|
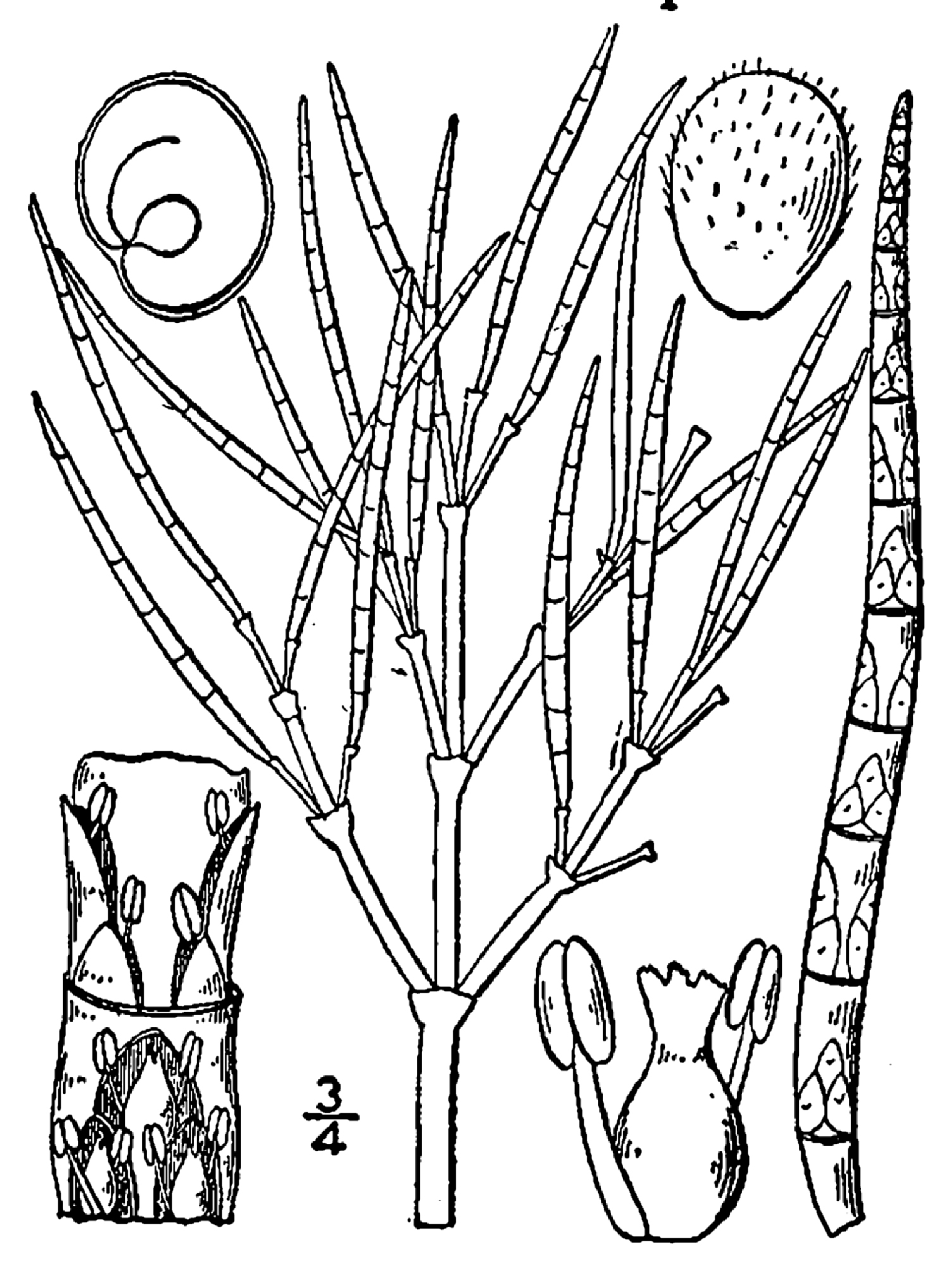
Korthalsella Salicornioides
''Korthalsella salicornioides'' or dwarf mistletoe is an endemic parasitic plant in New Zealand. Description ''Korthalsella salicornicoides'' is named after the succulent coastal plant '' Salicornia'', because it has succulent stems. These appear as a dense mass of small fleshy leafless twigs, up to 10 cm long, usually growing on the host plants manuka ('' Leptospermum scoparium'') and kanuka ('' Kunzea ericoides''). It is reddish-yellow to green with tiny flowers and small yellow fruits from October to May. It is similar to the other two species of New Zealand leafless mistletoe in the genus '' Korthalsella'', but has denser stems arising at a narrower angle. Conservation This species is scattered across forests and scrublands in New Zealand, only abundant in small local patches. In some areas it is threatened by felling of ''Leptospermum'' and '' Kunzea'' for firewood, farming, or exotic forestry. It is classed as At Risk: Naturally Uncommon by the Department of Conserv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
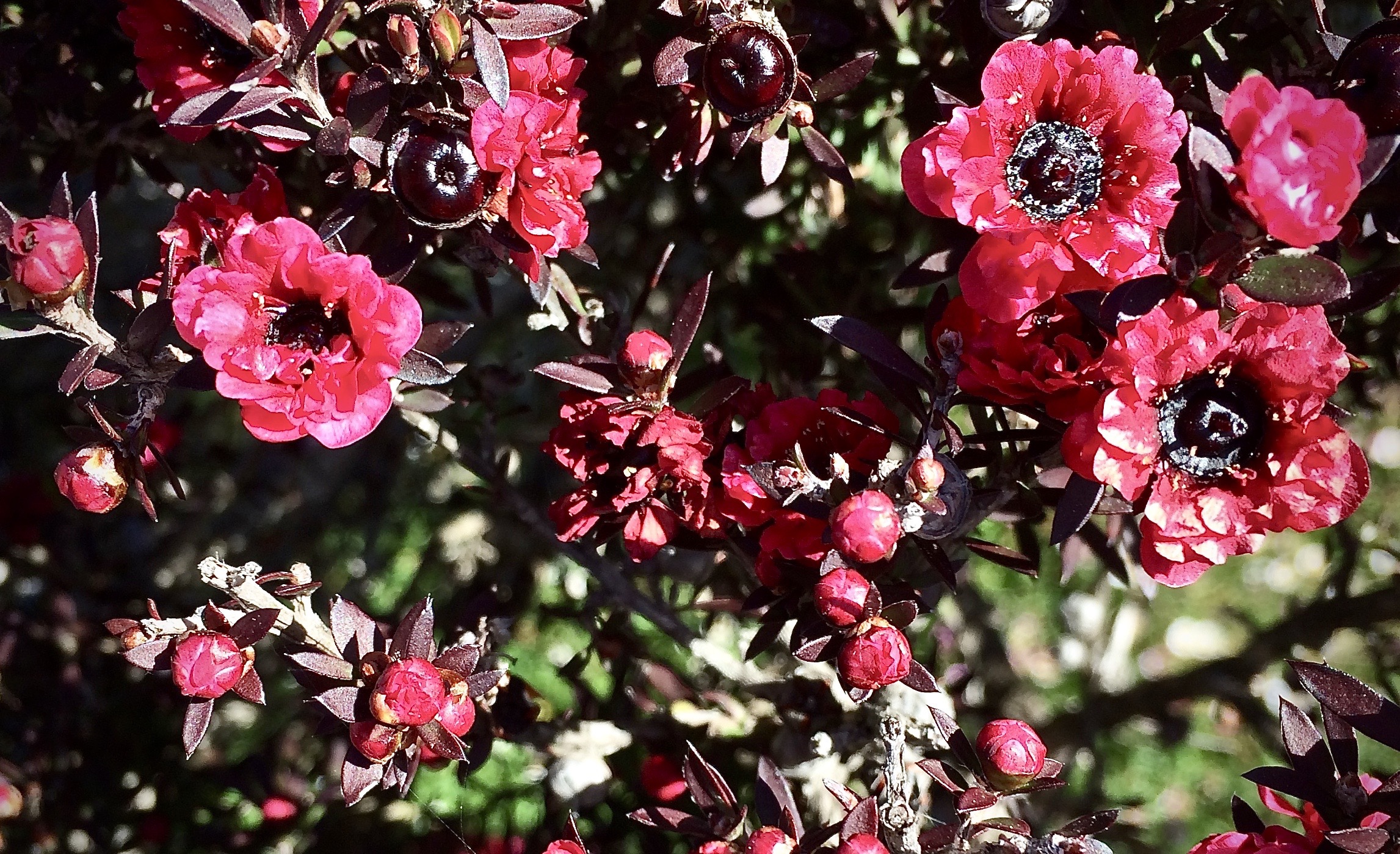
Leptospermum Scoparium
''Leptospermum scoparium'', commonly called mānuka, () mānuka myrtle, New Zealand teatree, broom tea-tree, or just tea tree, is a species of flowering plant in the myrtle family Myrtaceae, native to New Zealand (including the Chatham Islands) and south-east Australia. Its nectar produces Mānuka honey. Description Mānuka is a prolific shrub-type tree and is often one of the first species to regenerate on cleared land. It is typically a shrub growing to tall, but can grow into a moderately sized tree, up to or so in height. It is evergreen, with dense branching and small leaves long and broad, with a short spine tip. The flowers are white, occasionally pink, – rarely up to – in diameter, with five petals. The wood is tough and hard. Mānuka is often confused with the related species kānuka (''Kunzea ericoides'') – the easiest way to tell the difference between the two species in the field is to feel their foliage – mānuka leaves are prickly, while kānuka lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mistletoe
Mistletoe is the common name for obligate hemiparasitic plants in the order Santalales. They are attached to their host tree or shrub by a structure called the haustorium, through which they extract water and nutrients from the host plant. The name mistletoe originally referred to the species ''Viscum album'' (European mistletoe, of the family Santalaceae in the order Santalales); it is the only species native to the British Isles and much of Europe. A related species with red rather than white fruits, ''Viscum cruciatum'', occurs in Southwest Spain and Southern Portugal, as well as in Morocco in North Africa and in southern Africa. The genus ''Viscum'' is not native to North America, but ''Viscum album'' was introduced to Northern California in 1900. The eastern mistletoe native to North America, ''Phoradendron leucarpum'', belongs to a distinct genus of the family Santalaceae. European mistletoe has smooth-edged, oval, evergreen leaves borne in pairs along the woody st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic (ecology)
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as Armillaria mellea, honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the Orobanchaceae, broomrapes. There are six major parasitic Behavioral ecology#Evolutionarily stable strategy, strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), wikt:trophic, trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), Disease vector, vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropreda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicornia
''Salicornia'' is a genus of succulent, halophytic (salt tolerant) flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae that grow in salt marshes, on beaches, and among mangroves. ''Salicornia'' species are native to North America, Europe, Central Asia, and southern Africa. Common names for the genus include glasswort, pickleweed, picklegrass, and marsh samphire; these common names are also used for some species not in ''Salicornia''. To French speakers in Atlantic Canada, they are known colloquially as ''titines de souris'' ('mouse tits'). The main European species is often eaten, called marsh samphire in Britain, and the main North American species is occasionally sold in grocery stores or appears on restaurant menus as sea beans, samphire greens or sea asparagus. Description The ''Salicornia'' species are small annual herbs. They grow prostrate to erect, their simple or branched stems are succulent, hairless, and appear to be jointed. The opposite leaves are strongly reduced to sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunzea Ericoides
''Kunzea ericoides'', commonly known as kānuka, kanuka, white tea-tree or burgan, is a tree or shrub in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to New Zealand. It has white or pink flowers similar to those of ''Leptospermum'' and from its first formal description in 1832 until 1983 was known as ''Leptospermum ericoides''. The flowers have five petals and up to 25 stamens which are mostly longer than the petals. Description ''Kunzea ericoides'' is a spreading shrub or tree, sometimes growing to a height of with bark which peels in long strips and young branches which tend to droop. The leaves are variable in shape from linear to narrow elliptic or lance-shaped, long and wide with a petiole up to long. The flowers are white or pale pink, crowded on side branches or in the axils of upper leaves. The floral cup is covered with soft, downy hairs and is on a pedicel long. There are five triangular sepals about long and five petals about long. There are up to 25 stamens w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korthalsella
''Korthalsella'' (korthal mistletoe) is a genus of flowering plants in the sandalwood family, Santalaceae (sometimes/formerly considered to be in Viscaceae). It contains about 25 species distributed in Asia, Africa, Australia, New Zealand, and some Pacific Islands. Selected species *''Korthalsella arthroclada'' Cranfield (Australia) *''Korthalsella breviarticulata'' (Tiegh.) Danser (Australia) *''Korthalsella complanata'' (v. Tiegh.) Engl. - ''Kaumahana'' (Hawaii) *''Korthalsella cylindrica'' (v. Tiegh.) Engl. - Hawaii korthal mistletoe (Hawaii) *'' Korthalsella degeneri'' Danser - Degener's korthal mistletoe (Island of Oahu in Hawaii) *''Korthalsella disticha'' (Endl.) Engl. (Australia) *''Korthalsella emersa'' Barlow (Australia) *''Korthalsella grayi'' Barlow (Australia) *''Korthalsella japonica'' (Thunb.) Engl. (Australia) *''Korthalsella latissima'' (v. Tiegh.) Danser - Kauai korthal mistletoe (Hawaii) *''Korthalsella leucothrix'' Barlow (Australia) *''Korthalsella papuana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Department Of Conservation (New Zealand)
The Department of Conservation (DOC; Māori: ''Te Papa Atawhai'') is the public service department of New Zealand charged with the conservation of New Zealand's natural and historical heritage. An advisory body, the New Zealand Conservation Authority (NZCA) is provided to advise DOC and its ministers. In addition there are 15 conservation boards for different areas around the country that provide for interaction between DOC and the public. Function Overview The department was formed on 1 April 1987, as one of several reforms of the public service, when the ''Conservation Act 1987'' was passed to integrate some functions of the Department of Lands and Survey, the Forest Service and the Wildlife Service. This act also set out the majority of the department's responsibilities and roles. As a consequence of Conservation Act all Crown land in New Zealand designated for conservation and protection became managed by the Department of Conservation. This is about 30% of New Z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santalaceae
The Santalaceae, sandalwoods, are a widely distributed family of flowering plants (including small trees, shrubs, perennial herbs, and epiphytic climbersHewson & George t al.br>''Santalaceae'' taxonomy, 1984, pp. 191-194.) which, like other members of Santalales, are partially parasitic on other plants. Its flowers are bisexual or, by abortion ("flower drop"), unisexual.Pilger, R''Santalaceae''(with 17 figures). R. Br. Prodr. Fl. Nov. Holl. (1810) 350, pp. 1-45. Modern treatments of the Santalaceae include the family Viscaceae (mistletoes), previously considered distinct. The APG II system of 2003 recognises the family and assigns it to the order Santalales in the clade core eudicots. However, the circumscription by APG is much wider than accepted by previous classifications, including the plants earlier treated in families Eremolepidaceae and Viscaceae. It includes about 1,000 species in 43 genera. Many have reported traditional and cultural uses, including as medicine. Genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)