|
Kornblum Oxidation
The Kornblum oxidation, named after Nathan Kornblum, is an organic oxidation reaction that converts alkyl halides and tosylates into carbonyl compounds. Mechanism Similar to sulfonium-based oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes reactions, the Kornblum oxidation creates an alkoxysulphonium ion, which, in the presence of a base, such as triethylamine (Et3N), undergoes an elimination reaction to form the aldehyde or ketone. Extensions The first step is an SN2 reaction, so it is subject to the usual leaving group limitations of that reaction. While iodides work well, even bromides are often not reactive enough to be displaced by the DMSO. However, using an additive such as silver tetrafluoroborate allows the reaction to work on a wider range of substrates, as often seen for alkyl-halide substitutions, or they can be converted first to the corresponding alkyl tosylate. The reaction was initially limited to activated substrates, such as benzylic In organic chemistry, benzyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathan Kornblum
Nathan Kornblum (March 22, 1914 – March 13, 1993) was a professor of Organic Chemistry and a researcher at Purdue University. He received grants for projects from 1970 to 1983. He was born in New York City on March 22, 1914, to immigrant parents, Frances (Newmark) and Samuel Kornblum. His main research focus was electron transfer substitution reactions. His most famous work was the discovery of the Kornblum oxidation and also the Kornblum substitution. He was also known for Kornblum's rule HSAB concept is a jargon for "hard and soft (Lewis) acids and bases". HSAB is widely used in chemistry for explaining stability of compounds, reaction mechanisms and pathways. It assigns the terms 'hard' or 'soft', and 'acid' or 'base' to chemic ... in acid-base chemistry. He was the Plutonium chapter advisor for Iota Sigma Pi Honors Society for Women in Chemistry, which was established in February 1963. In 1952, he received a Guggenheim Fellowship award. He authored a chapter in an Org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganem Oxidation
In organic chemistry, the Ganem oxidation is a name reaction that allows for the preparation of carbonyls from primary or secondary alkyl halides with the use of trialkylamine ''N''-oxides, such as ''N''-methylmorpholine ''N''-oxide or trimethylamine ''N''-oxide. Mechanism As in other oxoammonium-catalyzed oxidation reactions, the negatively charged oxygen atom of the trialkylamine ''N''-oxide molecule attacks the alkyl halide in a SN2 manner, kicking of the halide as a leaving group. A trialkylamine deprotonates the α-carbon atom, the resulting electron pair shifts onto the oxygen atom, which shifts its own excess electron pair onto the nitrogen atom. This generates the desired carbonyl, as well as the aforementioned trialkylamine. The reaction is an enhancement of the Kornblum oxidation protocol, which was originally developed using dimethyl sulfoxide or pyridine-''N''-oxide as the nucleophile. Applications The Ganem oxidation has been used as an intermediate step in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine-N-oxide
Pyridine-''N''-oxide is the heterocyclic compound with the formula C5H5NO. This colourless, hygroscopic solid is the product of the oxidation of pyridine. It was originally prepared using peroxyacids as the oxidising agent. The compound is used infrequently as an oxidizing reagent in organic synthesis. Structure The structure of pyridine-N-oxide is very similar to that of pyridine with respect to the parameters for the ring. The molecule is planar. The N-O distance is 1.34Å. The C-N-C angle is 124°, 7° wider than in pyridine. Synthesis The oxidation of pyridine can be achieved with a number of peracids including peracetic acid and perbenzoic acid. Oxidation can also be effected by a modified Dakin reaction using a urea-hydrogen peroxide complex, and sodium perborate or, using methylrhenium trioxide () as catalyst, with sodium percarbonate. Reactions Pyridine ''N''-oxide is five orders of magnitude less basic than pyridine, but it is isolable as a hydrochloride salt, 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzylic
In organic chemistry, benzyl is the substituent or molecular fragment possessing the structure . Benzyl features a benzene ring () attached to a methylene group () group. Nomenclature In IUPAC nomenclature, the prefix benzyl refers to a substituent, for example benzyl chloride or benzyl benzoate. Benzyl is not to be confused with phenyl with the formula . The term benzylic is used to describe the position of the first carbon bonded to a benzene or other aromatic ring. For example, is referred to as a "benzylic" carbocation. The benzyl free radical has the formula . The benzyl cation or phenylcarbenium ion is the carbocation with formula ; the benzyl anion or phenylmethanide ion is the carbanion with the formula . None of these species can be formed in significant amounts in the solution phase under normal conditions, but they are useful referents for discussion of reaction mechanisms and may exist as reactive intermediates. Abbreviations The abbreviation "Bn" denotes benzyl. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Tetrafluoroborate
Silver tetrafluoroborate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula AgBF4. It is a white solid that dissolves in polar organic solvents as well as water. In its solid state, the Ag+ centers are bound to fluoride. Preparation Silver tetrafluoroborate is prepared by the reaction between boron trifluoride and silver oxide in the presence of benzene. Laboratory uses In the inorganic and organometallic chemistry laboratory, silver tetrafluoroborate, sometimes referred to "silver BF-4", is a useful reagent. In dichloromethane, silver tetrafluoroborate is a moderately strong oxidant. Similar to silver hexafluorophosphate, it is commonly used to replace halide anions or ligands with the weakly coordinating tetrafluoroborate anions. The abstraction of the halide is driven by the precipitation of the appropriate silver halide A silver halide (or silver salt) is one of the chemical compounds that can form between the element silver (Ag) and one of the halogens. In particular, br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromide
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant materials, and cell stains. Although uncommon, chronic toxicity from bromide can result in bromism, a syndrome with multiple neurological symptoms. Bromide toxicity can also cause a type of skin eruption, see potassium bromide. The bromide ion has an ionic radius of 196 pm. Natural occurrence Bromide is present in typical seawater (35 PSU) with a concentration of around 65 mg/L, which is about 0.2% of all dissolved salts. Seafood and deep sea plants generally have higher levels than land-derived foods. Bromargyrite—natural, crystalline silver bromide—is the most common bromide mineral known but is still very rare. In addition to silver, bromine is also in minerals combined with mercury and copper. Formation and react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodide
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt, which many governments mandate. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disability. Structure and characteristics of inorganic iodides Iodide is one of the largest monatomic anions. It is assigned a radius of around 206 picometers. For comparison, the lighter halides are considerably smaller: bromide (196 pm), chloride (181 pm), and fluoride (133 pm). In part because of its size, iodide forms relatively weak bonds with most elements. Most iodide salts are soluble in water, but often less so than the related chlorides and bromides. Iodide, being large, is less hydrophilic compared to the smaller anions. One consequence of this is that sodium iodide is highly soluble in acetone, whereas sodium chloride is not. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
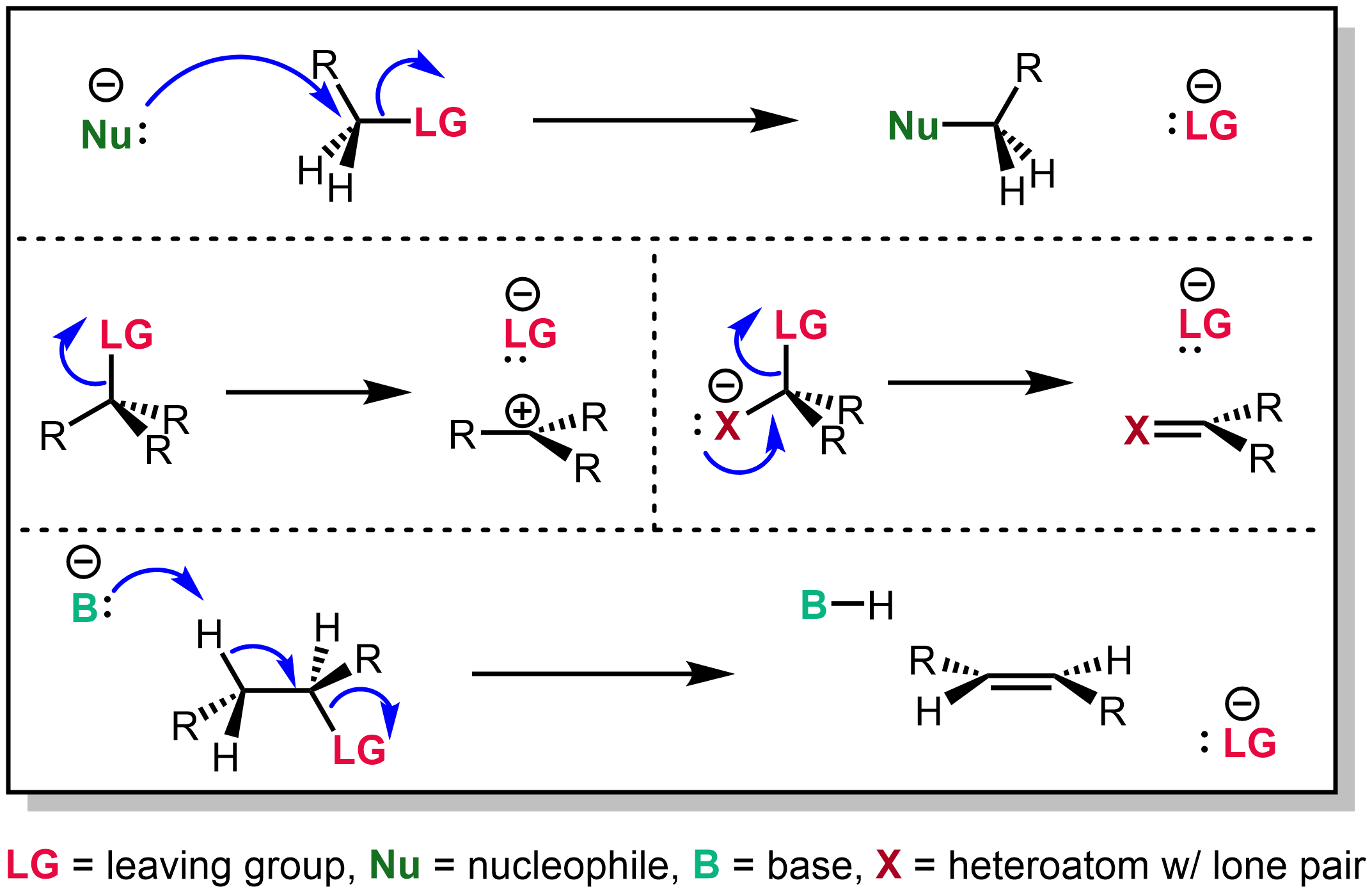
Leaving Group
In chemistry, a leaving group is defined by the IUPAC as an atom or group of atoms that detaches from the main or residual part of a substrate during a reaction or elementary step of a reaction. However, in common usage, the term is often limited to a fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. In this usage, a leaving group is a less formal but more commonly used synonym of the term '' nucleofuge''. In this context, leaving groups are generally anions or neutral species, departing from a neutral or cationic substrates, respectively, though in rare cases, cations leaving from a dicationic substrate are also known. A species' ability to serve as a leaving group depends on its ability to stabilize the additional electron density that results from bond heterolysis. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters such as tosylate (TsO−), while water (H2O), alcohols (HOR), and amines (R3N) are common neutr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN2 Reaction
The SN2 reaction is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistry. In this mechanism, one bond is broken and one bond is formed in a concerted way, i.e., in one step. The name SN2 refers to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism: "SN" indicates that the reaction is a nucleophilic substitution, and "2" that it proceeds via a bi-molecular mechanism, which means both the reacting species are involved in the rate-determining step. The other major type of nucleophilic substitution is the SN1, but many other more specialized mechanisms describe substitution reactions. The SN2 reaction can be considered as an analogue of the associative substitution in the field of inorganic chemistry. Reaction mechanism The reaction most often occurs at an aliphatic sp3 carbon center with an electronegative, stable leaving group attached to it (often denoted X), which is frequently a halide atom. The breaking of the C–X bond and the formation of the new bond (often deno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' is methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Oxidation Reaction
Organic reductions or organic oxidations or organic redox reactions are redox reactions that take place with organic compounds. In organic chemistry oxidations and reductions are different from ordinary redox reactions, because many reactions carry the name but do not actually involve electron transfer.March Jerry; (1985). Advanced Organic Chemistry reactions, mechanisms and structure (3rd ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons, inc. Instead the relevant criterion for organic oxidation is gain of oxygen and/or loss of hydrogen, respectively.''Organic Redox Systems: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications'', Tohru Nishinaga 2016 Simple functional groups can be arranged in order of increasing oxidation state. The oxidation numbers are only an approximation: When methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide its oxidation number changes from −4 to +4. Classical reductions include alkene reduction to alkanes and classical oxidations include oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes. In oxidatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |