|
Kurt Wintgens
''Leutnant'' Kurt Wintgens (1 August 1894 – 25 September 1916) was a German World War I fighter ace. He was the first military fighter pilot to score a victory over an opposing aircraft, while piloting an aircraft armed with a synchronized machine gun. Wintgens was the recipient of the Iron Cross and the Pour le Mérite (Blue Max). Background Wintgens was born into a military family in Neustadt in Oberschlesien. His military service commenced when he joined the Telegraphen-Bataillon Nr. 2 in Frankfurt/Oder as a ''Fahnenjunker'' (cadet officer) in 1913. Involvement in First World War Though still in military school when the war began in 1914, Wintgens was sent to the Eastern Front as a leutnant and won the Iron Cross, 2nd Class. On transferring to the German Air Service, Wintgens flew first as an observer, apparently alternating with telegraph duty. However, in early 1915 he entered pilot training at the Fokker school in Schwerin, where ''Leutnant'' Otto Parschau had alread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prudnik
Prudnik (, szl, Prudnik, Prōmnik, german: Neustadt in Oberschlesien, Neustadt an der Prudnik, la, Prudnicium) is a town in southern Poland, located in the southern part of Opole Voivodeship near the border with the Czech Republic. It is the administrative seat of Prudnik County and Gmina Prudnik. Its population numbers 21,368 inhabitants (2016). Since 2015, Prudnik is a member of the Cittaslow, Cittaslow International. The town was founded in the 1250s, and was historically part of the Polish-ruled Duchy of Opole, and afterwards was located within the Habsburg monarchy, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Poland, Habsburg Monarchy again, Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia, Germany, and eventually Poland again. It was once an important industrial hub known for its shoe-making traditions and more recently towel making by the Zakłady Przemysłu Bawełnianego "Frotex", ZPB "Frotex" Company, one of the largest towel manufacturers in Europe. The town also possesses numerous architectural m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Parschau
''Leutnant'' Otto Parschau (11 November 1890 – 21 July 1916) was a German World War I flying ace and recipient of the Pour le Mérite, Royal House Order of Hohenzollern, and Iron Cross, First Class. He was noted as one of the pre-eminent aces on the Fokker Eindecker. He was one of the world's first flying aces. Parschau and ''Leutnant'' Kurt Wintgens were the pilots chosen to fly the prototype of the revolutionary Fokker Eindecker fighter plane with a machine gun synchronized to fire safely through its propeller arc via use of a gun synchronizer. Background Parschau was born in Klausen (now Klutznick, Poland), in the Allenstein district of East Prussia. He became a commissioned officer a year after having joined the ''Infanterie-Regiment Nr. 151'' in 1910. Parschau was trained as a pilot in Johannisthal, Darmstadt, and in Hanover and received his licence on 4 July 1913. World War I Upon the outbreak of hostilities in August 1914 Parschau was already serving with the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
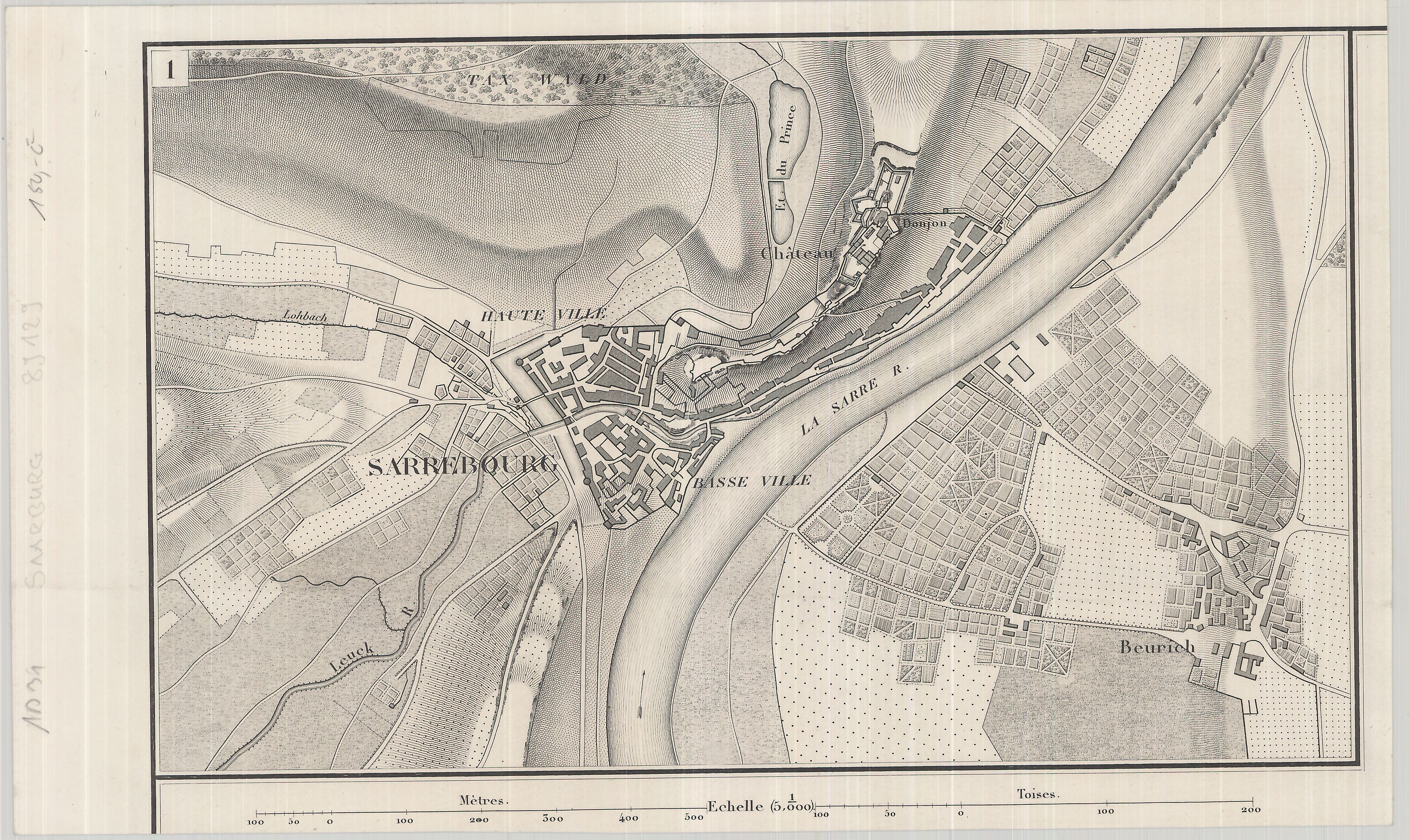
Lunéville
Lunéville ( ; German, obsolete: ''Lünstadt'' ) is a commune in the northeastern French department of Meurthe-et-Moselle. It is a subprefecture of the department and lies on the river Meurthe at its confluence with the Vezouze. History Lunéville was a renowned resort in the 18th century, known as the capital of Lorraine. The grand Château de Lunéville, built in 1702 for Leopold, Duke of Lorraine to replace an older palace, was the residence of the duke of Lorraine until the duchy was annexed by France in 1766. The château was designed in the style of Versailles to satisfy Leopold's wife, Élisabeth Charlotte d'Orléans, the niece of Louis XIV, and became known as the "Versailles of Lorraine". It includes a chapel designed by Germain Boffrand. Leopold and his wife were the parents of Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine and Francis I, Holy Roman Emperor (through him they were the grandparents of Marie Antoinette). The last duke of Lorraine was Stanislaus I, the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Du Peuty
Paul may refer to: *Paul (given name), a given name (includes a list of people with that name) *Paul (surname), a list of people People Christianity * Paul the Apostle (AD c.5–c.64/65), also known as Saul of Tarsus or Saint Paul, early Christian missionary and writer *Pope Paul (other), multiple Popes of the Roman Catholic Church *Saint Paul (other), multiple other people and locations named "Saint Paul" Roman and Byzantine empire *Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus (c. 229 BC – 160 BC), Roman general *Julius Paulus Prudentissimus (), Roman jurist *Paulus Catena (died 362), Roman notary * Paulus Alexandrinus (4th century), Hellenistic astrologer *Paul of Aegina or Paulus Aegineta (625–690), Greek surgeon Royals * Paul I of Russia (1754–1801), Tsar of Russia * Paul of Greece (1901–1964), King of Greece Other people * Paul the Deacon or Paulus Diaconus (c. 720 – c. 799), Italian Benedictine monk * Paul (father of Maurice), the father of Maurice, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morane-Saulnier Type L
The Morane-Saulnier L, or Morane-Saulnier Type L, or officially MoS-3, was a French parasol wing one or two-seat scout aeroplane of the First World War. The Type L became one of the first successful fighter aircraft when it was fitted with a single machine gun that fired through the arc of the propeller, which was protected by armoured deflector wedges. Its immediate effectiveness in this role launched an arms race in fighter development, and the Type L was swiftly rendered obsolete. The original Type L used wing warping for lateral control, but a later version designated Type LA was fitted with ailerons.Taylor 1989, p. 684. Built by Morane-Saulnier, large numbers of the Type L were ordered by the French '' Aviation Militaire'' at the outbreak of the war. In total about 600 Type Ls were built and, in addition to the French air force, they served with the Royal Flying Corps, Royal Naval Air Service and the Imperial Russian Air Service. The type was also produced under lic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Spandau Triple Mount
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early Branch, a stream in Missouri * Early County, Georgia Other uses * ''Early'' (Scritti Politti album), 2005 * ''Early'' (A Certain Ratio album), 2002 * Early (name) * Early effect, an effect in transistor physics * Early Records, a record label * the early part of the morning See also * Earley (other) Earley is a town in England. Earley may also refer to: * Earley (surname), a list of people with the surname Earley * Earley (given name), a variant of the given name Earlene * Earley Lake, a lake in Minnesota *Earley parser, an algorithm *Earley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morane-Saulnier L Drawing
Aéroplanes Morane-Saulnier was a French aircraft manufacturing company formed in October 1911 by Raymond Saulnier (1881–1964) and the Morane brothers, Léon (1885–1918) and Robert (1886–1968). The company was taken over and diversified in the 1960s. History Model development Morane-Saulnier's first product was the Morane-Borel monoplane, a development of a monoplane design produced by the Morane company (sometimes called Type A) in partnership with Gabriel Borel). Using a wing-warping mechanism for control, this was the type in which Jules Védrines won the Paris-Madrid race on May 26, 1911. Morane-Saulnier's first commercially successful design was the Morane-Saulnier G, a wire-braced shoulder-wing monoplane with wing warping. This led to the development of a series of aircraft and was very successful in racing and setting records. The Type G was a 2-seater, and was reduced slightly in size to produce the Morane-Saulnier H, a single-seater, and was given a fair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fokker M5K-MG E5-15
Fokker was a Dutch aircraft manufacturer named after its founder, Anthony Fokker. The company operated under several different names. It was founded in 1912 in Berlin, Germany, and became famous for its fighter aircraft in World War I. In 1919 the company moved its operations to the Netherlands. During its most successful period in the 1920s and 1930s, it dominated the civil aviation market. Fokker went into bankruptcy in 1996, and its operations were sold to competitors. History Fokker in Germany At age 20, while studying in Germany, Anthony Fokker built his initial aircraft, the ''Spin'' (Spider)—the first Dutch-built plane to fly in his home country. Taking advantage of better opportunities in Germany, he moved to Berlin, where in 1912, he founded his first company, Fokker Aeroplanbau, later moving to the Görries suburb just southwest of Schwerin (at ), where the current company was founded, as Fokker Aviatik GmbH, on 12 February 1912. World War I Fokker capitalized on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Kissenberth
Otto Kissenberth (26 February 1893 – 2 August 1919) was a German flying ace of World War I credited with 20 aerial victories. He was a prewar mechanical engineer who joined the German air service in 1914. After being trained and after serving as a reconnaissance pilot, he became one of the first German fighter pilots, flying with ''Kampfeinsitzerkommando'' (Combat Single-Seater Command) KEK Einsisheim. He scored six victories with this unit as it morphed into a fighter squadron, '' Jagdstaffel 16''. His success brought him command of '' Jagdstaffel 23'' on 4 August 1917. He would run his victory tally to 20, downing his final victim using a captured British Sopwith Camel on 20 May 1918. Nine days later, a crash while flying the Camel ended Kissenberth's combat career. His injuries were severe enough he was not returned to combat, instead being assigned to command Schleissheim's flying school. Although Otto Kissenberth survived the war, he died soon after in a mountaineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pince-nez
Pince-nez ( or , plural form same as singular; ) is a style of glasses, popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, that are supported without earpieces, by pinching the bridge of the nose. The name comes from French ''pincer'', "to pinch", and ''nez'', "nose". Although pince-nez were used in Europe since the late 14th century, modern ones appeared in the 1840s and reached their peak popularity around 1880 to 1900. Because they did not always stay on the nose when placed, and because of the stigma sometimes attached to the constant wearing of eyeglasses, pince-nez were often connected to the wearer's clothing or ear via a suspension chain, cord, or ribbon so that they could be easily removed and not lost. Varieties Rivet spectacles The earliest form of eyewear for which any archaeological record exists comes from the middle of the 15th century. It is a primitive pince-nez whose frames were made from pieces of either metacarpal bone from the forelimb of a bull or fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saarburg
Saarburg (, ) is a city of the Trier-Saarburg district, in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, on the banks of the river Saar (river), Saar in the hilly country a few kilometers upstream from the Saar's junction with the Moselle. Now known as a tourist attraction, the river Leuk flows into the town center and makes a spectacular drop of some 60 feet before joining the larger Saar that bisects the town. The waterfall is the result of a 13th-century project to redirect the Leuk through the city center. Saarburg is the seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") Saarburg-Kell. The area around Saarburg is noted for the cultivation of Riesling grapes. History The history of the city begins with the construction of the now-ruined castle by Graf Siegfried of Luxembourg in 964. It received its town charter in 1291. The city has a bell (instrument), bell foundry, the Glockengießerei Mabilion, which has been in operation since the 1770s, and the only one in Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feldflieger Abteilung
Feldflieger Abteilung (''FFA'', Field Flying Company) was the title of the pioneering field aviation units of what became the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' (German air service) by October 1916, during World War I. Composition The use of aircraft as a tactical reconnaissance tool, to serve within the ''Deutsches Heer'''s ''Fliegertruppen des deutschen Kaiserreiches'' air service formed in 1910, was established by the German Army in its annual exercise in June 1911. Early usage was limited to providing post-flight situation reports. At the start of World War I, there were thirty-three units, comprising one allocated to each of the eight Army Headquarters and one to each of the twenty-five regular Corps Headquarters.Cowin, H.W. p.13 Each unit, having a designation number usually matching that of the army group it was assigned to, was equipped with either six Idflieg Category A (unarmed monoplane) or Category B (unarmed biplane) two-seater aircraft. By March 1915 the number of Feldflieger Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |