century, and Old Norse began to develop into the modern North Germanic languages in the mid-to-late 14th century, ending the language phase known as Old Norse. These dates, however, are not absolute, since written Old Norse is found well into the 15th century. Old Norse was divided into three dialects: Old West Norse, ''Old West Norse'' or ''Old West Nordic'' (often referred to as ''Old Norse''), Old East Norse, ''Old East Norse'' or ''Old East Nordic'', and ''Ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old East Slavic
Old East Slavic (traditionally also Old Russian; be, старажытнаруская мова; russian: древнерусский язык; uk, давньоруська мова) was a language used during the 9th–15th centuries by East Slavs in Kievan Rus' and its successor states, from which the Belarusian, Russian, Rusyn, and Ukrainian languages later evolved. Terminology The name of the language is known as ''Old East Slavic'', in reference to the modern family of East Slavic languages. Its original speakers were the Slavic tribes inhabiting territories of today's Belarus, the western edge of Russia, and western and central Ukraine. However, the term ''Old East Slavic'' is not universally applied. The language is traditionally also known as ''Old Russian'', (; russian: древнерусский язык, translit=drevnerusskij jazyk), however the term has been described as a misnomer, because the initial stages of the language which it denotes predate the dialecta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnic Peoples
The Finnic or Fennic peoples, sometimes simply called Finns, are the nations who speak languages traditionally classified in the Finnic (now commonly '' Finno-Permic'') language family, and which are thought to have originated in the region of the Volga River. The largest Finnic peoples by population are the Finns (or more precisely the Suomi, 6 million), the Estonians (1 million), the Mordvins (800,000), the Mari (570,000), the Udmurts (550,000), the Komis (330,000) and the Sami (100,000). The scope of the name "Finn" and "Finnic" varies by country. Today, Finnish and Estonian scholars restrict the term "Finnic" to the Baltic Finns, who include the Western Finns of Finland and their closest relatives but not the Sami. In Russia, however, where the Eastern Finns live, the word continues to be used in the broad sense, and sometimes implies the Volga Finns who have their own national republics. Three groups of people are covered by the names "Finn" and "Finnic" in the broad se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnic Paganism
Finnish paganism is the indigenous pagan religion in Finland and Karelia prior to Christianisation. It was a polytheistic religion, worshipping a number of different deities. The principal god was the god of thunder and the sky, Ukko; other important gods included Jumo (Jumala), Ahti, and Tapio. Jumala was a sky god; today, the word "Jumala" refers to all gods in general. Ahti was a god of the sea, waters and fish. Tapio was the god of forests and hunting. Finnish paganism shows many similarities with the religious practices of related cultures, such as Estonian, Mordvin, Mari, Sami and other Eurasian paganism. It shares some features with its neighbouring Baltic, Norse and Germanic paganisms. The organic tradition was sidelined due to Christianization starting from ca. 12th century and finally broken by the early 20th century, when folk magic and oral traditions went extinct. Finnish paganism provided the inspiration for a contemporary pagan movement Suomenusko (Finnis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |