|
Króka-Refs Saga
''Króka-Refs saga'' () or the ''Saga of Ref the Sly'' is one of the Icelanders' sagas. Written in the 14th century the saga relates the adventures of Ref Steinsson, whose unpromising origins lead him to greatness in both combat and subterfuge. History Although first recorded between 1350-1400 AD, the only completely preserved saga is dated to the second half of the fifteenth century.Clark, George. "Saga of Ref the Sly". Trans. of Islendinga sogur III, Reykjavik, 1987. Taking place between 950-1050 AD, the saga spans much of the Norse world, including Iceland, Greenland, Norway, and Denmark. The Christianization of Scandinavia occurs during the timeline of the saga, with the main character, Ref, converting as well. Synopsis The saga begins in Iceland with an old man named Stein, who has a wife named Thorgerd (''Þorgerðr''). They have a son named Ref who is known for being very lazy.Kellogg, Robert, and George Clark. "The Saga of Ref the Sly." The Sagas of Icelanders: A S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icelanders' Sagas
The sagas of Icelanders ( is, Íslendingasögur, ), also known as family sagas, are one genre of Icelandic sagas. They are prose narratives mostly based on historical events that mostly took place in Iceland in the ninth, tenth, and early eleventh centuries, during the so-called Saga Age. They were written in Old Icelandic, a western dialect of Old Norse. They are the best-known specimens of Icelandic literature. They are focused on history, especially genealogical and family history. They reflect the struggle and conflict that arose within the societies of the early generations of Icelandic settlers. The Icelandic sagas are valuable and unique historical sources about medieval Scandinavian societies and kingdoms, in particular in regards to pre-Christian religion and culture. Eventually many of these Icelandic sagas were recorded, mostly in the 13th and 14th centuries. The 'authors', or rather recorders of these sagas are largely unknown. One saga, ''Egil's Saga'', is belie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization Of Scandinavia
The Christianization of Scandinavia, as well as other Nordic countries and the Baltic countries, took place between the 8th and the 12th centuries. The realms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden established their own Archdioceses, responsible directly to the Pope, in 1104, 1154 and 1164, respectively. The conversion to Christianity of the Scandinavian people required more time, since it took additional efforts to establish a network of churches. The earliest signs of Christianization were in the 830s with Ansgar's construction of churches in Birka and Hedeby in the 830s. The conversion of Scandinavian kings occurred over the period 960–1020. Subsequently, Scandinavian kings sought to establish churches, dioceses and Christian kingship, as well as destroy pagan temples. Denmark was the first Scandinavian country to Christianize, as Harald Bluetooth declared this around AD 975, and raised the larger of the two Jelling Stones. According to historian Anders Winroth, Christianity was not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
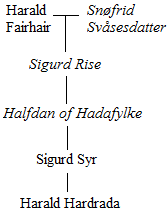
Harald Hardrada
Harald Sigurdsson (; – 25 September 1066), also known as Harald III of Norway and given the epithet ''Hardrada'' (; modern no, Hardråde, roughly translated as "stern counsel" or "hard ruler") in the sagas, was King of Norway from 1046 to 1066. Additionally, he unsuccessfully claimed both the Danish throne until 1064 and the English throne in 1066. Before becoming king, Harald had spent around fifteen years in exile as a mercenary and military commander in Kievan Rus' and as a chief of the Varangian Guard in the Byzantine Empire. In his chronicle, Adam of Bremen called him the "Thunderbolt of the North". When he was fifteen years old, in 1030, Harald fought in the Battle of Stiklestad together with his half-brother Olaf Haraldsson (later Saint Olaf). Olaf sought to reclaim the Norwegian throne, which he had lost to the Danish king Cnut the Great two years prior. In the battle, Olaf and Harald were defeated by forces loyal to Cnut, and Harald was forced into exile to Kievan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweyn II Of Denmark
Sweyn Estridsson Ulfsson ( on, Sveinn Ástríðarson, da, Svend Estridsen; – 28 April 1076) was King of Denmark (being Sweyn II) from 1047 until his death in 1076. He was the son of Ulf Thorgilsson and Estrid Svendsdatter, and the grandson of Sweyn Forkbeard through his mother's line. He was married three times, and fathered 20 children or more out of wedlock, including the five future kings Harald Hen, Canute the Saint, Oluf Hunger, Eric Evergood, and Niels. He was courageous in battle, but did not have much success as a military commander. His skeleton reveals that he was a tall, powerfully built man who walked with a limp. Biography Accession to the throne Sweyn was born in England, Bricka, Carl Frederik, ''Dansk Biografisk Lexikon'', vol. XVII vend Tveskjæg – Tøxen 1903pp.3–5 as the son of Ulf Thorgilsson and Estrid Svendsdatter, the latter of whom was the daughter of King Sweyn I Forkbeard and sister of Kings Harald II and Canute the Great. Sweyn grew up a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norns
The Norns ( non, norn , plural: ) are deities in Norse mythology responsible for shaping the course of human destinies.'' Nordisk familjebok'' (1907) In the ''Völuspá'', the three primary Norns Urðr (Wyrd), Verðandi, and Skuld draw water from their sacred well to nourish the tree at the center of the cosmos and prevent it from rot.The article Nornor' in '' Nordisk familjebok'' (1913). These three Norns are described as powerful maiden giantesses ( Jotuns) whose arrival from Jötunheimr ended the golden age of the gods. The Norns are also described as maidens of Mögþrasir in the ''Vafþrúðnismál''. Beside the three Norns tending Yggdrasill, pre-Christian Scandinavians attested to Norns who visit a newborn child in order to determine the person's future. These Norns could be malevolent or benevolent: the former causing tragic events in the world while the latter were kind and protective. Etymology The origin of the name ''norn'' is uncertain; it may derive from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
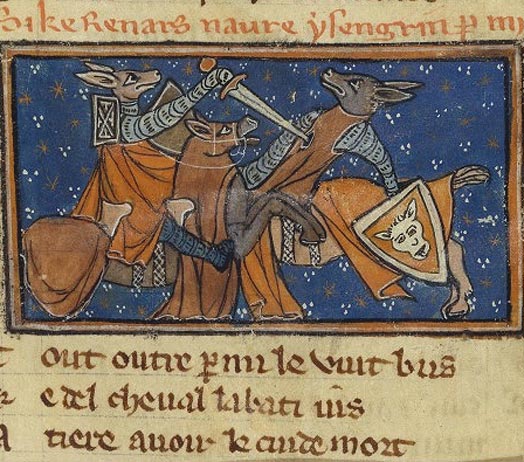
Reynard
Reynard the Fox is a literary cycle of medieval allegorical Dutch, English, French and German fables. The first extant versions of the cycle date from the second half of the 12th century. The genre was popular throughout the Late Middle Ages, as well as in chapbook form throughout the Early Modern period. The stories are largely concerned with the main character Reynard, an anthropomorphic red fox, trickster figure. His adventures usually involve his deceiving other anthropomorphic animals for his own advantage or trying to avoid their retaliatory efforts. His main enemy and victim across the cycle is his uncle, the wolf, Isengrim (or Ysengrim). While the character of Reynard appears in later works, the core stories were written during the Middle Ages by multiple authors and are often seen as parodies of medieval literature such as courtly love stories and chansons de geste, as well as a satire of political and religious institutions.Bianciotto, G. (2005). Introduction. In ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Ships
Viking ships were marine vessels of unique structure, used in Scandinavia from the Viking Age throughout the Middle Ages. The boat-types were quite varied, depending on what the ship was intended for, but they were generally characterized as being slender and flexible boats, with symmetrical ends with true keel. They were Clinker (boat building), clinker built, which is the overlapping of planks riveted together. Some might have had a dragon's head or other circular object protruding from the bow and stern for design, although this is only inferred from historical sources. Viking ships were used both for military purposes and for long-distance trade, exploration and colonization. In the literature, Viking ships are usually seen divided into two broad categories: merchant ships and warships, the latter resembling narrow "war canoes" with less load capacity, but higher speed. However, these categories are overlapping; some transport ships would also form part of war fleets. As a ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
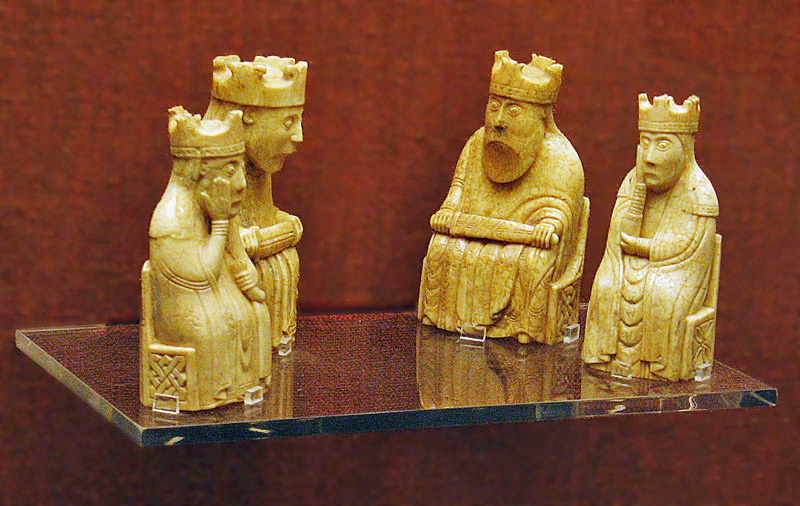
Lewis Chessmen
The Lewis chessmen ( no, Lewisbrikkene; gd, Fir-Tàilisg; sco, Lewis chesmen) or Uig chessmen, named after the island or the bay where they were found, are a group of distinctive 12th-century chess pieces, along with other game pieces, most of which are carved from walrus ivory. Discovered in 1831 on Lewis in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland, they may constitute some of the few complete, surviving medieval chess sets, although it is not clear if a set as originally made can be assembled from the pieces. When found, the hoard contained 93 artifacts: 78 chess pieces, 14 tablemen and one belt buckle. Today, 82 pieces are owned and usually exhibited by the British Museum in London, and the remaining 11 are at the National Museum of Scotland in Edinburgh. Additionally, a newly identified piece, a "warder", the equivalent of a castle or rook, was sold for £735,000 in July 2019. Four other major pieces, and many pawns, remain missing from the chess sets. Origin Most accounts ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagas Of Icelanders
The sagas of Icelanders ( is, Íslendingasögur, ), also known as family sagas, are one genre of Icelandic sagas. They are prose narratives mostly based on historical events that mostly took place in Iceland in the ninth, tenth, and early eleventh centuries, during the so-called Saga Age. They were written in Old Icelandic, a western dialect of Old Norse. They are the best-known specimens of Icelandic literature. They are focused on history, especially genealogical and family history. They reflect the struggle and conflict that arose within the societies of the early generations of Icelandic settlers. The Icelandic sagas are valuable and unique historical sources about medieval Scandinavian societies and kingdoms, in particular in regards to pre-Christian religion and culture. Eventually many of these Icelandic sagas were recorded, mostly in the 13th and 14th centuries. The 'authors', or rather recorders of these sagas are largely unknown. One saga, ''Egil's Saga'', is beli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |