|
Kusudama
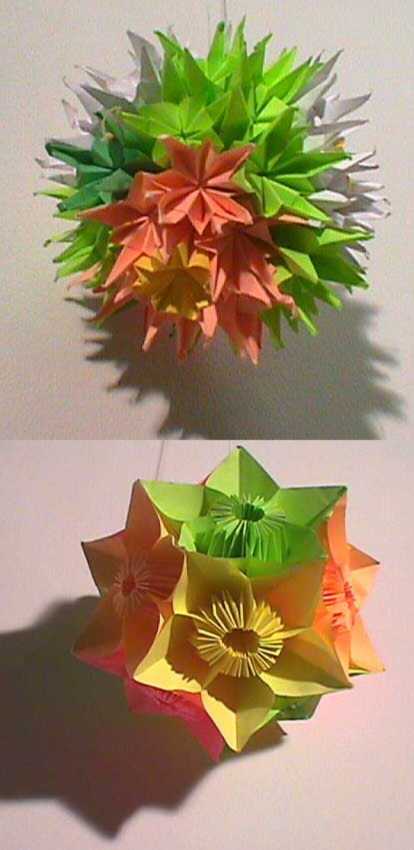
The Japanese kusudama (薬玉; lit. medicine ball) is a paper model that is usually (although not always) created by sewing multiple identical pyramidal units together using underlying geometric principles to form a spherical shape. Alternately the individual components may be glued together. (e.g. the kusudama in the lower photo is entirely glued, not threaded together) Occasionally, a tassel is attached to the bottom for decoration. The term ''kusudama'' originates from ancient Japanese culture, where they were used for incense and potpourri; possibly originally being actual bunches of flowers or herbs. The word itself is a combination of two Japanese words ''kusuri'' ("medicine") and ''tama'' ("ball"). They are now typically used as decorations, or as gifts. The kusudama is important in origami particularly as a precursor to modular origami. It is often confused with modular origami, but is not such because the units are strung or pasted together, instead of folded together as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Origami
Modular origami or unit origami is a paperfolding technique which uses two or more sheets of paper to create a larger and more complex structure than would be possible using single-piece origami techniques. Each individual sheet of paper is folded into a module, or unit, and then modules are assembled into an integrated flat shape or three-dimensional structure, usually by inserting flaps into pockets created by the folding process. These insertions create tension or friction that holds the model together. Definition and restrictions Modular origami can be classified as a sub-set of multi-piece origami, since the rule of restriction to one sheet of paper is abandoned. However, all the other rules of origami still apply, so the use of glue, thread, or any other fastening that is not a part of the sheet of paper is not generally acceptable in modular origami. The additional restrictions that distinguish modular origami from other forms of multi-piece origami are using many iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modular Origami
Modular origami or unit origami is a paperfolding technique which uses two or more sheets of paper to create a larger and more complex structure than would be possible using single-piece origami techniques. Each individual sheet of paper is folded into a module, or unit, and then modules are assembled into an integrated flat shape or three-dimensional structure, usually by inserting flaps into pockets created by the folding process. These insertions create tension or friction that holds the model together. Definition and restrictions Modular origami can be classified as a sub-set of multi-piece origami, since the rule of restriction to one sheet of paper is abandoned. However, all the other rules of origami still apply, so the use of glue, thread, or any other fastening that is not a part of the sheet of paper is not generally acceptable in modular origami. The additional restrictions that distinguish modular origami from other forms of multi-piece origami are using many iden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origami
) is the Japanese paper art, art of paper folding. In modern usage, the word "origami" is often used as an inclusive term for all folding practices, regardless of their culture of origin. The goal is to transform a flat square sheet of paper into a finished sculpture through folding and sculpting techniques. Modern origami practitioners generally discourage the use of cuts, glue, or markings on the paper. Origami folders often use the Japanese word ' to refer to designs which use cuts. On the other hand, in the detailed Japanese classification, origami is divided into stylized ceremonial origami (儀礼折り紙, ''girei origami'') and recreational origami (遊戯折り紙, ''yūgi origami''), and only recreational origami is generally recognized as origami. In Japan, ceremonial origami is generally called "origata" (:ja:折形) to distinguish it from recreational origami. The term "origata" is one of the old terms for origami. The small number of basic Origami techniques, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomoko Fuse
Tomoko Fuse (, ''Fuse Tomoko'', born in Niigata, 1951) is a Japanese origami artist and author of numerous books on the subject of modular origami, and is by many considered as a renowned master in such discipline. Fuse first learned origami while in the hospital as a child. When she was 19 years old, she studied for two and a half years with origami master Toyoaki Kawai. She started publishing origami books in 1981, and has since published more than 60 books (plus overseas editions) . She has created numerous origami designs, including boxes, ''kusudama'', paper toys, masks, modular polyhedra, as well as other geometric forms and objects, such as origami tessellations, with publications in Japanese, Korean and English. She now resides with her husband Taro Toriumi, a respected woodblock printmaker and etcher, in rural Nagano prefecture is a landlocked prefecture of Japan located in the Chūbu region of Honshū. Nagano Prefecture has a population of 2,052,493 () and has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origami
) is the Japanese paper art, art of paper folding. In modern usage, the word "origami" is often used as an inclusive term for all folding practices, regardless of their culture of origin. The goal is to transform a flat square sheet of paper into a finished sculpture through folding and sculpting techniques. Modern origami practitioners generally discourage the use of cuts, glue, or markings on the paper. Origami folders often use the Japanese word ' to refer to designs which use cuts. On the other hand, in the detailed Japanese classification, origami is divided into stylized ceremonial origami (儀礼折り紙, ''girei origami'') and recreational origami (遊戯折り紙, ''yūgi origami''), and only recreational origami is generally recognized as origami. In Japan, ceremonial origami is generally called "origata" (:ja:折形) to distinguish it from recreational origami. The term "origata" is one of the old terms for origami. The small number of basic Origami techniques, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
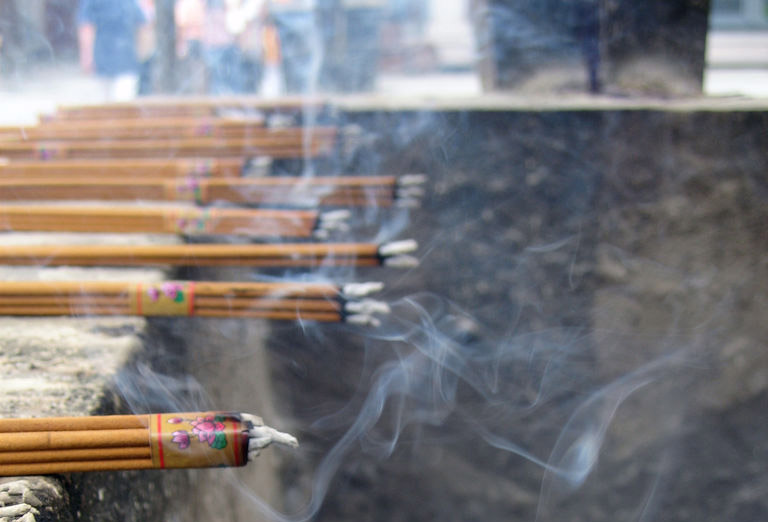
Incense
Incense is aromatic biotic material that releases fragrant smoke when burnt. The term is used for either the material or the aroma. Incense is used for aesthetic reasons, religious worship, aromatherapy, meditation, and ceremony. It may also be used as a simple deodorant or insect repellent. Incense is composed of aromatic plant materials, often combined with essential oils. The forms taken by incense differ with the underlying culture, and have changed with advances in technology and increasing number of uses. Incense can generally be separated into two main types: "indirect-burning" and "direct-burning". Indirect-burning incense (or "non-combustible incense") is not capable of burning on its own, and requires a separate heat source. Direct-burning incense (or "combustible incense") is lit directly by a flame and then fanned or blown out, leaving a glowing ember that smoulders and releases a smoky fragrance. Direct-burning incense is either a paste formed around a bamboo stic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potpourri
Potpourri ( ) is a mixture of dried, naturally fragrant plant materials used to provide a gentle natural scent, commonly in residential settings. It is often placed in a decorative bowl. The word "potpourri" comes into English from the French word . The French term has two connotations. It is the French name for a Spanish stew with a wide variety of ingredients called , a specialty of the city of Burgos. The word in French has the same meaning as it does in English (and as does in Spanish), while the word , like Spanish , means "rotten". History Potpourri has been used in rooms since ancient times, in a variety of ways, including just scattering it on the floor. In early 17th-century France, fresh herbs and flowers were gathered—beginning in spring and continuing throughout the summer. The herbs were left for a day or two to become limp, then layered with coarse sea salt. The aging mixture was stirred occasionally as layers were added to it. Often the mixture would fer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
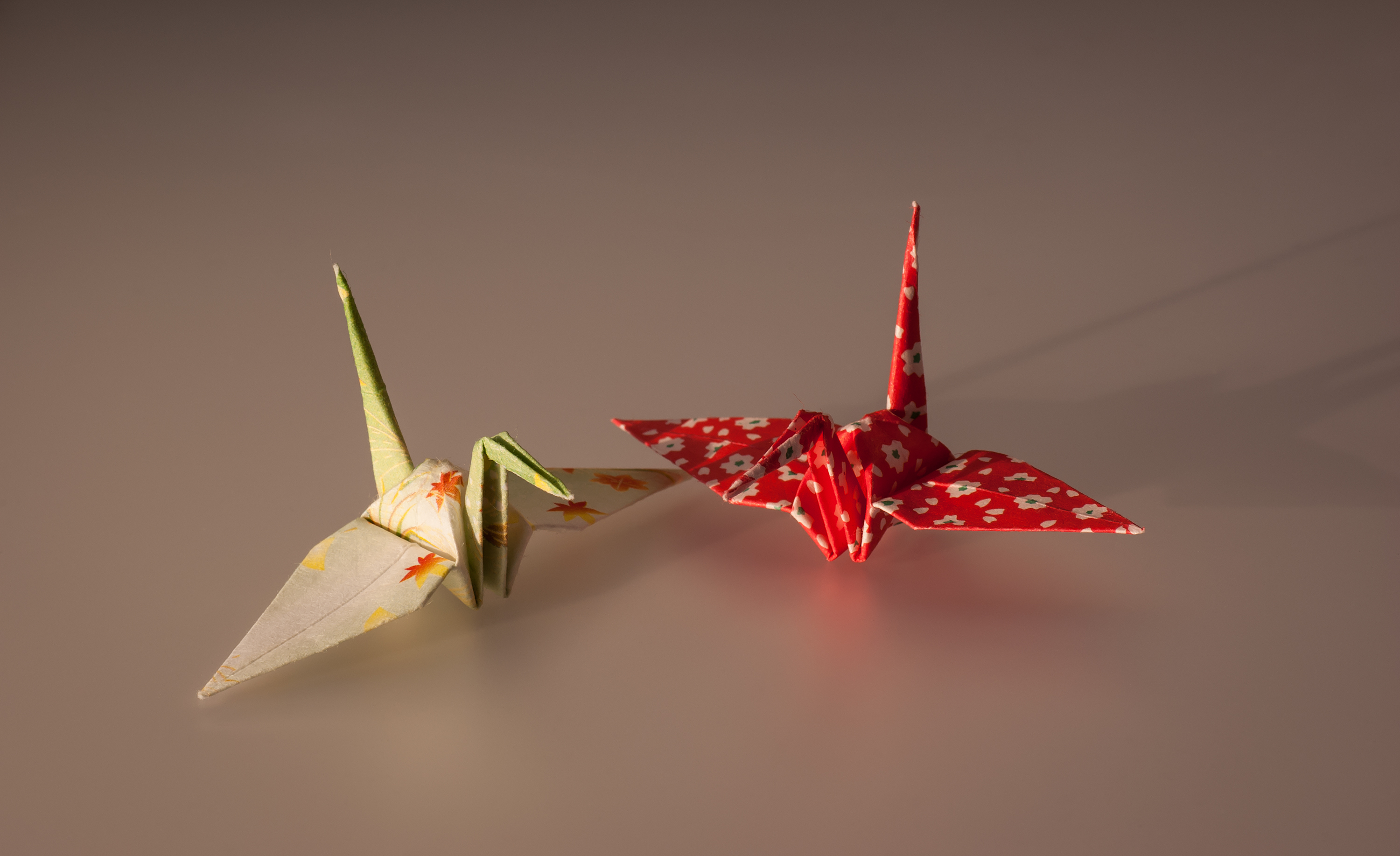
Thousand Origami Cranes
The crane in Japan is one of the mystical or holy creatures (others include the dragon and the tortoise) and is said to live for a thousand years: That is why cranes are made, one for each year. In some stories it is believed that the 1000 cranes must be completed within one year and they must all be made by the person (or group of people) who will make the wish at the end. Cultural significance In Japan cranes have been thought a symbol of long life. An old fix phrases says "cranes live a thousand years". Here "a thousand" is not necessary to designate the exact number, but a poetic expression of huge amounts. Historically well-wishers offered a picture of a crane to shrines and temples as well as paper cranes. Origami, specially crafted and pattern-printed paper was invented in Edo period, and in the late 17th century books referring not only to "paper cranes" but also to "one thousand cranes" were publish Nowadays cranes are often given to a person who is seriously ill, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senbazuru
The crane in Japan is one of the mystical or holy creatures (others include the dragon and the tortoise) and is said to live for a thousand years: That is why cranes are made, one for each year. In some stories it is believed that the 1000 cranes must be completed within one year and they must all be made by the person (or group of people) who will make the wish at the end. Cultural significance In Japan cranes have been thought a symbol of long life. An old fix phrases says "cranes live a thousand years". Here "a thousand" is not necessary to designate the exact number, but a poetic expression of huge amounts. Historically well-wishers offered a picture of a crane to shrines and temples as well as paper cranes. Origami, specially crafted and pattern-printed paper was invented in Edo period, and in the late 17th century books referring not only to "paper cranes" but also to "one thousand cranes" were publish Nowadays cranes are often given to a person who is seriously ill, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology Technical standard, standard for the consistent character encoding, encoding, representation, and handling of Character (computing), text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, which is maintained by the Unicode Consortium, defines as of the current version (15.0) 149,186 characters covering 161 modern and historic script (Unicode), scripts, as well as symbols, emoji (including in colors), and non-visual control and formatting codes. Unicode's success at unifying character sets has led to its widespread and predominant use in the internationalization and localization of computer software. The standard has been implemented in many recent technologies, including modern operating systems, XML, and most modern programming languages. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Universal Coded Character Set, ISO/IEC 10646, each being code-for-code id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |