|
Kveim Test
The Kveim test, Nickerson-Kveim or Kveim-Siltzbach test is a skin test used to detect sarcoidosis, where part of a spleen from a patient with known sarcoidosis is injected into the skin of a patient suspected to have the disease. If non caseating granulomas are found (4–6 weeks later), the test is positive. If the patient has been on treatment (e.g. glucocorticoids), the test may be false negative. The test is not commonly performed, and in the UK no substrate has been available since 1996. There is a concern that certain infections, such as bovine spongiform encephalopathy Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), commonly known as mad cow disease, is an incurable and invariably fatal neurodegenerative disease of cattle. Symptoms include abnormal behavior, trouble walking, and weight loss. Later in the course of ..., could be transferred through a Kveim test. It is named for the Norwegian pathologist Morten Ansgar Kveim, who first reported the test in 1941 using lymph no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin Test
A skin test is a medical test in which a substance is injected into the skin. Examples * Casoni test * Corneometry * Dick test * Fernandez reaction * Frei test * Hair perforation test * Kveim test * Leishmanin skin test * Lepromin * Patch test * Schick test * Skin allergy test * Sweat diagnostics * Sweat test The sweat test measures the concentration of chloride that is excreted in sweat. It is used to screen for cystic fibrosis (CF). Due to defective chloride channels (CFTR), the concentration of chloride in sweat is elevated in individuals with CF. ... * Tine test * Transepidermal water loss * Trichoscopy References * {{Med-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
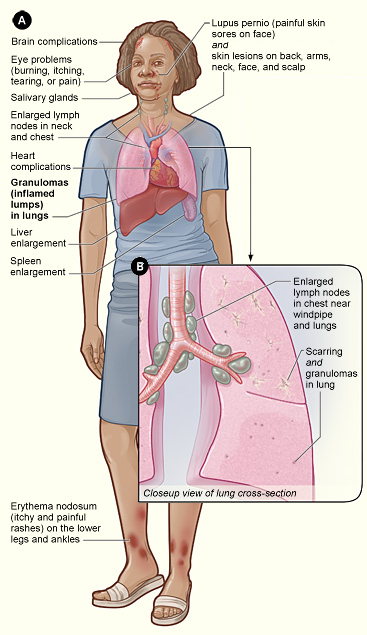
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and brain. Any Organ (anatomy), organ can be affected though. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no, or only mild, symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, large lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs and symptoms, which may be supported by tissue biopsy, biopsy. Findings that make i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .σπλήν Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, ''A Greek-English Lexicon'', on Perseus Digital Library The spleen plays very important roles in regard to red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the . It removes old red blood cells and holds a reserve of blood, which can be valuable in case of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such substances include infectious organisms including bacteria and fungi, as well as other materials such as foreign objects, keratin, and suture fragments. Definition In pathology, a granuloma is an organized collection of macrophages. In medical practice, doctors occasionally use the term ''granuloma'' in its more literal meaning: "a small nodule". Since a small nodule can represent any tissue from a harmless nevus to a malignant tumor, this use of the term is not very specific. Examples of this use of the term ''granuloma'' are the lesions known as vocal cord granuloma (known as contact granuloma), pyogenic granuloma, and intubation granuloma, all of which are examples of granulation tissue, not granulomas. "Pulmonary hyalinizing granuloma" is a lesion characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. The name "glucocorticoid" is a portmanteau (glucose + cortex + steroid) and is composed from its role in regulation of glucose metabolism, synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and its steroidal structure (see structure below). Glucocorticoids are part of the feedback mechanism in the immune system, which reduces certain aspects of immune function, such as inflammation. They are therefore used in medicine to treat diseases caused by an overactive immune system, such as allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and sepsis. Glucocorticoids have many diverse ( pleiotropic) effects, including potentially harmful side effects. They also interfere with some of the abnormal mechanisms in cancer cells, so they are used in high doses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), commonly known as mad cow disease, is an incurable and invariably fatal neurodegenerative disease of cattle. Symptoms include abnormal behavior, trouble walking, and weight loss. Later in the course of the disease the cow becomes unable to function normally. There is conflicting information around the time between infection and onset of symptoms. In 2002, the WHO suggested it to be approximately four to five years. Time from onset of symptoms to death is generally weeks to months. Spread to humans is believed to result in variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (vCJD). As of 2018, a total of 231 cases of vCJD had been reported globally. BSE is thought to be due to an infection by a misfolded protein, known as a prion. Cattle are believed to have been infected by being fed meat-and-bone meal (MBM) that contained either the remains of cattle who spontaneously developed the disease or scrapie-infected sheep products. The outbreak increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morten Ansgar Kveim
Morten Ansgar Kveim (27 December 1892 – 24 March 1966) was a Norwegian pathologist most remembered for describing the Kveim test. Kveim was born at Gjerstad in Aust-Agder, Norway. First starting in philology, he completed his medical training at the University of Oslo (1924).He qualified in medicine in 1925, and worked in private practice at a number of small towns in Norway. After 1929 he worked in the department of diseases of the skin in the Rikshospitalet in Oslo Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ..., becoming assistant physician in 1936. References External links 1892 births 1966 deaths People from Aust-Agder University of Oslo alumni Norwegian pathologists Oslo University Hospital people {{Norway-med-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berylliosis
Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease (CBD), is a chronic allergic-type lung response and chronic lung disease caused by exposure to beryllium and its compounds, a form of beryllium poisoning. It is distinct from acute beryllium poisoning, which became rare following occupational exposure limits established around 1950. Berylliosis is an occupational lung disease. While there is no cure, symptoms can be treated. Signs and symptoms With single or prolonged exposure by inhalation the lungs may become sensitized to beryllium. Berylliosis has a slow onset and progression. Some people who are sensitized to beryllium may not have symptoms.OSHBeryllium Health EffectsPage accessed March 29, 2016 Continued exposure causes the development of small inflammatory nodules, called granulomas. Of note, the authors of a 2006 study suggested that beryllium inhalation was not the only form of exposure and perhaps skin exposure was also a cause, as they found that a reduction in beryllium inhala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |