|
Kornblum–DeLaMare Rearrangement
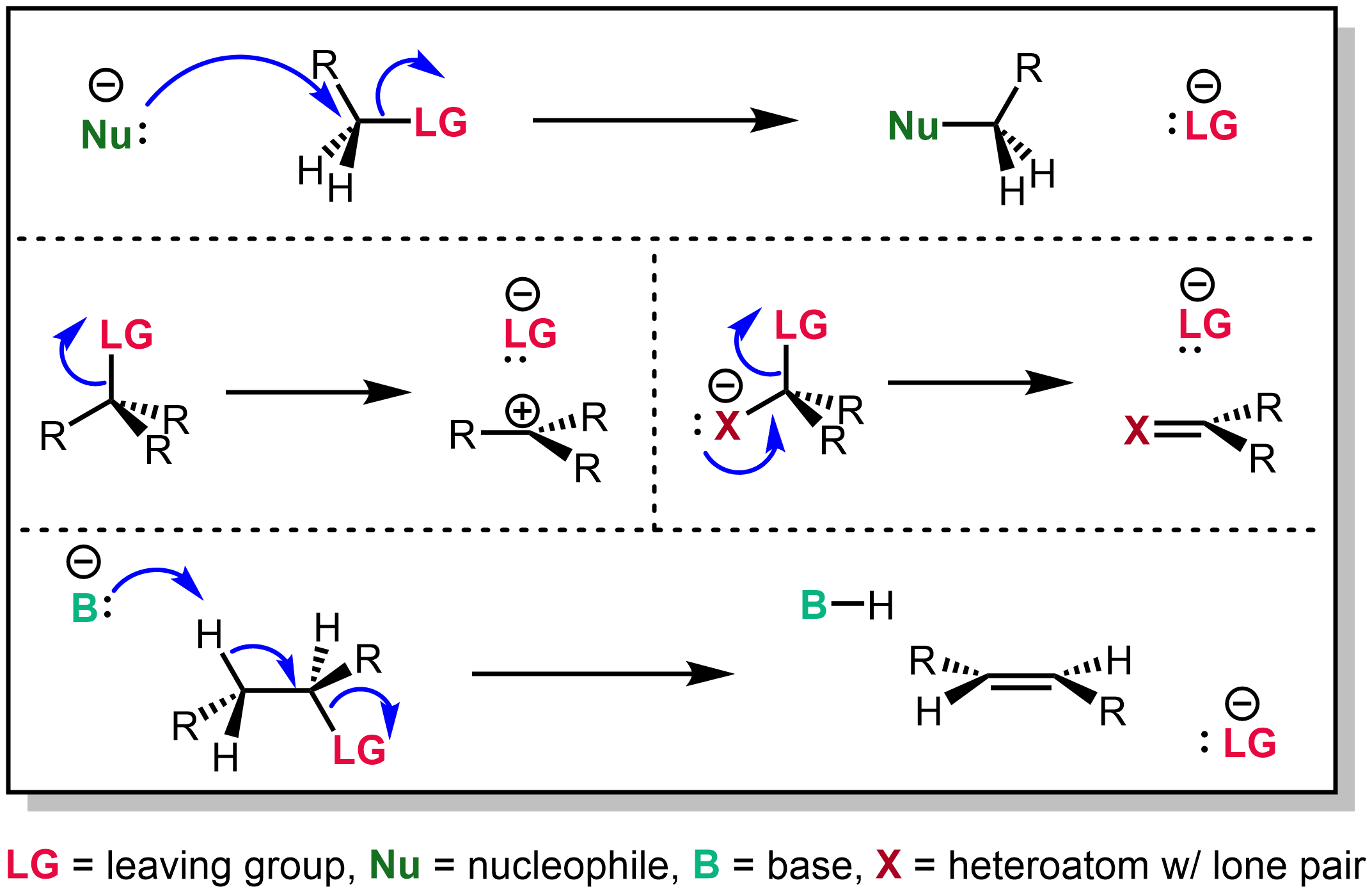
The Kornblum–DeLaMare rearrangement is a rearrangement reaction in organic chemistry in which a primary or secondary organic peroxide is converted to the corresponding ketone and alcohol under acid or base catalysis. The reaction is relevant as a tool in organic synthesis and is a key step in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins. : The base can be a hydroxide such as potassium hydroxide or an amine such as triethylamine. Reaction mechanism In the reaction mechanism for this organic reaction the base abstracts the acidic α-proton of the peroxide 1 to form the carbanion 4 as a reactive intermediate which rearranges to the ketone 2 with expulsion of the hydroxyl anion 3'. This intermediate gains a proton forming the alcohol 3. : Deprotonation and rearrangement can also be a concerted reaction without formation of 4. An alternative reaction mechanism involving direct nucleophilic displacement on the peroxide link of the amine followed by an elimination reaction is consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rearrangement Reaction
In organic chemistry, a rearrangement reaction is a broad class of organic reactions where the carbon skeleton of a molecule is rearranged to give a structural isomer of the original molecule. Often a substituent moves from one atom to another atom in the same molecule, hence these reactions are usually intramolecular. In the example below, the substituent R moves from carbon atom 1 to carbon atom 2: :\underset\ce\ce\underset\ce\ce Intermolecular rearrangements also take place. A rearrangement is not well represented by simple and discrete electron transfers (represented by curved arrows in organic chemistry texts). The actual mechanism of alkyl groups moving, as in Wagner-Meerwein rearrangement, probably involves transfer of the moving alkyl group fluidly along a bond, not ionic bond-breaking and forming. In pericyclic reactions, explanation by orbital interactions give a better picture than simple discrete electron transfers. It is, nevertheless, possible to draw the curv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deprotonation
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.edu/hjakubowski/classes/ch331/protstructure/PS_2A3_AA_Charges.html, accessed 12/2/2020 The species formed is the conjugate base of that acid. The complementary process, when a proton is added (transferred) to a Brønsted–Lowry base, is protonation (or hydronation). The species formed is the conjugate acid of that base. A species that can either accept or donate a proton is referred to as amphiprotic. An example is the H2O (water) molecule, which can gain a proton to form the hydronium ion, H3O+, or lose a proton, leaving the hydroxide ion, OH−. The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its p''K''a value. A low p''K''a value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pummerer Rearrangement
The Pummerer rearrangement is an organic reaction whereby an alkyl sulfoxide rearranges to an α- acyloxy–thioether (monothioacetal-ester) in the presence of acetic anhydride. The stoichiometry of the reaction is: :RS(O)CHR'2 + Ac2O → RSC(OAc)R'2 + AcOH Synthetic implementation Aside from acetic anhydride, trifluoroacetic anhydride and trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride have been employed as activators. Common nucleophiles besides acetates are arenes, alkenes, amides, and phenols. The usage of α-acyl sulfoxides and Lewis acids, such as TiCl4 and SnCl4, allow the reaction to proceed at lower temperatures (0 °C). Thionyl chloride can be used in place of acetic anhydride to trigger the elimination for forming the electrophilic intermediate and supplying chloride as the nucleophile to give an α-chloro-thioether: Other anhydrides and acyl halides can give similar products. Inorganic acids can also give this reaction. This product can be converted to aldehyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,2-Wittig Rearrangement
A 1,2-Wittig rearrangement is a categorization of chemical reactions in organic chemistry, and consists of a 1,2-rearrangement of an ether with an alkyllithium compound. The reaction is named for Nobel Prize winning chemist Georg Wittig. : \mathsf The intermediate product is an alkoxy lithium salt and the final product an alcohol. When R" is a good leaving group and electron withdrawing group such as a cyanide (CN) group,''Preparation of aryl benzyl ketones by ,2Wittig rearrangement'' Alan R. Katritzky, Yuming Zhang, Sandeep K. Singh Arkivoc pp. 146–50 2002 (viilink this group is eliminated and the corresponding ketone is formed. : \mathsf Reaction mechanism The reaction mechanism centers on the formation of a free radical pair with lithium migrating from the carbon atom to the oxygen atom. The R radical then recombines with the ketyl.''Wittig Rearrangement of Lithiated Allyl Aryl Ethers: A Mechanistic Study'' Sven Strunk, Manfred Schlosser European Journal of Organic Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula , where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl or aryl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anaesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin. Structure and bonding Ethers feature bent C–O–C linkages. In dimethyl ether, the bond angle is 111° and C–O distances are 141 pm. The barrier to rotation about the C–O bonds is low. The bonding of oxygen in ethers, alcohols, and water is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaving Group
In chemistry, a leaving group is defined by the IUPAC as an atom or group of atoms that detaches from the main or residual part of a substrate during a reaction or elementary step of a reaction. However, in common usage, the term is often limited to a fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a leaving group is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term '' nucleofuge''. In this context, leaving groups are generally anions or neutral species, departing from a neutral or cationic substrates, respectively, though in rare cases, cations leaving from a dicationic substrate are also known. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group depends on its ability to stabilize the additional electron density that results from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (TsO−), while water (H2O), alcohols (HOR), and amines (R3N) are common neutr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Triflate
Methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate, also commonly called methyl triflate and abbreviated MeOTf, is the organic compound with the formula CF3SO2OCH3. It is a colourless liquid which finds use in organic chemistry as a powerful methylating agent. The compound is closely related to methyl fluorosulfonate (FSO2OCH3). Although there has yet to be a reported human fatality, several cases were reported for methyl fluorosulfonate (LC50 (rat, 1 h) = 5 ppm), and methyl triflate is expected to have similar toxicity based on available evidence. Synthesis Methyl triflate is commercially available, however it may also be prepared in the laboratory by treating dimethyl sulfate with triflic acid. :CF3SO2OH + (CH3O)2SO2 → CF3SO2OCH3 + CH3OSO2OH Reactivity Hydrolysis Upon contact with water, methyl triflate loses its methyl group, forming triflic acid and methanol: :CF3SO2OCH3 + H2O → CF3SO2OH + CH3OH Methylation One ranking of methylating agents is (CH3)3O+ > CF3SO2OCH3 ≈ FSO2OCH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylation
In the chemical sciences, methylation denotes the addition of a methyl group on a substrate, or the substitution of an atom (or group) by a methyl group. Methylation is a form of alkylation, with a methyl group replacing a hydrogen atom. These terms are commonly used in chemistry, biochemistry, soil science, and the biological sciences. In biological systems, methylation is catalyzed by enzymes; such methylation can be involved in modification of heavy metals, regulation of gene expression, regulation of protein function, and RNA processing. In vitro methylation of tissue samples is also one method for reducing certain histological staining artifacts. The reverse of methylation is demethylation. In biology In biological systems, methylation is accomplished by enzymes. Methylation can modify heavy metals, regulate gene expression, RNA processing and protein function. It has been recognized as a key process underlying epigenetics. Methanogenesis Methanogenesis, the process th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium Salt
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups (indicated by R). Acid–base properties The ammonium ion is generated when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Brønsted acids (proton donors): :H+ + NH3 -> H4 The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Brønsted bases to return to the uncharged ammonia molecule: : H4 + B- -> HB + NH3 Thus, treatment of concentrated solutions of ammonium salts with strong base gives ammonia. When ammonia is dissolved in water, a tiny amount of it converts to ammonium ions: :H2O + NH3 OH- + H4 The degree to which ammonia forms the ammonium ion depends on the pH of the solution. If the pH is low, the equilibrium shifts to the right: more ammonia molecules are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Diisopropylamide
Lithium diisopropylamide (commonly abbreviated LDA) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula . It is used as a strong base and has been widely utilized due to its good solubility in non-polar organic solvents and non-nucleophilic nature. It is a colorless solid, but is usually generated and observed only in solution. It was first prepared by Hamell and Levine in 1950 along with several other hindered lithium diorganylamides to effect the deprotonation of esters at the α position without attack of the carbonyl group. Preparation and structure LDA is commonly formed by treating a cooled (0 to −78 °C) mixture of tetrahydrofuran and diisopropylamine with ''n''-butyllithium. When dissociated, the diisopropylamide anion can become protonated to form diisopropylamine. Diisopropylamine has a p''K''a value of 36. Therefore, its conjugate base is suitable for the deprotonation of compounds with greater acidity, importantly, such weakly acidic compounds (carbon acids) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroxylamine
Hydroxylamine is an inorganic compound with the formula . The material is a white crystalline, hygroscopic compound.Greenwood and Earnshaw. ''Chemistry of the Elements.'' 2nd Edition. Reed Educational and Professional Publishing Ltd. pp. 431–432. 1997. Hydroxylamine is almost always provided and used as an aqueous solution. It is consumed almost exclusively to produce Nylon-6. It is also an intermediate in biological nitrification. The oxidation of to hydroxylamine is a step in biological nitrification. History Hydroxylamine was first prepared as hydroxylammonium chloride in 1865 by the German chemist Wilhelm Clemens Lossen (1838-1906); he reacted tin and hydrochloric acid in the presence of ethyl nitrate. It was first prepared in pure form in 1891 by the Dutch chemist Lobry de Bruyn and by the French chemist Léon Maurice Crismer (1858-1944). The coordination complex , known as Crismer's salt, releases hydroxylamine upon heating. Production Hydroxylamine or its salts can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |