|
Kramerspitz
Kramerspitz (or The Kramer) is a mountain overlooking the Garmisch side of Garmisch-Partenkirchen in Bavaria, Germany. It forms the most visible western boundary of the Loisach River Valley. It stands across the valley from the Wank Wank may refer to: * WANK (computer worm), a computer worm that attacked DEC VAX/VMS systems through DECnet in 1989 * WXTY, a radio station (99.9 FM) licensed to serve Lafayette, Florida, United States, which held the call sign WANK from 2010 to 2 ... to the east on the Partenkirchen side. Normal climbing route Kramerspitz can be climbed directly from Garmisch-Partenkirchen in 4 hours, but a round trip will take closer to eight. The access is from the east side. At the altitude of 1028 m, you will pass St. Martin hut, and from there just continue through the woods generally in the west direction. You do not need any special equipment, any hiking shoes or boots will be good enough. External links Kramerspitzin Mountains for Everybody. Mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammergau Alps
The Ammergau Alps (german: Ammergauer Alpen or ''Ammergebirge'') are a mountain range in the Northern Limestone Alps in the states of Bavaria (Germany) and Tyrol (Austria). They cover an area of about 30 x 30 km and begin at the outer edge of the Alps. The highest summit is the Daniel which has a height of . Geography and tourist infrastructure The Ammergau Alps are a cross-border range shared between the German Free State of Bavaria (ca. 3/4 of the area) and the Austrian state of Tyrol. The towns of Füssen, Oberammergau, Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Ehrwald and Reutte lie around the perimeter of the mountains. The Ammergau Alps are an ideal region for the average walker thanks to the comparatively low height of their summits and their location on the northern edge of the Alps with its proximity to the population centres of south Germany. Most of the summits are accessible within a day's round trip from bases in the valleys. As a result, there is only a small number of Alpine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total land area of Germany. With over 13 million inhabitants, it is second in population only to North Rhine-Westphalia, but due to its large size its population density is below the German average. Bavaria's main cities are Munich (its capital and largest city and also the third largest city in Germany), Nuremberg, and Augsburg. The history of Bavaria includes its earliest settlement by Iron Age Celtic tribes, followed by the conquests of the Roman Empire in the 1st century BC, when the territory was incorporated into the provinces of Raetia and Noricum. It became the Duchy of Bavaria (a stem duchy) in the 6th century AD following the collapse of the Western Roman Empire. It was later incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire, became an ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic and North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before AD 100. In 962, the Kingdom of Germany formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garmisch-Partenkirchen
Garmisch-Partenkirchen (; Bavarian: ''Garmasch-Partakurch''), nicknamed Ga-Pa, is an Alpine ski town in Bavaria, southern Germany. It is the seat of government of the district of Garmisch-Partenkirchen (abbreviated ''GAP''), in the Oberbayern region, which borders Austria. Nearby is Germany's highest mountain, Zugspitze, at above sea level. The town is known as the site of the 1936 Winter Olympic Games, the first to include alpine skiing, and hosts a variety of winter sports competitions. History Garmisch (in the west) and Partenkirchen (in the east) were separate towns for many centuries, and still maintain quite separate identities. Partenkirchen originated as the Roman town of ''Partanum'' on the trade route from Venice to Augsburg and is first mentioned in the year A.D. 15. Its main street, Ludwigsstrasse, follows the original Roman road. Garmisch was first mentioned some 800 years later as ''Germaneskau'' ("German District"), suggesting that at some po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loisach
The Loisach is a river that flows through Tyrol, Austria and Bavaria, Germany. Its name might be Celtic in origin, from Proto-Celtic ''*lawo'' and ''*iskā'', both of which mean "water". The Loisach goes through the great swamp . The Loisach is a left tributary to the Isar. The source of the Loisach is near Ehrwald in Austria. The Loisach flows past Garmisch-Partenkirchen and into the Kochelsee. At the Kochelsee the water that was diverted from the upper river Isar for the Walchensee Hydroelectric Power Station joins the Loisach. The Loisach then flows out of Kochelsee and joins the Isar at Wolfratshausen. A canal joins the Isar and the Loisach returning the water diverted for power generation to the Isar before Wolfratshausen to reduce the risk of flooding in the town. The most important tributaries of the Loisach entering from the right-hand side are the Hammersbach, the Partnach near Garmisch-Partenkirchen, the streams Kuhflucht near Farchant, Röhrlbach and Lauterbach near O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
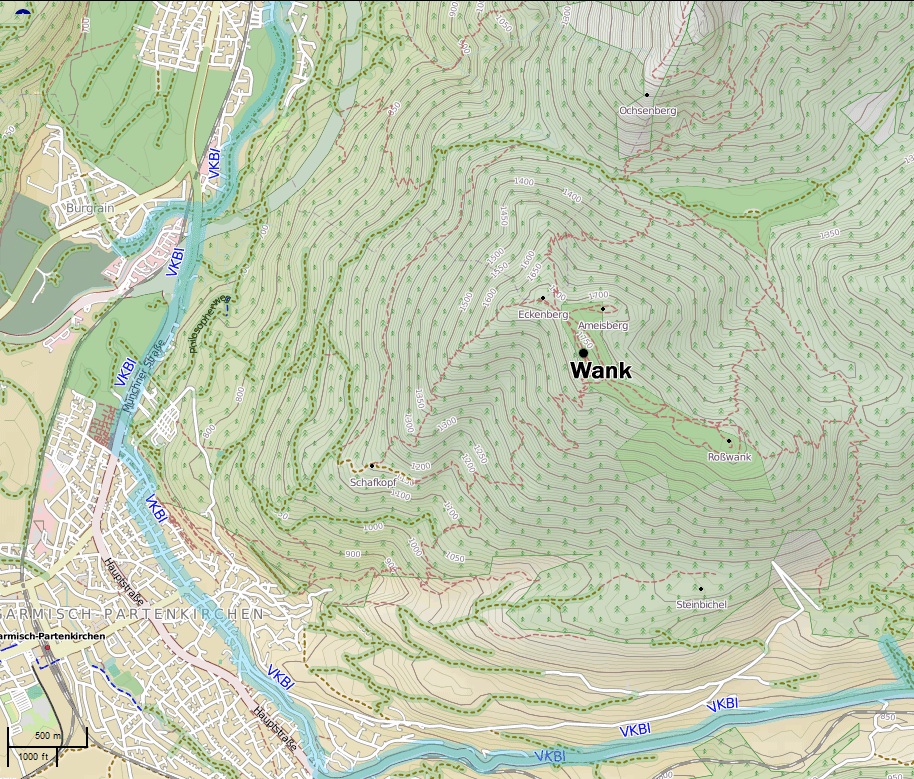
Wank (mountain)
The Wank () is a mountain in southern Germany, situated in the Loisach valley close to the Austrian border in the southwestern Ester Mountains range near Garmisch-Partenkirchen. It rises from about above mean sea level up to at the summit.Rennenberg, H.; Polle, A.; Reuther, M.: "Role of Ozone in Forest Decline on Wank Mountain (Alps)", in Sandermann, H.; Wellburn, A.; Heath, Robert L.: ''Forest decline and ozone: a comparison of controlled chamber and field experiments'', pp. 136-7. Springer, 1997. The mountain is crowned by a grassy summit which has views over Garmisch-Partenkirchen and the surrounding region. The summit can be reached via the eponymous Wankbahn, a cable car system that runs during the summer months, or by a network of footpaths that criss-cross the area. A mountain hut on the summit, the Wank-Haus, provides food and accommodation, and a nearby scientific observatory plays a role in monitoring atmospheric and climatic conditions. The Wank is a destination for hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Bavaria
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |