|
Kummer's Congruences
In mathematics, Kummer's congruences are some congruences involving Bernoulli numbers, found by . used Kummer's congruences to define the p-adic zeta function. Statement The simplest form of Kummer's congruence states that : \frac\equiv \frac \pmod p \text h\equiv k \pmod where ''p'' is a prime, ''h'' and ''k'' are positive even integers not divisible by ''p''−1 and the numbers ''B''''h'' are Bernoulli numbers. More generally if ''h'' and ''k'' are positive even integers not divisible by ''p'' − 1, then : (1-p^)\frac\equiv (1-p^)\frac \pmod whenever : h\equiv k\pmod where φ(''p''''a''+1) is the Euler totient function In number theory, Euler's totient function counts the positive integers up to a given integer that are relatively prime to . It is written using the Greek letter phi as \varphi(n) or \phi(n), and may also be called Euler's phi function. In oth ..., evaluated at ''p''''a''+1 and ''a'' is a non negative integer. At ''a'' = 0, the expression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congruence Relation
In abstract algebra, a congruence relation (or simply congruence) is an equivalence relation on an algebraic structure (such as a group (mathematics), group, ring (mathematics), ring, or vector space) that is compatible with the structure in the sense that algebraic operations done with equivalent elements will yield equivalent elements. Every congruence relation has a corresponding Equivalence class, quotient structure, whose elements are the equivalence classes (or congruence classes) for the relation. Definition The definition of a congruence depends on the type of algebraic structure under consideration. Particular definitions of congruence can be made for group (mathematics), groups, ring (mathematics), rings, vector spaces, module (mathematics), modules, semigroups, lattice (order), lattices, and so forth. The common theme is that a congruence is an equivalence relation on an algebraic object that is compatible with the algebraic structure, in the sense that the operat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
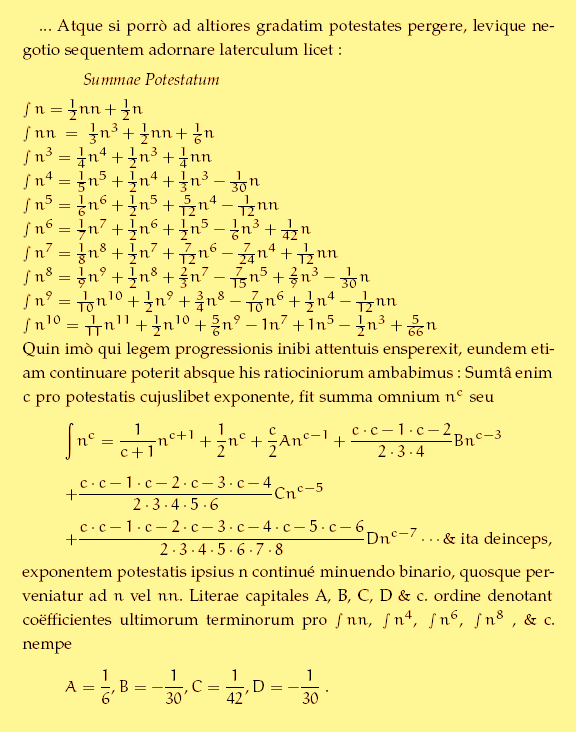
Bernoulli Numbers
In mathematics, the Bernoulli numbers are a sequence of rational numbers which occur frequently in analysis. The Bernoulli numbers appear in (and can be defined by) the Taylor series expansions of the tangent and hyperbolic tangent functions, in Faulhaber's formula for the sum of ''m''-th powers of the first ''n'' positive integers, in the Euler–Maclaurin formula, and in expressions for certain values of the Riemann zeta function. The values of the first 20 Bernoulli numbers are given in the adjacent table. Two conventions are used in the literature, denoted here by B^_n and B^_n; they differ only for , where B^_1=-1/2 and B^_1=+1/2. For every odd , . For every even , is negative if is divisible by 4 and positive otherwise. The Bernoulli numbers are special values of the Bernoulli polynomials B_n(x), with B^_n=B_n(0) and B^+_n=B_n(1). The Bernoulli numbers were discovered around the same time by the Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli, after whom they are named, and ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-adic Zeta Function
In mathematics, a ''p''-adic zeta function, or more generally a ''p''-adic ''L''-function, is a function analogous to the Riemann zeta function, or more general ''L''-functions, but whose domain and target are ''p-adic'' (where ''p'' is a prime number). For example, the domain could be the ''p''-adic integers Z''p'', a profinite ''p''-group, or a ''p''-adic family of Galois representations, and the image could be the ''p''-adic numbers Q''p'' or its algebraic closure. The source of a ''p''-adic ''L''-function tends to be one of two types. The first source—from which Tomio Kubota and Heinrich-Wolfgang Leopoldt gave the first construction of a ''p''-adic ''L''-function —is via the ''p''-adic interpolation of special values of ''L''-functions. For example, Kubota–Leopoldt used Kummer's congruences for Bernoulli numbers to construct a ''p''-adic ''L''-function, the ''p''-adic Riemann zeta function ζ''p''(''s''), whose values at negative odd integers are those of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernoulli Number
In mathematics, the Bernoulli numbers are a sequence of rational numbers which occur frequently in analysis. The Bernoulli numbers appear in (and can be defined by) the Taylor series expansions of the tangent and hyperbolic tangent functions, in Faulhaber's formula for the sum of ''m''-th powers of the first ''n'' positive integers, in the Euler–Maclaurin formula, and in expressions for certain values of the Riemann zeta function. The values of the first 20 Bernoulli numbers are given in the adjacent table. Two conventions are used in the literature, denoted here by B^_n and B^_n; they differ only for , where B^_1=-1/2 and B^_1=+1/2. For every odd , . For every even , is negative if is divisible by 4 and positive otherwise. The Bernoulli numbers are special values of the Bernoulli polynomials B_n(x), with B^_n=B_n(0) and B^+_n=B_n(1). The Bernoulli numbers were discovered around the same time by the Swiss mathematician Jacob Bernoulli, after whom they are named, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler Totient Function
In number theory, Euler's totient function counts the positive integers up to a given integer that are relatively prime to . It is written using the Greek letter phi as \varphi(n) or \phi(n), and may also be called Euler's phi function. In other words, it is the number of integers in the range for which the greatest common divisor is equal to 1. The integers of this form are sometimes referred to as totatives of . For example, the totatives of are the six numbers 1, 2, 4, 5, 7 and 8. They are all relatively prime to 9, but the other three numbers in this range, 3, 6, and 9 are not, since and . Therefore, . As another example, since for the only integer in the range from 1 to is 1 itself, and . Euler's totient function is a multiplicative function, meaning that if two numbers and are relatively prime, then . This function gives the order of the multiplicative group of integers modulo (the group of units of the ring \Z/n\Z). It is also used for defining the RS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Staudt–Clausen Theorem
In number theory, the von Staudt–Clausen theorem is a result determining the fractional part of Bernoulli numbers, found independently by and . Specifically, if is a positive integer and we add to the Bernoulli number for every prime such that divides , then we obtain an integer; that is, B_ + \sum_ \frac1p \in \Z . This fact immediately allows us to characterize the denominators of the non-zero Bernoulli numbers as the product of all primes such that divides ; consequently, the denominators are square-free and divisible by 6. These denominators are : 6, 30, 42, 30, 66, 2730, 6, 510, 798, 330, 138, 2730, 6, 870, 14322, 510, 6, 1919190, 6, 13530, ... . The sequence of integers B_ + \sum_ \frac1p is : 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, -6, 56, -528, 6193, -86579, 1425518, -27298230, ... . Proof A proof of the Von Staudt–Clausen theorem follows from an explicit formula for Bernoulli numbers which is: : B_=\sum_^\sum_^ and as a corollary: : B_=\sum_^(-1)^jS(2n,j) where are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer-Verlag
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graduate Texts In Mathematics
Graduate Texts in Mathematics (GTM) () is a series of graduate-level textbooks in mathematics published by Springer-Verlag. The books in this series, like the other Springer-Verlag mathematics series, are yellow books of a standard size (with variable numbers of pages). The GTM series is easily identified by a white band at the top of the book. The books in this series tend to be written at a more advanced level than the similar Undergraduate Texts in Mathematics series, although there is a fair amount of overlap between the two series in terms of material covered and difficulty level. List of books #''Introduction to Axiomatic Set Theory'', Gaisi Takeuti, Wilson M. Zaring (1982, 2nd ed., ) #''Measure and Category – A Survey of the Analogies between Topological and Measure Spaces'', John C. Oxtoby (1980, 2nd ed., ) #''Topological Vector Spaces'', H. H. Schaefer, M. P. Wolff (1999, 2nd ed., ) #''A Course in Homological Algebra'', Peter Hilton, Urs Stammbach (1997, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Für Die Reine Und Angewandte Mathematik
''Crelle's Journal'', or just ''Crelle'', is the common name for a mathematics journal, the ''Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik'' (in English: ''Journal for Pure and Applied Mathematics''). History The journal was founded by August Leopold Crelle (Berlin) in 1826 and edited by him until his death in 1855. It was one of the first major mathematical journals that was not a proceedings of an academy. It has published many notable papers, including works of Niels Henrik Abel, Georg Cantor, Gotthold Eisenstein, Carl Friedrich Gauss and Otto Hesse. It was edited by Carl Wilhelm Borchardt from 1856 to 1880, during which time it was known as ''Borchardt's Journal''. The current editor-in-chief is Daniel Huybrechts (Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn). Past editors * 1826–1856: August Leopold Crelle * 1856–1880: Carl Wilhelm Borchardt * 1881–1888: Leopold Kronecker, Karl Weierstrass Karl Theodor Wilhelm Weierstrass (; ; 31 October 1815 � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theorems In Number Theory
In mathematics and formal logic, a theorem is a statement that has been proven, or can be proven. The ''proof'' of a theorem is a logical argument that uses the inference rules of a deductive system to establish that the theorem is a logical consequence of the axioms and previously proved theorems. In mainstream mathematics, the axioms and the inference rules are commonly left implicit, and, in this case, they are almost always those of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory with the axiom of choice (ZFC), or of a less powerful theory, such as Peano arithmetic. Generally, an assertion that is explicitly called a theorem is a proved result that is not an immediate consequence of other known theorems. Moreover, many authors qualify as ''theorems'' only the most important results, and use the terms ''lemma'', ''proposition'' and ''corollary'' for less important theorems. In mathematical logic, the concepts of theorems and proofs have been formalized in order to allow mathematical reasoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |