|
Kureinji
The Kureinji, otherwise known as the Keramin, are an Aboriginal group whose traditional lands are located in southwest New South Wales, Australia, along the north side of the Murray River roughly between today's settlements of Euston and Wentworth. Language Kureinji was one of 35 languages spoken in this area of southwestern New South Wales, around and north of the border with Victoria. Linguistically the tribe was part of the Lower Murray Areal group, and with Yitayita and Dadi Dadi forms a distinct subfamily. Country According to Norman Tindale the Kureinji's traditional lands embraced some of territory, running in good part along the northern banks of the Murray River, ranging from the vicinity of Euston to Wentworth downstream. Across the river from the Kureinji, Mildura, which is in Latjilatji tribal land, was first settled by Europeans in 1847. Kemendok National Park is part of their traditional land, and traces of their habitation remains in scar trees, fire hear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kureinji Language
Kureinji is an extinct language of southwest New South Wales ) , nickname = , image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , es .... It is also called Keramin and Kemendok, though it is not clear if these are dialects or synonyms. ''Keramin'' is also spelled ''Karin, Kerinma, Karinma, Karingma, Keramin;'' other names are ''Orangema, Pintwa''. Horgen suggests that ''Yerreyerre'' is another name for Keramin, but this name may refer to other languages. References Lower Murray languages {{ia-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euston, New South Wales
Euston is a small town on the banks of the Murray River, southern New South Wales, Australia in Balranald Shire. The twin town of Robinvale is on the other side of the river in the state of Victoria. At the , Euston had a population of 822 people. Until the irrigation development at Robinvale, Euston was the main town in the area. A post office opened on 1 May 1852. It closed in 1853, then reopened in 1856. History Charles Sturt passed through the general country in 1830, and Charles Lockhart in 1862. In 1876 the settlement at Euston was described in the following terms: Euston is a crossing-place for sheep and cattle. There is a Custom-house officer here, though I should judge that his avocations were not of an extremely onerous nature, and the township also possesses a post and telegraph office. If the building can be taken as a type of the township, Euston has not a long life before it. The walls appear as if rent apart by an earthquake. The hotels and about a dozen small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jitajita
The Jitajita, otherwise spelt ''Yitayita,'' are an indigenous Australian people of southern New South Wales. Language The Yitayita spoke one of the languages of the lower Murray river group that included Dadi Dadi and Kureinji, as is distinctive for the large number of monosyllables in its vocabulary. Name The tribal name Jitajita is a reduplicative endonym formed from their word for 'no' (''jita''). Numerous tribes in the area defined themselves in terms of the negative used. Early ethnographers marveled at the variety of words for 'no' among the Riverine tribes, as an index of the differences in their languages. Peter Beveridge remarked: Each tribes possesses a ''gnalla wattow'' or postman, who can speak and understand the dialects of all the tribes within a radius of 150 miles. The persons of these officials are held sacred, even by tribes which are at feud with their own: they therefore negotiate all matters of barter and trade policy. Country The Jitajita lands covered som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Australians
Indigenous Australians or Australian First Nations are people with familial heritage from, and membership in, the ethnic groups that lived in Australia before British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups: the Aboriginal peoples of the Australian mainland and Tasmania, and the Torres Strait Islander peoples from the seas between Queensland and Papua New Guinea. The term Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples or the person's specific cultural group, is often preferred, though the terms First Nations of Australia, First Peoples of Australia and First Australians are also increasingly common; 812,728 people self-identified as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin in the 2021 Australian Census, representing 3.2% of the total population of Australia. Of these indigenous Australians, 91.4% identified as Aboriginal; 4.2% identified as Torres Strait Islander; while 4.4% identified with both groups. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scar Tree
A scarred tree or scar tree, also known as a canoe tree and shield tree, is a tree which has had Bark (botany), bark removed by Aboriginal Australians for the creation of Canoe#Australia, bark canoes, humpy, shelters, weapons such as shields, tools, traps, containers (such as Coolamon (vessel), coolamons) or other Cultural artifact, artefacts. Carved trees are created as a form of artistic and spiritual expression by some Aboriginal peoples, to mark sites of significance such as burial sites. Description Bark was removed by making deep cuts in a tree with a stone pickaxe or other similar tool. The area of bark removed is typically regular in shape, often with parallel sides and slightly pointed or rounded ends, and the scar usually stops above ground level. Australian native Eucalypt species such as Eucalyptus melliodora, box and Eucalyptus camaldulensis, red gum (especially in Victoria, Australia, Victoria), or whichever species are native in the area. Scars remain in trees th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANU Press
ANU Press (or Australian National University Press; originally ANU E Press) is an open-access scholarly publisher of books, textbooks and journals. It was established in 2004 to explore and enable new modes of scholarly publishing. In 2014, ANU E Press changed its name to ANU Press to reflect the changes the publication industry had seen since its foundation. History ANU Press was Australia's first primarily electronic academic publisher. ANU Press justified its foundation by mentioning the desire to publish scholarly works that would not necessarily gain profit, and the belief that online publishing was an viable alternative to traditional academic publishing that overcame the inaccessibility, costs, and requirements for setup that were inherent in traditional publishing. Activities ANU Press produces on average 50–60 fully peer-reviewed research publications each year, and maintains a website featuring over 700 recent and back-list titles. It is recognised by the De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Environment And Heritage (New South Wales)
The New South Wales Office of Environment and Heritage (OEH), a former division of the Government of New South Wales between April 2011 and July 2019, was responsible for the care and protection of the environment and heritage, which includes the natural environment, Aboriginal country, culture and heritage, and built heritage in New South Wales, Australia. The OEH supported the community, business and government in protecting, strengthening and making the most of a healthy environment and economy within the state. The OEH was part of the Department of Planning and Environment cluster and managed national parks and reserves. Following the 2019 state election, the agency was abolished and most functions of the agency were assumed by the Department of Planning, Industry and Environment with effect from 1 July 2019. The heritage functions were assumed by the Department of Premier and Cabinet, but would be transferred back to the Department of Planning and Environment on 1 Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal History
''Aboriginal History'' is an annual Peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal published as an open access journal by Aboriginal History Inc. It was established in 1977 (co-founded and edited by Diane Barwick) and covers interdisciplinary historical studies in the field of the interactions between Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and non-Indigenous peoples. The Journal has been described as "... a flagship of the field of Australian Aboriginal history." The journal's scope includes the areas of Australian Indigenous history and oral histories, languages, biographies, bibliographic guides and archival research. It has also brought previously unpublished manuscripts and research in the fields of Australian archaeology, anthropology, linguistics, demography, sociology, law and geography to the professional and wider public. A focus on cultural, political and economic history is complemented by critiques of current events of relevance to Aboriginal and Torres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Sturt
Charles Napier Sturt (28 April 1795 – 16 June 1869) was a British officer and explorer of Australia, and part of the European exploration of Australia. He led several expeditions into the interior of the continent, starting from Sydney and later from Adelaide. His expeditions traced several of the westward-flowing rivers, establishing that they all merged into the Murray River, which flows into the Southern Ocean. He was searching to prove his own passionately held belief that an " inland sea" was located at the centre of the continent. He reached the rank of Captain, served in several appointed posts, and on the Legislative Council. Born to British parents in Bengal, British India, Sturt was educated in England for a time as a child and youth. He was placed in the British Army because his father was not wealthy enough to pay for Cambridge. After assignments in North America, Sturt was assigned to accompany a ship of convicts to Australia in 1827. Finding the place to his lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
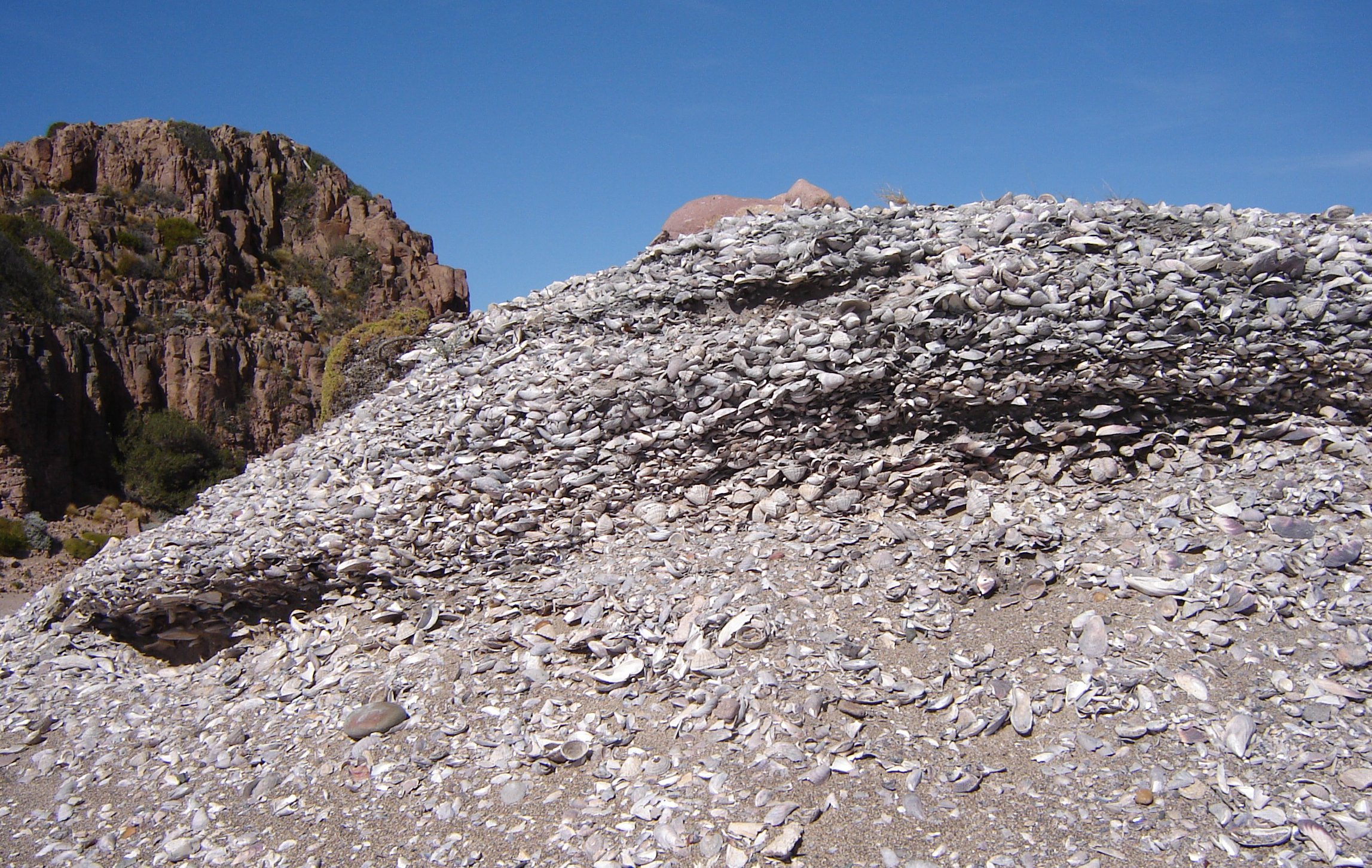
Midden
A midden (also kitchen midden or shell heap) is an old dump for domestic waste which may consist of animal bone, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and ecofacts associated with past human occupation. These features provide a useful resource for archaeologists who wish to study the diets and habits of past societies. Middens with damp, anaerobic conditions can even preserve organic remains in deposits as the debris of daily life are tossed on the pile. Each individual toss will contribute a different mix of materials depending upon the activity associated with that particular toss. During the course of deposition sedimentary material is deposited as well. Different mechanisms, from wind and water to animal digs, create a matrix which can also be analysed to provide seasonal and climatic information. In some middens individual dumps of material can be discerned and analysed. Shells A shell mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
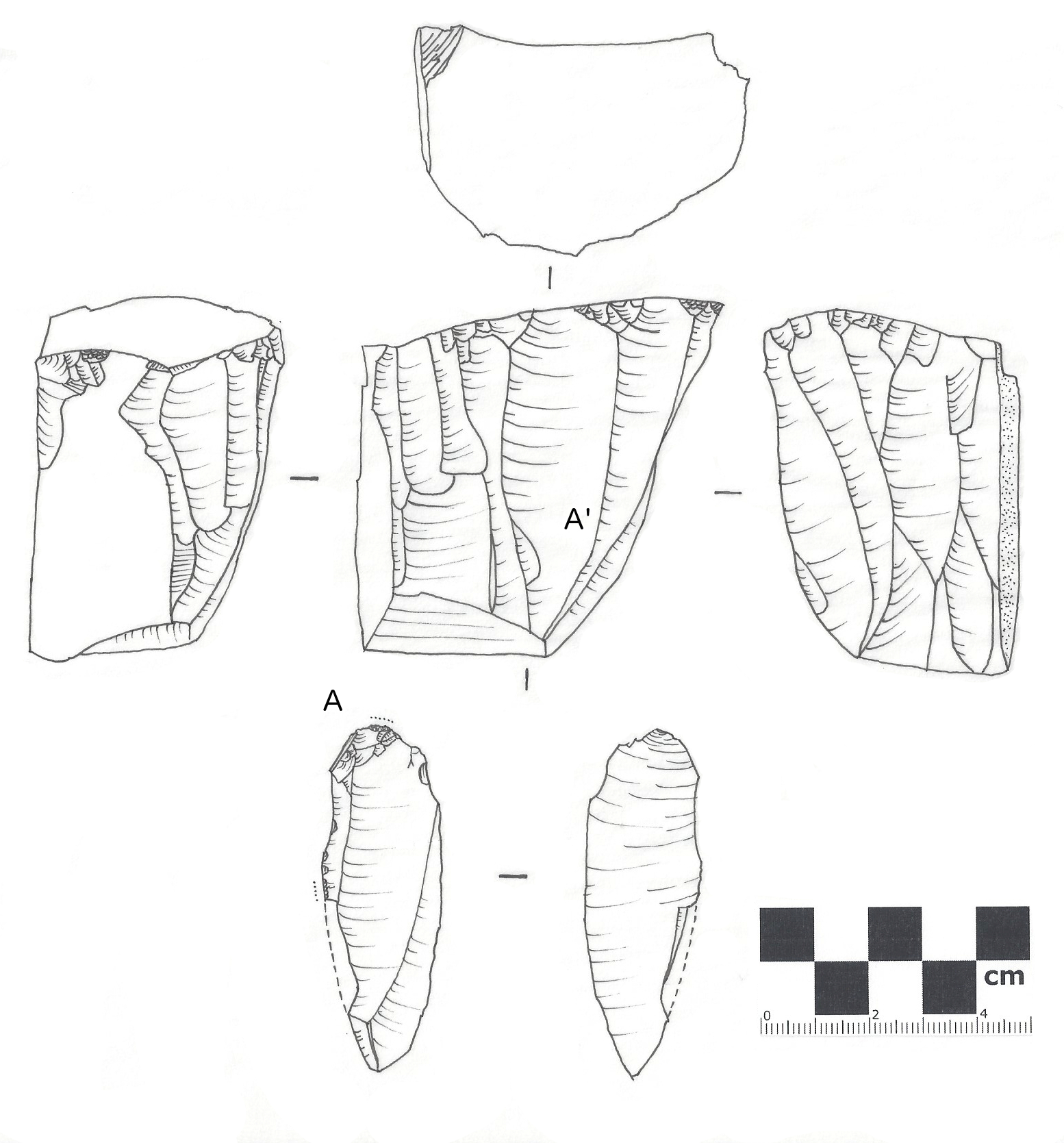
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90°) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)