|
Kvant-1 (1995-02-06) Cropped
Kvant-1 (russian: Квант-1; English language, English: Quantum-I/1) (37KE) was the first module to be attached in 1987 to the Mir Core Module, which formed the core of the Soviet Union, Soviet space station ''Mir''. It remained attached to ''Mir'' until the entire space station was deorbited in 2001. The Kvant-1 module contained scientific instruments for astrophysical observations and materials science experiments. It was used to conduct research into the physics of active galaxies, quasars and neutron stars and it was uniquely positioned for studies of the Supernova SN 1987A. Furthermore, it supported biotechnology experiments in anti-viral preparations and fractions. Some additions to Kvant-1 during its lifetime were solar arrays and the ''Sofora'' and ''Rapana'' girders. The Kvant-1 module was based on the TKS (spacecraft), TKS spacecraft and was the first, experimental version of a planned series of '37K' type modules. The 37K modules featured a jettisonable TKS-E type p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvant-1 (1995-02-06) Cropped
Kvant-1 (russian: Квант-1; English language, English: Quantum-I/1) (37KE) was the first module to be attached in 1987 to the Mir Core Module, which formed the core of the Soviet Union, Soviet space station ''Mir''. It remained attached to ''Mir'' until the entire space station was deorbited in 2001. The Kvant-1 module contained scientific instruments for astrophysical observations and materials science experiments. It was used to conduct research into the physics of active galaxies, quasars and neutron stars and it was uniquely positioned for studies of the Supernova SN 1987A. Furthermore, it supported biotechnology experiments in anti-viral preparations and fractions. Some additions to Kvant-1 during its lifetime were solar arrays and the ''Sofora'' and ''Rapana'' girders. The Kvant-1 module was based on the TKS (spacecraft), TKS spacecraft and was the first, experimental version of a planned series of '37K' type modules. The 37K modules featured a jettisonable TKS-E type p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 1267
Kosmos 1267 (russian: Космос 1267 meaning ''Cosmos 1267''), also known as TKS-2, was an unmanned TKS spacecraft which docked to the Soviet space station Salyut 6 Salyut 6 (russian: Салют-6; lit. Salute 6), DOS-5, was a Soviet orbital space station, the eighth station of the Salyut programme. It was launched on 29 September 1977 by a Proton rocket. Salyut 6 was the first space station to receiv ... as part of tests to attach scientific expansion modules to stations in Earth orbit. The module which docked to the station was the FGB component of a TKS vehicle launched on April 25, 1981. The spacecraft's VA return capsule separated and landed in the Soviet Union on 1982-05-26. References Kosmos satellites 1981 in the Soviet Union Salyut program Spacecraft launched in 1981 {{USSR-spacecraft-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvant-2
Kvant-2 (russian: Квант-2; English: Quantum-II/2) (77KSD, TsM-D, 11F77D) was the third module and second major addition to the Mir space station. Its primary purpose was to deliver new science experiments, better life support systems, and an airlock to Mir. It was launched on November 26, 1989 on a Proton rocket. It docked to Mir on December 6. Its control system was designed by the NPO "Electropribor" (Kharkiv, Ukraine). Description Kvant-2 was the first Mir module based on the TKS spacecraft (77k module). Kvant-2 was divided into three compartments. They were the EVA airlock, the instrument/cargo compartment, and the instrument/experiment compartment. The instrument/cargo compartment could be sealed off and act as an extension or a back-up to the airlock. Before Kvant-2 docked to the station, EVAs had to be carried by depressurizing the docking node on the Core Module. Kvant-2 also carried the Soviet version of the Manned Maneuvering Unit for the Orlan space suit. It de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Cargo Block
The Functional Cargo Block or FGB (from the Russian ', ', GRAU index 11F77) was part of the Soviet TKS spacecraft. The TKS spacecraft was intended to be used as a resupply craft for Almaz space stations and saw some test flights in the Salyut space station program. The TKS spacecraft was formed by mating a FGB with a VA spacecraft, with both the VA and the FGB being capable of independent operation. Following the development of the FGB for the TKS spacecraft, the FGB (without VA spacecraft) formed the basis for space station modules in the Soviet and Russian space program – these space station modules are to some extent called Functional Cargo Block (FGB) as well, like the Zarya FGB module. The FGB provides "functional" support in the form of electrical power, propulsion, guidance and docking; The support for "cargo" operations is supplied in the form of a pressurized habitable cargo storage section (accessible by the crew) and the externally mounted fuel tanks. History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
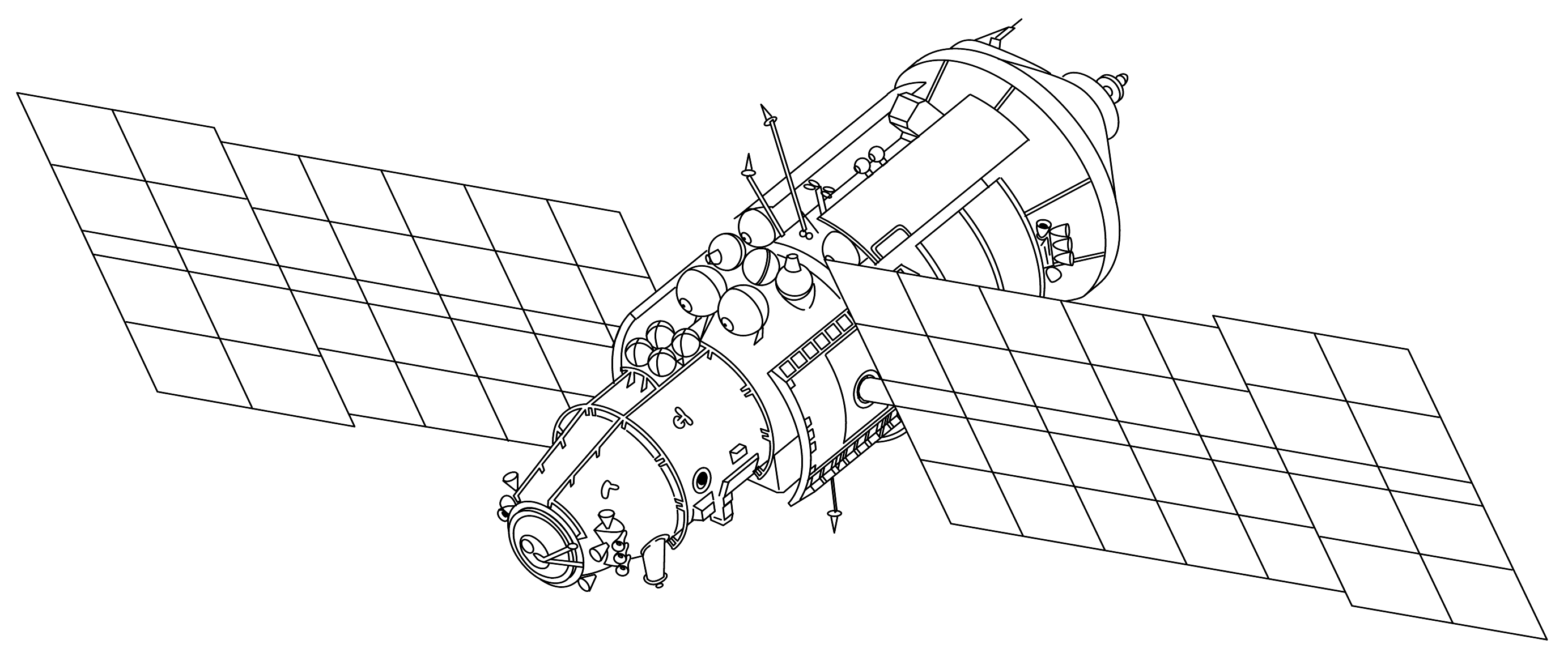
TKS Spacecraft
The TKS spacecraft (russian: Транспортный корабль снабжения, , ''Transport Supply Spacecraft'', GRAU index 11F72) was a Soviet spacecraft conceived in the late 1960s for resupply flights to the military Almaz space station. The spacecraft was designed for both crewed and autonomous uncrewed cargo resupply flights, but was never used operationally in its intended role – only four test missions were flown (including three that docked to Salyut space stations) during the program. The Functional Cargo Block (FGB) of the TKS spacecraft later formed the basis of several space station modules, including the Zarya FGB module on the International Space Station. The TKS spacecraft consisted of two spacecraft mated together, both of which could operate independently: * The VA spacecraft (known mistakenly in the West as the ''Merkur spacecraft''), which would have housed the cosmonauts during launch and reentry of a TKS spacecraft, while traveling to and fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvant Module Drawing
{{disambiguation, surname ...
Kvant is Russian for "quantum". See quantum (other). Kvant may also refer to: * ''Kvant'' (magazine), a Russian popular science magazine * ''Kvant'', a journal published by the Danish Physical Society * Kvant-1, a module of the Soviet orbital station ''Mir'' launched in 1987 * Kvant-2, a module of the Soviet orbital station ''Mir'' launched in 1989 * MAI Kvant, a Soviet aerobatic trainer airplane * NPP Kvant, a Soviet research and production institute (now a subsidiary of the Russian space flight corporation Roscosmos) * FC Kvant Obninsk, a Russian football club * Lars Kvant, a Swedish squash player * Kurt Kvant, a recurring character in detective novels by Maj Sjöwall and Per Wahlöö Martin Beck is a fictional Swedish police detective and the main character in the ten novels by Maj Sjöwall and Per Wahlöö, collectively titled ''The Story of a Crime''. Frequently referred to as the Martin Beck stories, all have been adapte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kvant Module And FSM Drawing
{{disambiguation, surname ...
Kvant is Russian for "quantum". See quantum (other). Kvant may also refer to: * ''Kvant'' (magazine), a Russian popular science magazine * ''Kvant'', a journal published by the Danish Physical Society * Kvant-1, a module of the Soviet orbital station ''Mir'' launched in 1987 * Kvant-2, a module of the Soviet orbital station ''Mir'' launched in 1989 * MAI Kvant, a Soviet aerobatic trainer airplane * NPP Kvant, a Soviet research and production institute (now a subsidiary of the Russian space flight corporation Roscosmos) * FC Kvant Obninsk, a Russian football club * Lars Kvant, a Swedish squash player * Kurt Kvant, a recurring character in detective novels by Maj Sjöwall and Per Wahlöö Martin Beck is a fictional Swedish police detective and the main character in the ten novels by Maj Sjöwall and Per Wahlöö, collectively titled ''The Story of a Crime''. Frequently referred to as the Martin Beck stories, all have been adapte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum. Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. Applications of gyroscopes include inertial navigation systems, such as in the Hubble Space Telescope, or inside the steel hull of a submerged submarine. Due to their precision, gyroscopes are also used in gyrotheodolites to maintain direction in tunnel mining. Gyroscopes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir Kvant-1 Module
''Mir'' (russian: Мир, ; ) was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996. It had a greater mass than any previous spacecraft. At the time it was the largest artificial satellite in orbit, succeeded by the International Space Station (ISS) after ''Mir'''s orbital decay, orbit decayed. The station served as a microgravity research laboratory in which crews conducted experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and spacecraft systems with a goal of developing technologies required for permanent occupation of Outer space, space. ''Mir'' was the first continuously inhabited long-term research station in orbit and held the record for the longest continuous human presence in space at 3,644 days, until it was surpassed by the ISS on 23 October 2010. It holds the record for the longes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Astronautica
The ''Encyclopedia Astronautica'' is a reference web site on space travel. A comprehensive catalog of vehicles, technology, astronauts, and flights, it includes information from most countries that have had an active rocket research program, from Robert Goddard to the NASA Space Shuttle and the Soviet Buran programme. Founded in 1994 and maintained for most of its existence by space enthusiast and author Mark Wade. He has been collecting such information for most of his life. Between 1996 and 2000 the site was hosted by ''Friends and Partners in Space''. The site is no longer updated or maintained and is now considered as partially unreliable. Although it contains a great deal of information, not all of it is correct. Reception and accolades The American Astronautical Society gave the site the Ordway Award for Sustained Excellence in Spaceflight History which "recognizes exceptional, sustained efforts to inform and educate on spaceflight and its history through one or more med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almaz
The Almaz (russian: Алмаз, lit=Diamond) program was a highly secret Soviet military space station program, begun in the early 1960s. Three crewed military reconnaissance stations were launched between 1973 and 1976: Salyut 2, Salyut 3 and Salyut 5. To cover the military nature of the program the three launched Almaz stations were designated as civilian Salyut space stations. Salyut 2 failed shortly after achieving orbit, but Salyut 3 and Salyut 5 both conducted successful crewed testing. Following Salyut 5, the Soviet Ministry of Defense judged in 1978 that the time and resources consumed by station maintenance outweighed the benefits relative to automatic reconnaissance satellites. The space stations' cores were known internally as OPS (russian: ОПС, GRAU index 11F71 and 11F71B), from "Orbital Piloted Station" (russian: Орбитальная Пилотируемая Станция). As part of the Almaz program, the Soviets developed several spacecraft for support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |