|
Kosmos 167
Kosmos 167 (russian: Космос 167 meaning ''Cosmos 167''), or 4V-1 No.311, was a 1967 Soviet Union, Soviet spacecraft intended to explore Venus. A spacecraft launched as part of the Venera, Venera programme, Kosmos 167 was intended to land on Venus but never departed low Earth orbit due to a launch failure. Beginning in 1962, the name Kosmos (satellite), Kosmos was given to Soviet spacecraft which remained in Earth orbit, regardless of whether that was their intended final destination. The designation of this mission as an intended planetary probe is based on evidence from Soviet and non-Soviet sources and historical documents. Typically, Soviet planetary missions were initially put into an Earth parking orbit as a launch platform with a rocket engine and attached probe. The probes were then launched toward their targets with an engine burn with a duration of roughly 4 minutes. If the engine misfired or the burn was not completed, the probes would be left in Earth orbit and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never far from the Sun, either as morning star or evening star. Aside from the Sun and Moon, Venus is the brightest natural object in Earth's sky, capable of casting visible shadows on Earth at dark conditions and being visible to the naked eye in broad daylight. Venus is the second largest terrestrial object of the Solar System. It has a surface gravity slightly lower than on Earth and has a very weak induced magnetosphere. The atmosphere of Venus, mainly consists of carbon dioxide, and is the densest and hottest of the four terrestrial planets at the surface. With an atmospheric pressure at the planet's surface of about 92 times the sea level pressure of Earth and a mean temperature of , the carbon dioxide gas at Venus's surface is in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos (satellite)
Kosmos (russian: Ко́смос, , meaning " (outer) space" or " Kosmos") is a designation given to many satellites operated by the Soviet Union and subsequently Russia. Kosmos 1, the first spacecraft to be given a Kosmos designation, was launched on 16 March 1962. History The first Soviet satellites orbiting Earth were named Sputnik, Polyot (starting in 1963), Elektron (in 1964), Proton (in 1965), and Molniya (in 1965), but most have been called Kosmos since Kosmos 1 on 16 March 1962. The program has included uncrewed tests of crewed spacecraft and satellites for scientific research and military purposes. , 2548 Kosmos satellites have been launched. The spacecraft do not form a single programme, but instead consist of almost all Soviet and Russian military satellites, as well as a number of scientific satellites, and spacecraft which failed during or immediately after launch, but still reached orbit. Most Soviet and subsequently Russian military satellites were given Kosm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Which Reentered In 1967
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spacecraft Launched In 1967
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including communications, Earth observation, meteorology, navigation, space colonization, planetary exploration, and transportation of humans and cargo. All spacecraft except single-stage-to-orbit vehicles cannot get into space on their own, and require a launch vehicle (carrier rocket). On a sub-orbital spaceflight, a space vehicle enters space and then returns to the surface without having gained sufficient energy or velocity to make a full Earth orbit. For orbital spaceflights, spacecraft enter closed orbits around the Earth or around other celestial bodies. Spacecraft used for human spaceflight carry people on board as crew or passengers from start or on orbit (space stations) only, whereas those used for robotic space missions operate either autonomously or telerobotically. Robotic spacecraft used to support scientific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Missions To Venus ...
There have been 46 (including gravity-assist flybys) space missions to the planet Venus. Missions to Venus constitute part of the exploration of Venus. List As of 2020, the Soviet Union, United States, European Space Agency and Japan have conducted missions to Venus. ;Mission Type Legend: Future missions Under development Venus Missions by Organization/Company Proposed missions References External links * {{Venus Venus * Venus Missions to Venus There have been 46 (including gravity-assist flybys) space missions to the planet Venus. Missions to Venus constitute part of the exploration of Venus. List As of 2020, the Soviet Union, United States, European Space Agency and Japan have c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars. For celestial objects in general, the sidereal period ( sidereal year) is referred to by the orbital period, determined by a 360° revolution of one body around its primary, e.g. Earth around the Sun, relative to the fixed stars projected in the sky. Orbital periods can be defined in several ways. The tropical period is more particularly about the position of the parent star. It is the basis for the solar year, and respectively the calendar year. The synodic period incorporates not only the orbital relation to the parent star, but also to other celestial objects, making it not a mere different approach to the orbit of an object around its parent, but a period of orbital relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly overhead (no more than about 23° from the zenith) every day, year-round. Consequently, the equator has a rather stable daytime temperature throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apsis
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion. General description There are two apsides in any elliptic orbit. The name for each apsis is created from the prefixes ''ap-'', ''apo-'' (), or ''peri-'' (), each referring to the farthest and closest point to the primary body the affixing necessary suffix that describes the primary body in the orbit. In this case, the suffix for Earth is ''-gee'', so the apsides' names are ''apogee'' and ''perigee''. For the Sun, its suffix is ''-helion'', so the names are ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion''. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic orbits are ellipses. The barycenter of the two bodies may lie well within the bigger body—e.g., the Earth–Moon barycenter is about 75% of the way from Earth's center to its surface. If, compared to the larger mass, the smaller mass is negligible (e.g., f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baikonur Cosmodrome Site 1
Gagarin's Start (russian: Гагаринский старт, ''Gagarinskiy start''), also known as Baikonur Site 1 or Site 1/5 is a launch site at Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan that was used for the Soviet space program and is now managed by Roscosmos. Overview The launchpad for the world's first human spaceflight made by Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1 in 1961, the site was referred to as Site No.1 (, ''Ploshchadka No. 1'') as the first one of its kind. It is also sometimes referred to as NIIP-5 LC1, Baikonur LC1, LC-1/5, LC-1 or GIK-5 LC1. On 17 March 1954, the Council of Ministers ordered several ministries to select a site for a proving ground to test the R-7 rocket by 1 January 1955. A special reconnaissance commission considered several possible geographic regions and selected Tyuratam in the Kazakh SSR. This selection was approved on 12 February 1955 by the Council of Ministers, with a completion of construction targeted for 1958. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
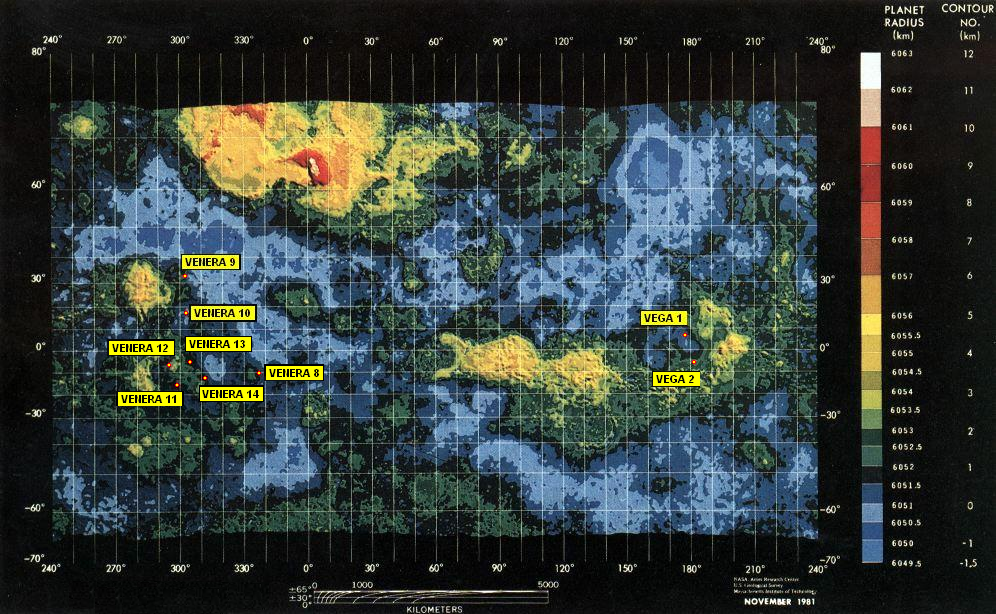
Venera
The Venera (, , which means "Venus" in Russian) program was the name given to a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Ten probes successfully landed on the surface of the planet, including the two Vega program and Venera-Halley probes, while thirteen probes successfully entered the Venusian atmosphere. Due to the extreme surface conditions on Venus, the probes could only survive for a short period on the surface, with times ranging from 23 minutes to two hours. The ''Venera'' program established a number of precedents in space exploration, among them being the first human-made devices to enter the atmosphere of another planet (Venera 3 on 1 March 1966), the first to make a soft landing on another planet (Venera 7 on 15 December 1970), the first to return images from another planet's surface (Venera 9 on 8 June 1975), the first to record sounds on another planet (Venera 13 on 30 October 1981) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)